What is Industry 4.0? Complete Guide for IT and Cybersecurity Leaders
Updated on September 4, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever wondered, what is Industry 4.0 and why does it matter for enterprises today? In today’s hyper-connected world, businesses face an unprecedented pace of digital transformation. From manufacturing plants to healthcare facilities, automation and data-driven decision-making are redefining operations.
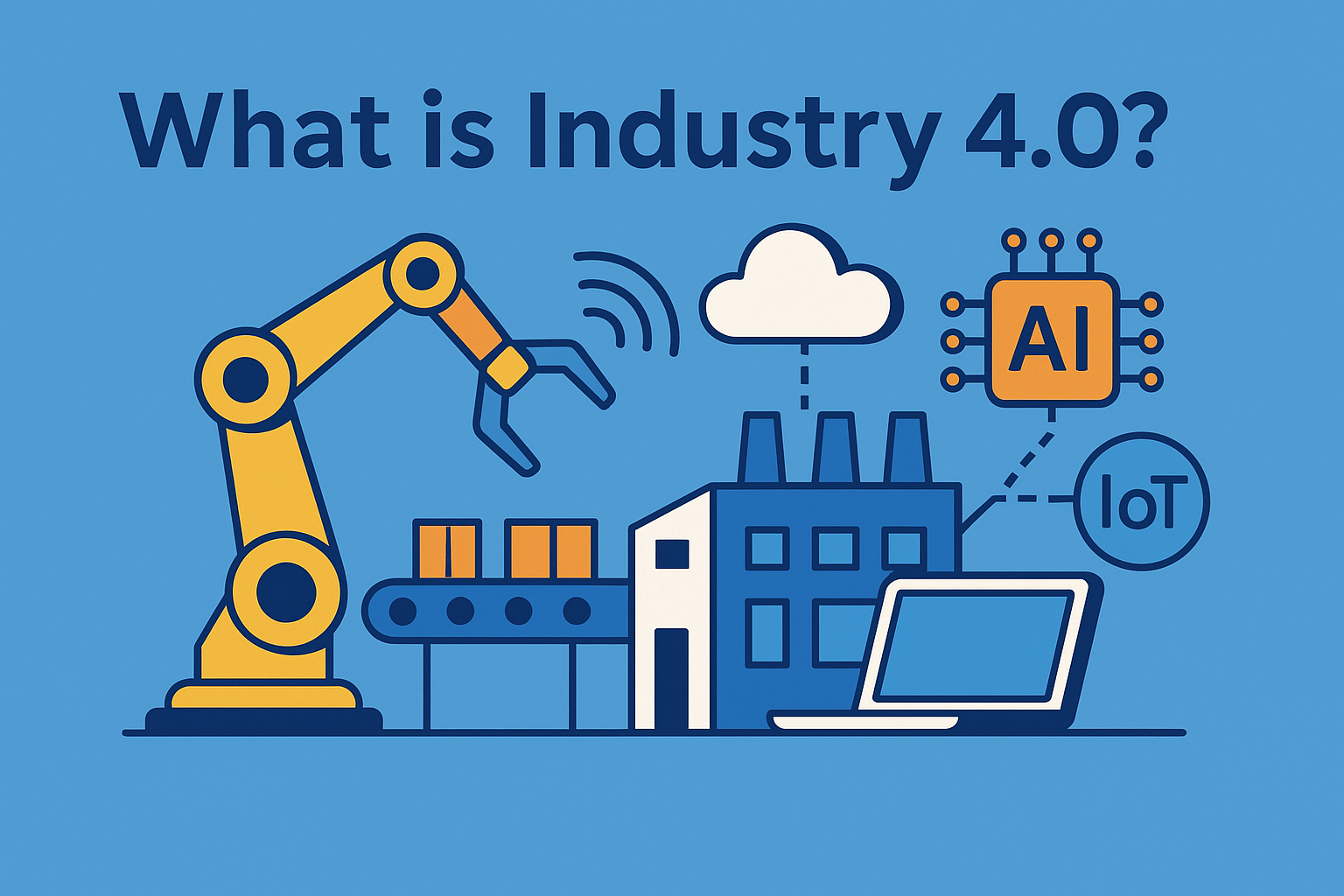
Industry 4.0, often called the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the integration of cyber-physical systems, IoT, artificial intelligence, and big data into industrial and business processes. For IT managers, cybersecurity leaders, and CEOs, Industry 4.0 isn’t just about efficiency—it’s about resilience, security, and competitiveness in a digital-first economy.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 represents the next phase of industrialization, powered by digital technologies that enable smart factories, intelligent automation, and connected systems. It builds on previous industrial revolutions:
- Industry 1.0 – Mechanization with steam engines.
- Industry 2.0 – Mass production with electricity and assembly lines.
- Industry 3.0 – Automation with computers and IT systems.
- Industry 4.0 – Intelligent, interconnected systems leveraging IoT, AI, robotics, and cloud computing.
👉 In simple terms: Industry 4.0 connects the physical and digital worlds, creating smart, data-driven enterprises.
Core Technologies of Industry 4.0
Understanding what is Industry 4.0 means recognizing the technologies driving it forward.
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices and sensors collect real-time data across production lines, logistics, and enterprise networks.
2. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI algorithms predict maintenance needs, optimize production, and detect cybersecurity threats.
