What Does CPU Stand For? A Beginner-to-Expert Guide
Updated on August 25, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever wondered what does CPU stand for when talking about computers? Whether you’re an IT manager, cybersecurity professional, or just a tech-savvy CEO, the CPU (Central Processing Unit) is at the heart of everything your device does. From running software applications to processing security protocols, the CPU is often called the brain of the computer—and for good reason.
In this blog, we’ll break down what a CPU is, how it works, why it’s so important, and what modern trends in CPUs mean for industries like IT and cybersecurity.
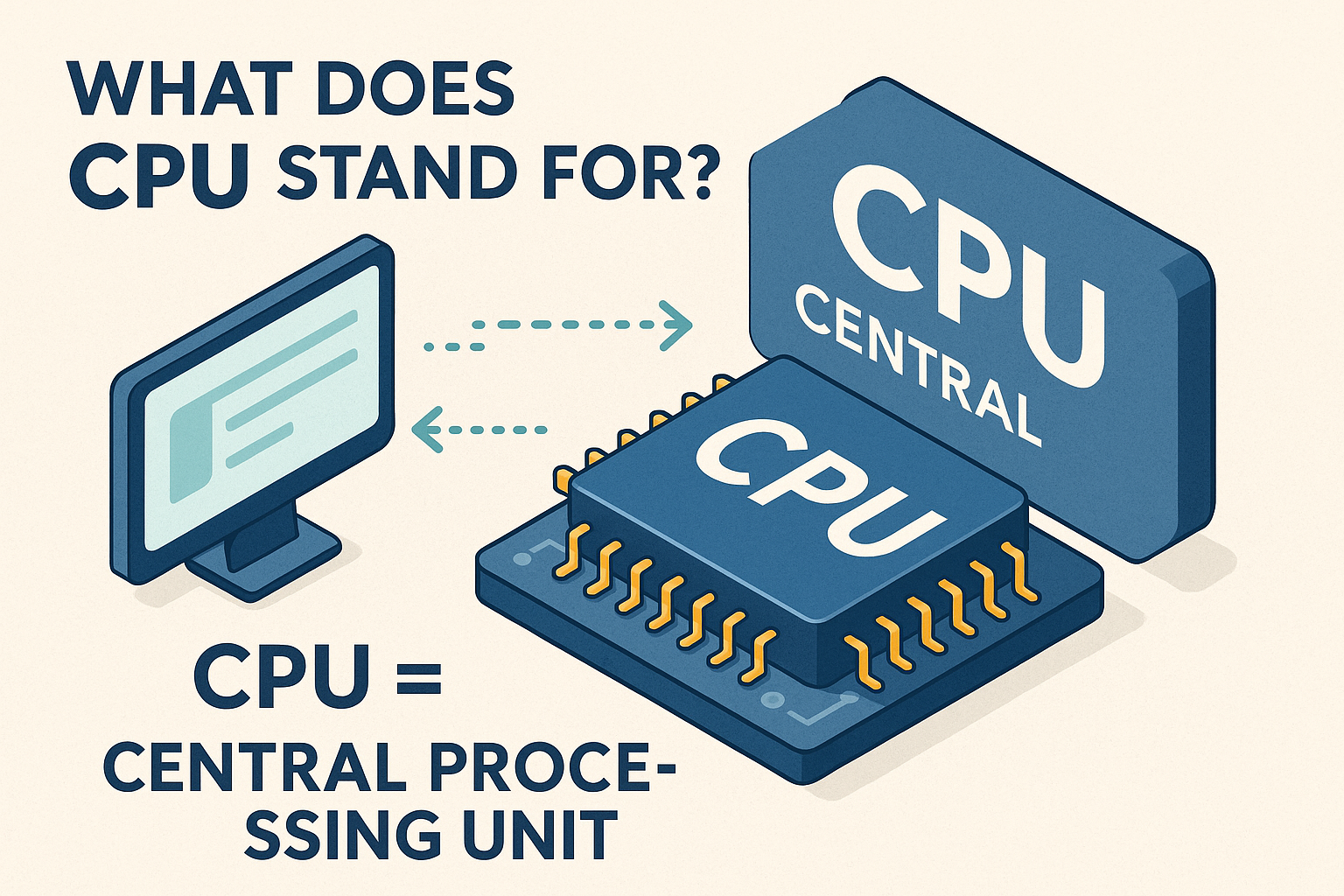
What Does CPU Stand For?
