How to Run a PowerShell Script: A Complete Guide for Windows Users
Updated on January 9, 2026, by Xcitium
Have you ever downloaded a PowerShell script but weren’t sure how to execute it safely? Many users search for how to run a PowerShell script only to face permission errors, execution policy warnings, or security concerns. PowerShell is a powerful automation tool, but using it incorrectly can expose systems to serious risks.
For IT managers, cybersecurity teams, and business leaders, understanding how to run a PowerShell script properly is essential. This guide walks you through every method—step by step—while highlighting best practices, security considerations, and real-world use cases.
What Is a PowerShell Script?
Before learning how to run a PowerShell script, it’s important to understand what it is.
A PowerShell script is a text file with a .ps1 extension that contains PowerShell commands. These scripts automate tasks such as system administration, configuration, reporting, and security operations.
PowerShell scripts are widely used because they:
-
Save time through automation
-
Reduce manual errors
-
Enable repeatable system tasks
-
Support enterprise-level management
Because of their power, PowerShell scripts are tightly controlled by Windows security settings.
Prerequisites to Run a PowerShell Script
To successfully learn how to run a PowerShell script, ensure the following:
1. PowerShell Is Installed
Modern versions of Windows include PowerShell by default. You can check by typing:
2. Script File Extension
Ensure the file ends with .ps1. PowerShell will not run scripts with other extensions.
3. Appropriate Permissions
You may need administrator privileges to run certain scripts.
Understanding PowerShell Execution Policy
One of the most common obstacles when learning how to run a PowerShell script is the execution policy.
The execution policy controls whether scripts are allowed to run and under what conditions.
Common execution policies:
-
Restricted – No scripts allowed (default)
-
RemoteSigned – Local scripts allowed, downloaded scripts must be signed
-
AllSigned – All scripts must be signed
-
Unrestricted – All scripts allowed (not recommended)
Check current execution policy:
Change execution policy (recommended approach):
⚠️ Always follow organizational security policies before changing execution settings.
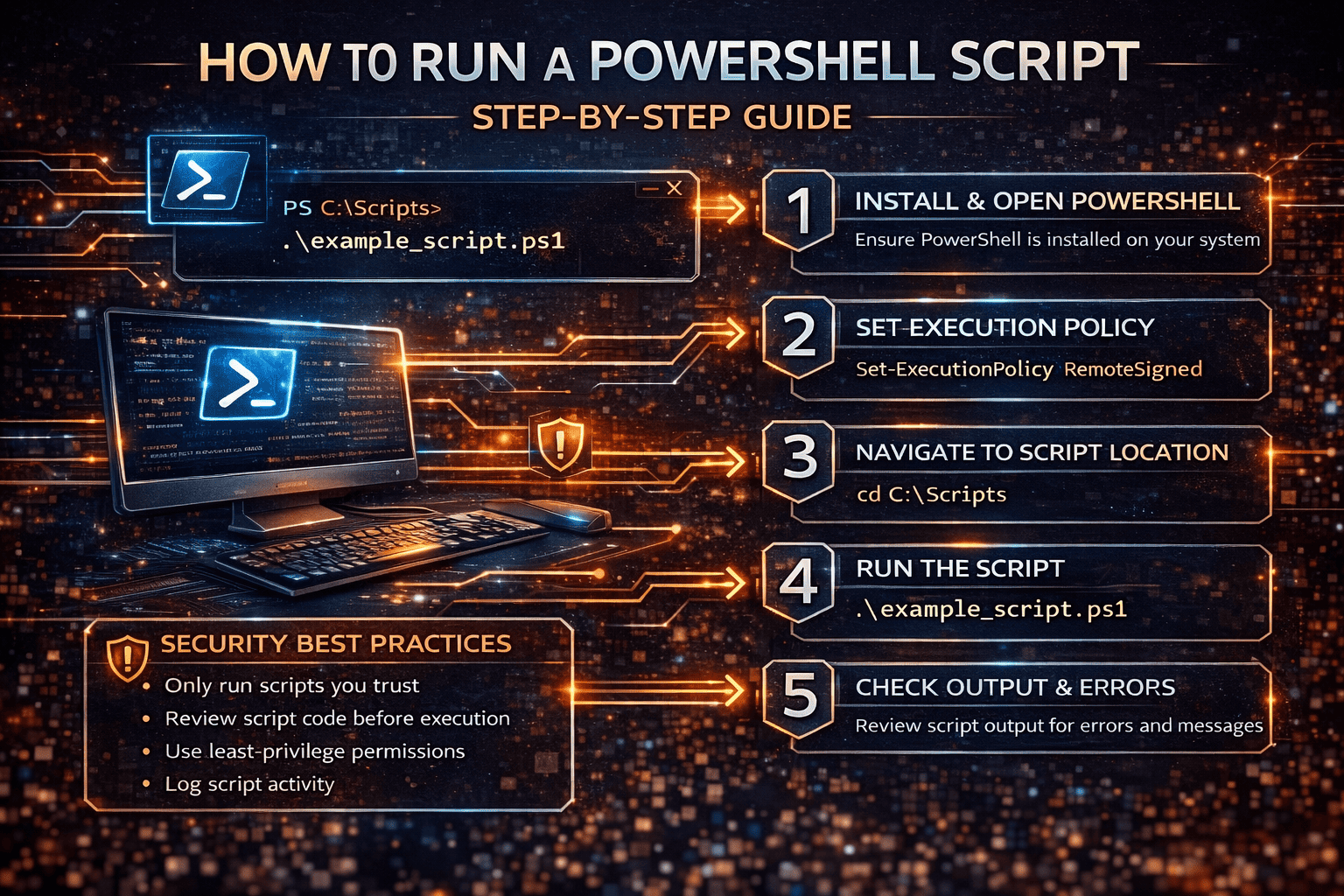
How to Run a PowerShell Script Using PowerShell Console
This is the most common and reliable method.
