What Does the SAP Stand For? Full Meaning, How It Works, and Why Businesses Use It
Updated on December 3, 2025, by Xcitium
If you’re searching for what does the SAP stand for, you’re not alone. SAP is one of the most widely used software platforms in the world, powering everything from supply chains and HR systems to finance, inventory, customer experience, and cybersecurity operations. Yet many IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, executives, and business leaders still wonder what SAP truly means, how it works, and why it’s so central to enterprise operations.
SAP Meaning and Definition
In today’s digital world—where data flows across departments, devices, and locations—organizations need centralized, integrated systems to run efficiently. SAP is the software ecosystem that connects all these moving parts. Understanding SAP is essential for anyone working in business, IT, cloud computing, cybersecurity, or digital transformation.
This detailed guide explains what SAP stands for, how the platform works, why companies use it, and how it affects modern enterprise security and operations.
What Does SAP Stand For? (Simple Definition)
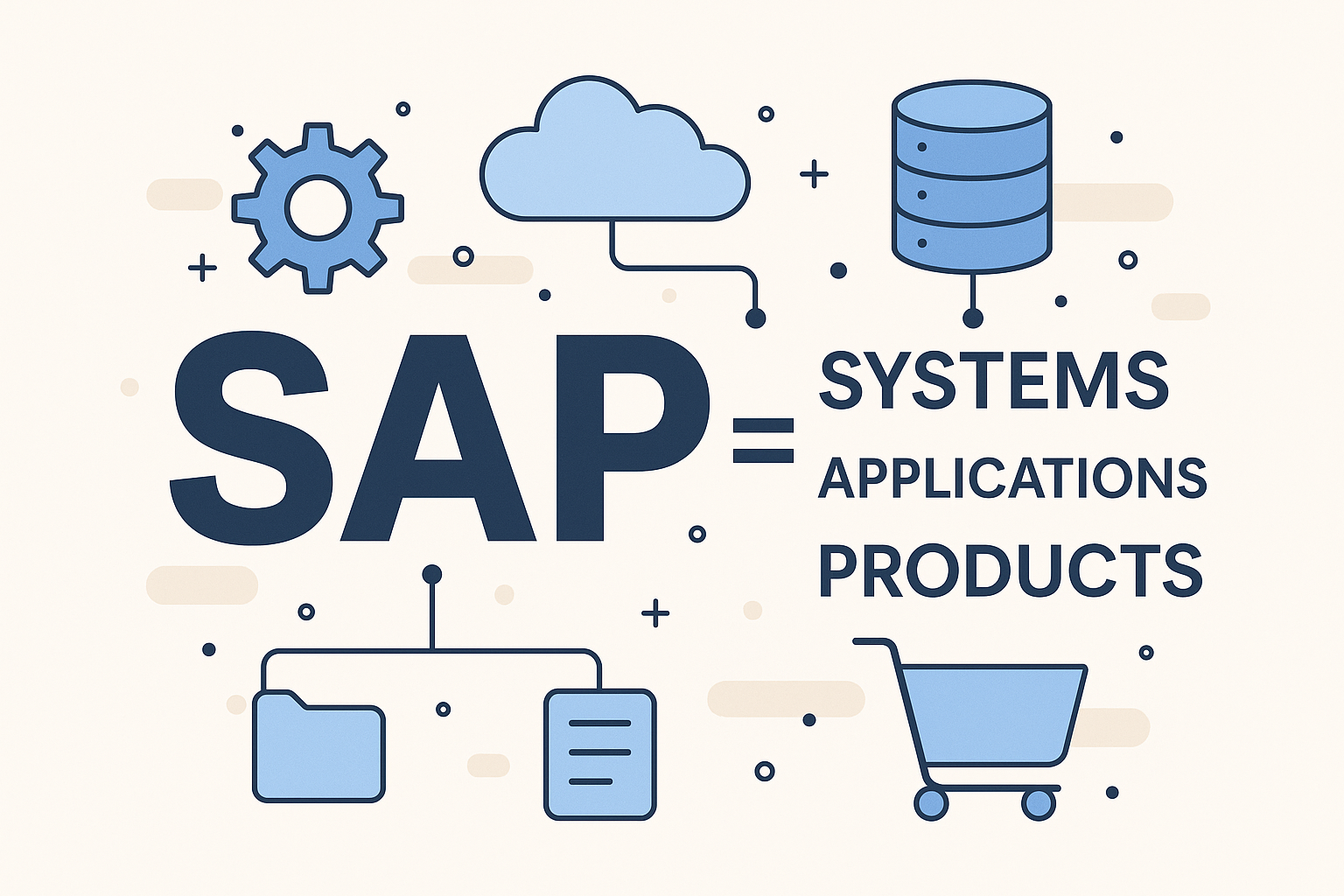
SAP stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing.