3. Big Data & Analytics
Vast amounts of machine and operational data are analyzed for insights, efficiency, and risk detection.
4. Cloud & Edge Computing
Enable scalable, secure, and real-time processing across global enterprises.
5. Robotics & Automation
Smart robots work alongside humans to enhance productivity.
6. Cybersecurity
Protects digital ecosystems from ransomware, insider threats, and supply chain attacks.
Industry 4.0 vs Industry 3.0
| Feature | Industry 3.0 (Automation) | Industry 4.0 (Smart Systems) |
| Focus | Computer-based automation | Data-driven, interconnected |
| Connectivity | Limited | IoT and real-time integration |
| Intelligence | Rule-based | AI and machine learning |
| Security Needs | Basic IT security | Advanced cyber resilience |
| Decision-Making | Human-guided | AI-augmented automation |
👉 Industry 4.0 shifts enterprises from automation to intelligence.
Why Industry 4.0 Matters for Enterprises
When IT leaders ask what is Industry 4.0 used for, the answer spans efficiency, innovation, and security.
1. Operational Efficiency
Real-time analytics reduce downtime, streamline supply chains, and optimize production.
2. Innovation & Agility
Organizations adapt faster to market shifts, customer needs, and emerging technologies.
3. Cybersecurity Readiness
Securing interconnected systems ensures compliance and protects sensitive data.
4. Business Growth
Digital-first operations unlock new revenue models and global expansion.
Benefits of Industry 4.0 for IT & Security Leaders
Operational Benefits:
- Reduced downtime with predictive maintenance.
- Better quality control with AI-driven inspections.
- Streamlined workflows through automation.
Cybersecurity Benefits:
- Stronger visibility into IT and OT (Operational Technology).
- Faster detection of anomalies in networks.
- Integration with Zero Trust architectures.
Business Benefits:
- Cost savings through automation.
- Competitive edge with faster innovation.
- Enhanced compliance readiness across industries.
Cybersecurity Challenges in Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 enables growth, it also expands the attack surface.
Key Risks:
- IoT Vulnerabilities: Billions of connected devices increase entry points.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Compromised vendors can expose entire ecosystems.
- Ransomware: Disrupts both IT and OT systems, halting operations.
- Insider Threats: Misuse of access in interconnected systems.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Industry 4.0:
- Adopt Zero Trust Security frameworks.
- Encrypt data across IoT and cloud ecosystems.
- Use AI-powered SIEM platforms for real-time threat detection.
- Segment networks to isolate OT from IT when possible.
- Conduct regular audits and compliance checks.
Use Cases of Industry 4.0
- Manufacturing: Smart factories with predictive maintenance and AI-driven quality checks.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring with IoT devices and real-time diagnostics.
- Finance: AI-powered fraud detection and secure blockchain transactions.
- Retail: Intelligent supply chain and personalized shopping experiences.
- Government & Defense: Secure communication, surveillance, and critical infrastructure.
Each case highlights how Industry 4.0 transforms operations, security, and business outcomes.
Challenges of Adopting Industry 4.0
Despite the benefits, adoption has hurdles:
- High Initial Investment: Infrastructure, IoT, and AI require significant funding.
- Complex Integration: Legacy systems may not connect easily with new tech.
- Cybersecurity Skills Gap: Many enterprises lack professionals trained for OT/IT security.
- Change Management: Cultural resistance to automation and AI.
The Future of Industry 4.0
The next evolution of Industry 4.0 is already emerging—Industry 5.0, where humans and intelligent machines collaborate even more closely.
Future trends include:
- AI-driven automation for faster, smarter decision-making.
- 5G integration enabling ultra-low latency IoT communications.
- Quantum-safe security to protect data in the post-quantum era.
- Sustainable manufacturing with green energy and smart resource usage.
👉 For IT and cybersecurity leaders, Industry 4.0 is the bridge to future-proof enterprises.
FAQs on Industry 4.0
Q1: What is Industry 4.0 in simple terms?
Industry 4.0 is the Fourth Industrial Revolution, where IoT, AI, and automation create smart, connected enterprises.
Q2: How does Industry 4.0 impact cybersecurity?
It increases vulnerabilities through connected systems but also enables stronger detection and Zero Trust defenses.
Q3: What industries benefit most from Industry 4.0?
Manufacturing, healthcare, finance, retail, and government gain efficiency, security, and innovation.
Q4: Is Industry 4.0 the same as digital transformation?
They overlap, but Industry 4.0 specifically focuses on industrial and operational systems becoming smart and connected.
Q5: What is the difference between Industry 4.0 and 5.0?
Industry 4.0 focuses on automation and connectivity, while Industry 5.0 emphasizes collaboration between humans and intelligent machines.
Conclusion: Why Industry 4.0 is Critical for Modern Enterprises
So, what is Industry 4.0? It’s the fusion of digital, physical, and cyber technologies that creates smarter, faster, and more secure enterprises. For IT managers, it improves efficiency. For cybersecurity leaders, it introduces new risks but also new defense capabilities. For CEOs, it unlocks growth, compliance, and innovation in a competitive market.
Enterprises that embrace Industry 4.0 today are building the foundation for long-term resilience and leadership in the digital economy.
👉 Ready to strengthen your enterprise with secure, future-ready solutions? Request a Demo with Xcitium