How to Remove Directory in Linux: A Complete Practical Guide
Updated on January 8, 2026, by Xcitium
Have you ever tried deleting a folder in Linux and been blocked by permissions, files, or cryptic errors? Knowing how to remove directory in Linux is a fundamental skill for system administrators, developers, and security teams alike. A single incorrect command can delete critical data—or fail when you need it most.
Linux directory management is simple once you understand the right commands and precautions. This guide walks you through safe, effective ways to remove directories in Linux, whether they are empty, full, protected, or part of a production system.
What Does “Remove Directory in Linux” Mean?
Understanding how to remove directory in Linux starts with understanding what a directory is. In Linux, a directory is a special file that stores references to other files and directories.
Removing a directory can mean:
-
Deleting an empty folder
-
Deleting a folder with files
-
Removing nested subdirectories
-
Deleting system or user-owned directories
Linux uses command-line tools to manage directories, giving users precise control—but also responsibility.
Common Commands to Remove Directory in Linux
There are two primary commands used to remove directories in Linux. Choosing the correct one depends on whether the directory is empty or contains files.
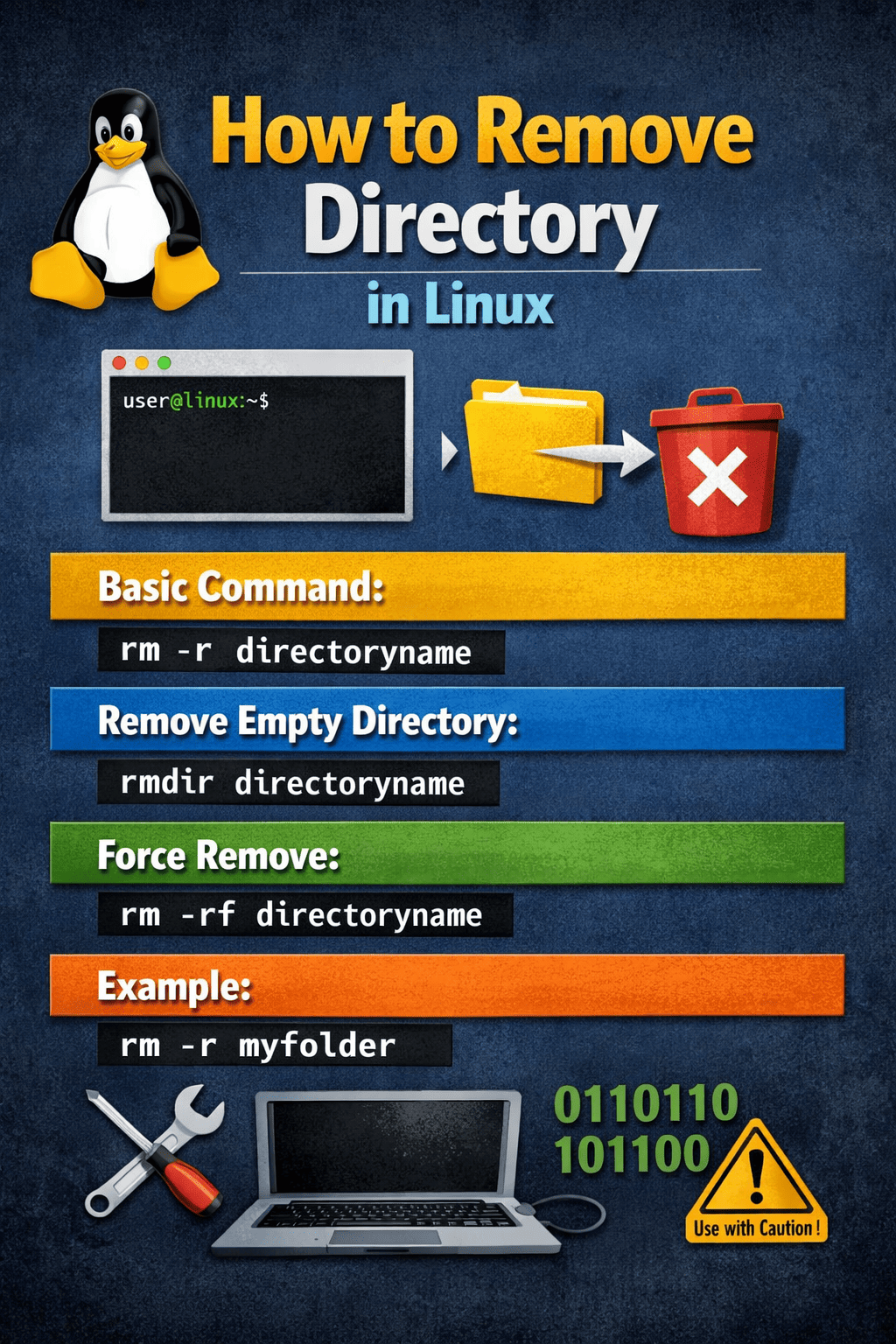
1. rmdir Command (For Empty Directories)
The rmdir command Linux tool removes empty directories only. It’s the safest option when you know a directory has no files.