The term CPU stands for Central Processing Unit. It is the primary component inside your computer that executes instructions, processes data, and controls the flow of information between hardware and software.
Think of it like this: If your computer were a company, the CPU would be the CEO—making quick decisions, allocating tasks, and ensuring the entire organization runs smoothly.
Key Functions of a CPU
Here’s what the CPU does every second you’re using a device:
- Fetch: Grabs instructions from memory.
- Decode: Interprets what the instructions mean.
- Execute: Performs the action (like opening a file or running a program).
- Store: Saves the results back into memory.
This loop—called the instruction cycle—happens billions of times per second in modern processors.
CPU vs GPU: What’s the Difference?
While the CPU is the general-purpose brain of your computer, the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) specializes in handling visual data and parallel computations.
- CPU: Handles a few tasks at once, very efficiently.
- GPU: Handles thousands of tasks at the same time (great for AI, gaming, and machine learning).
Types of CPUs
- Single-core processors – Old-school, one task at a time.
- Multi-core processors – Modern CPUs with 2, 4, 8, or more cores for multitasking.
- Server-grade CPUs – Designed for heavy-duty operations in data centers and cybersecurity workloads.
Why Is the CPU Called the “Brain” of the Computer?
The CPU coordinates every action inside a computer. It decides:
- Which apps get processing priority.
- How to allocate resources like RAM.
- When to communicate with other components like storage or network cards.
Without the CPU, your device would simply be a pile of electronic parts with no intelligence.
CPU Performance Metrics You Should Know
When choosing or analyzing CPUs, IT managers and cybersecurity teams often look at:
- Clock Speed (GHz): How fast the CPU executes instructions.
- Cores & Threads: More cores = more multitasking.
- Cache Memory: High-speed memory for quick access.
- Thermal Design Power (TDP): How much heat and power the CPU uses.
Real-World Applications of CPUs in Cybersecurity
- Encryption & Decryption – CPUs handle secure transactions in milliseconds.
- Threat Detection – Fast CPUs help security software scan files efficiently.
- Virtual Machines – CPUs support virtualization, essential for sandboxing threats.
- Incident Response – Cyber teams rely on CPU power for real-time log analysis.
Best Practices for Maximizing CPU Efficiency
- Regularly update BIOS/firmware.
- Use proper cooling systems.
- Monitor workloads with Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac).
- Offload graphics-heavy work to GPUs when possible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What does CPU stand for in computers?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, the main chip that processes data and runs programs. - Is CPU the same as a processor?
Yes, “processor” is another term commonly used for CPU. - What are examples of CPUs?
Intel Core i7, AMD Ryzen 9, and Apple M1/M2 are modern examples. - What is the difference between CPU and GPU?
CPU handles general-purpose tasks, while GPU is optimized for graphics and parallel workloads. - How does CPU affect cybersecurity operations?
A faster CPU allows quicker scanning, encryption, and analysis in security systems.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what does CPU stand for is more than just knowing the acronym. For IT managers and cybersecurity professionals, it means recognizing how vital this chip is for both day-to-day operations and advanced security strategies. Whether you’re buying new hardware or optimizing existing systems, the CPU will always be central to performance and protection.
Supercharge Your Security with Xcitium
At Xcitium, we help businesses secure their endpoints, servers, and networks with cutting-edge solutions. A strong CPU enables faster, smarter protection.