Step-by-step:
-
Open PowerShell (Run as Administrator if needed)
-
Navigate to the script location:
-
Run the script:
This method gives full visibility into errors and output, making it ideal for troubleshooting.
How to Run a PowerShell Script from File Explorer
If you prefer a graphical approach:
Steps:
-
Locate the
.ps1file -
Right-click the file
-
Select Run with PowerShell
This method is convenient but offers limited error feedback compared to the command line.
How to Run a PowerShell Script from Command Prompt
You can also run PowerShell scripts using Command Prompt, which is useful in automation or legacy environments.
Example:
This command temporarily bypasses execution policy restrictions without changing system-wide settings.
How to Run a PowerShell Script Automatically (Scheduled Tasks)
Automation is a major reason users search for how to run a PowerShell script.
Using Task Scheduler:
-
Open Task Scheduler
-
Create a new task
-
Set trigger (daily, weekly, on startup)
-
Action:
This approach is common for maintenance, monitoring, and reporting scripts.
How to Run a PowerShell Script with Parameters
Many PowerShell scripts accept input parameters.
Example:
Passing parameters makes scripts reusable and flexible for enterprise environments.
Common Errors When Running PowerShell Scripts
Understanding common errors helps you master how to run a PowerShell script efficiently.
1. “Script execution is disabled”
Cause: Execution policy restriction
Fix: Use RemoteSigned or temporary bypass
2. “File not found”
Cause: Incorrect path
Fix: Use cd and ls to confirm location
3. “Access denied”
Cause: Insufficient permissions
Fix: Run PowerShell as Administrator
Security Best Practices for Running PowerShell Scripts
From a cybersecurity perspective, knowing how to run a PowerShell script safely is just as important as knowing how to run it.
Best practices:
-
Never run scripts from unknown sources
-
Review script code before execution
-
Use least-privilege permissions
-
Log script activity
-
Disable PowerShell remoting if not needed
PowerShell is frequently abused by attackers, making strong controls essential.
PowerShell Scripts in Enterprise and IT Environments
IT managers rely heavily on PowerShell scripts for:
-
System configuration
-
Patch management
-
User provisioning
-
Security monitoring
Standardizing how scripts are executed reduces risk and improves reliability.
PowerShell vs Bash: Why PowerShell Matters
While Bash is common in Linux, PowerShell dominates Windows environments.
PowerShell advantages:
-
Object-based output
-
Deep Windows integration
-
Strong automation support
-
Enterprise-grade security controls
For Windows-centric organizations, PowerShell remains the automation standard.
When Not to Run a PowerShell Script
Knowing how to run a PowerShell script also means knowing when not to.
Avoid running scripts:
-
From untrusted websites
-
Without reviewing the code
-
On production systems without testing
-
With unrestricted execution policies
Caution prevents downtime and security incidents.
Final Thoughts: Mastering PowerShell Script Execution
Understanding how to run a PowerShell script is a critical skill for IT professionals, cybersecurity teams, and technical leaders. When used correctly, PowerShell improves efficiency, security, and operational consistency.
The key is combining technical knowledge with strong security practices.
Take the Next Step Toward Secure Automation
PowerShell automation is powerful—but visibility and protection are essential to prevent misuse and threats.
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I run a PowerShell script for the first time?
Set the execution policy to RemoteSigned, navigate to the script location, and run it using .\scriptname.ps1.
2. Why does PowerShell block my script?
PowerShell blocks scripts by default to prevent malicious execution. This is controlled by execution policies.
3. Can PowerShell scripts be dangerous?
Yes. Malicious scripts can harm systems, which is why security controls and script reviews are essential.
4. How do I run a PowerShell script without changing execution policy?
Use: powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File scriptname.ps1
5. Do I need admin rights to run PowerShell scripts?
Only if the script performs administrative tasks or modifies system-level settings.