SAP is both:
-
The name of the company (SAP SE), and
-
The name of its enterprise software suite, which includes ERP, CRM, SCM, HR, finance, analytics, security, and cloud solutions.
✔ Short version:
SAP = Systems + Applications + Products
✔ Long version:
SAP = Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing
This name reflects SAP’s core purpose:
👉 to help businesses use integrated systems and applications to manage data more efficiently.
What Is SAP Software? (Beyond the Acronym)
SAP is a global enterprise software platform used to manage business processes across the entire organization, including:
-
Finance
-
Human Resources
-
Supply Chain
-
Manufacturing
-
Sales & CRM
-
Inventory Management
-
Procurement
-
Compliance
-
Cybersecurity & Governance
-
Business Analytics
More than 400,000+ companies use SAP worldwide, including industries such as:
-
Banking
-
Retail
-
Healthcare
-
Government
-
Energy
-
Manufacturing
-
eCommerce
-
Cybersecurity
SAP helps companies automate processes, eliminate data silos, strengthen security, and gain real-time visibility across the entire business.
Why the Name “SAP” Matters
The acronym reflects SAP’s fundamental approach to enterprise computing:
Systems
SAP integrates disparate systems and departments into one unified platform.
Applications
SAP includes hundreds of applications for finance, HR, supply chain, operations, cybersecurity, and more.
Products
SAP offers modular software products and solutions that can be customized for different industries.
Together, the name represents SAP’s central mission: integrating all business processes through smart data processing.
Brief History of SAP Software
SAP was founded in 1972 in Germany by five former IBM engineers. Their vision was groundbreaking:
Build real-time business software that integrates everything.
Unlike traditional systems that processed data overnight, SAP allowed businesses to access fresh, real-time information—revolutionizing enterprise operations.
Today, SAP SE is the world’s largest provider of enterprise software and a leader in:
-
ERP systems
-
Business intelligence
-
Cloud applications
-
Security and governance
-
Supply chain automation
-
AI-driven analytics
How SAP Works (Simple Overview)
At its core, SAP functions as an integrated ecosystem where all business processes talk to each other.
Here’s how:
1. Centralized Database
All business data (HR, finance, logistics, orders, customers) flows into one central system.
No duplication. No inconsistencies.
2. Integrated Modules
SAP uses modules—individual applications that work together.
Example modules:
-
SAP FI (Financial Accounting)
-
SAP HR / HCM
-
SAP MM (Materials Management)
-
SAP SD (Sales & Distribution)
-
SAP SCM (Supply Chain Management)
-
SAP PP (Production Planning)
Each module shares data with others automatically.
3. Real-Time Processing
Data is updated instantly across the organization.
Example:
When a sales order is created, inventory is updated, production is triggered, finance records it, and logistics receives a task—all in real time.
4. Automation & Workflow
SAP automates:
-
Approvals
-
Data entry
-
Reports
-
Inventory movement
-
Financial transactions
5. Cloud and On-Premises Options
Modern SAP platforms run in:
-
On-prem data centers
-
Public cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP)
-
Private cloud
-
SAP S/4HANA Cloud
SAP Modules (Core Components Explained)
Understanding SAP modules helps explain why enterprises rely on it.
1. SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
The central SAP system used for daily operations.
Includes:
-
Finance
-
Inventory
-
HR
-
Procurement
2. SAP S/4HANA
Next-generation SAP built on the powerful HANA in-memory database.
Benefits:
-
Faster processing
-
Better analytics
-
AI-enhanced workflows
3. SAP SuccessFactors
Cloud-based HR system for:
-
Payroll
-
Recruiting
-
Employee management
4. SAP Ariba
Procurement and supplier management platform.
5. SAP Customer Experience (CX)
CRM, marketing automation, and eCommerce management.
6. SAP BW/BI (Business Intelligence)
Enterprise analytics and dashboards.
7. SAP SCM & IBP
Supply chain and inventory optimization.
8. SAP Security & GRC
Governance, risk, and compliance tools used for cybersecurity.
Key Benefits of SAP Software for Businesses
SAP’s strength lies in its unified approach to enterprise operations.
1. Real-Time Data Visibility
Decision-makers see the entire business instantly.
2. Stronger Cybersecurity & Compliance
SAP includes built-in controls for:
-
User authorization
-
Data privacy
-
Auditing
-
Risk management
3. Automation of Manual Processes
Saves time, reduces human error.
4. Scalability
Works for small businesses and large global enterprises.
5. Integrated Business Processes
Every department works from the same data source.
6. Better Productivity
Employees access accurate information without delays or duplicate work.
Why Cybersecurity Teams Care About SAP
For IT and cybersecurity professionals, SAP is crucial because:
✔ It contains sensitive data
Financial reports, customer information, HR data, supply chain records.
✔ SAP systems are high-value attack targets
Cybercriminals often target SAP servers.
✔ SAP requires strong security controls
Identity management, MFA, authorization checks, change monitoring.
✔ SAP is often integrated with cloud apps
More integration → more attack surface.
Cybersecurity teams must ensure SAP systems are protected from:
-
Insider threats
-
Ransomware
-
Misconfigurations
-
Privilege escalation
-
API vulnerabilities
Common SAP Misconceptions (Explained Clearly)
1. “SAP is only for large companies.”
False—small and mid-sized companies use SAP Business One and SAP ByDesign.
2. “SAP is just ERP software.”
It now includes HR, CRM, cybersecurity, cloud automation, and AI.
3. “SAP is only for finance.”
SAP spans over 25 business areas.
SAP in the Cloud Era (2026 Update)
Modern organizations are migrating from traditional SAP ECC to SAP S/4HANA, often hosted on cloud platforms.
Benefits include:
-
Faster processing
-
AI-enhanced automation
-
Better analytics
-
Simplified architecture
-
Lower infrastructure costs
Cloud-based SAP is becoming the new standard.
Industries That Use SAP (Top Sectors)
✔ Manufacturing
✔ Energy & Utilities
✔ Healthcare
✔ Retail & eCommerce
✔ Government & Defense
✔ Transportation
✔ Banking & Finance
✔ Cybersecurity & IT Services
Each industry uses SAP to streamline processes and secure critical data.
How SAP Supports Compliance & Cybersecurity
SAP includes built-in tools for:
1. Access Control (SAP GRC)
Manages privileged access.
2. Continuous Monitoring
Detects suspicious activity.
3. Data Encryption
Protects sensitive information.
4. Role-Based Authorization
Ensures least-privilege access.
5. Audit Trails
Tracks all system changes.
6. Integration with EDR/XDR Tools
Enhances threat detection across SAP environments.
Future Trends in SAP Software (2025–2030)
SAP technology will continue evolving through:
-
AI-driven automation
-
Natural-language interfaces
-
Predictive analytics
-
Cloud-first deployments
-
Digital twins
-
Advanced identity protection
-
Zero-trust security models
SAP is moving toward more intelligent, autonomous enterprise systems.
FAQs: What Does SAP Stand For?
1. What does the SAP stand for?
SAP stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing.
2. Is SAP a software or a company?
Both. SAP SE is the company, and SAP is also the name of their software suite.
3. What is SAP used for?
To manage business processes like finance, HR, inventory, manufacturing, sales, and analytics.
4. Is SAP an ERP system?
Yes—SAP ERP is one of SAP’s core products.
5. Is SAP hard to learn?
It depends on the modules. Finance, HR, and logistics modules have learning curves but are manageable with training.
Final Thoughts
Now you know exactly what the SAP stands for and why it plays such a crucial role in modern business operations. SAP is far more than an acronym—it’s the backbone of enterprise digital transformation, data security, workflow automation, and operational intelligence.
As organizations continue to adopt cloud technologies, AI, and cybersecurity frameworks, SAP remains at the center of those transformations, helping companies operate efficiently and securely.
🚀 Ready to Strengthen Your Enterprise Security?
👉 Request a Demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/