Syntax:
Example:
If the directory is not empty, Linux will return an error. This built-in safety makes rmdir ideal for cautious administrators.
2. rm Command (For Non-Empty Directories)
When learning how to remove directory in Linux, the rm command is the most powerful—and dangerous.
To remove a directory with files, you must use the recursive option.
Syntax:
Example:
The -r flag tells Linux to delete everything inside the directory, including subfolders.
How to Remove Directory in Linux Safely
Deleting directories can be risky, especially on production systems. Follow these best practices to avoid costly mistakes.
Use the Interactive Mode
The interactive flag (-i) prompts confirmation before deletion.
This is a recommended approach for IT managers and security teams working on sensitive systems.
Preview Before Deleting
Before removing a directory, list its contents:
This simple step helps prevent accidental deletion of important data.
Removing Directories with Permissions Issues
One common challenge when learning how to remove directory in Linux is permission errors.
Use sudo (With Caution)
If a directory belongs to another user or requires elevated privileges, use:
⚠️ Always double-check the directory path before using sudo.
Change Ownership or Permissions
Alternatively, update ownership:
Or modify permissions:
This approach is safer in controlled environments.
How to Remove Multiple Directories at Once
Linux allows deleting multiple directories in a single command.
This is useful for cleanup tasks but increases risk. Always confirm directory names carefully.
Removing Directories by Pattern (Wildcard)
Advanced users often delete directories using wildcards.
Example:
This removes all directories starting with “test.”
🚨 Wildcards can be dangerous. A typo can delete unintended files.
How to Remove Directory in Linux Without Prompt
The -f (force) option removes directories without confirmation.
This command:
-
Ignores warnings
-
Deletes files recursively
-
Bypasses confirmation
For cybersecurity and production environments, use this only in scripts or automated processes after extensive testing.
Difference Between rm and rmdir in Linux
Understanding the distinction is critical when mastering how to remove directory in Linux.
| Feature | rmdir | rm -r |
|---|---|---|
| Removes empty directories | ✅ | ❌ |
| Removes directories with files | ❌ | ✅ |
| Safer by default | ✅ | ❌ |
| Common in scripts | ❌ | ✅ |
For everyday operations, start with rmdir and escalate only when necessary.
Security Considerations When Removing Directories
From a cybersecurity perspective, deleting directories is not just about cleanup—it’s about risk management.
Risks include:
-
Accidental data loss
-
Removal of audit logs
-
Breaking application dependencies
-
Compliance violations
Best security practices:
-
Maintain backups before deletion
-
Log deletion activities
-
Restrict
sudoaccess -
Use automation with safeguards
Understanding how to remove directory in Linux securely is essential for maintaining system integrity.
Removing Directories in Automated Scripts
Many organizations automate cleanup using shell scripts. While efficient, automation requires safeguards.
Safe scripting tips:
-
Use absolute paths
-
Avoid wildcards where possible
-
Add logging
-
Test in staging environments
Automation should reduce human error—not amplify it.
Troubleshooting Common Errors
“Directory not empty”
Use rm -r instead of rmdir.
“Permission denied”
Use sudo or adjust ownership.
“No such file or directory”
Verify spelling and path.
Most issues stem from incorrect paths or permissions.
Best Practices for Linux Directory Management
To master how to remove directory in Linux, follow these best practices:
-
Double-check paths before deletion
-
Use
lsandpwdto confirm location -
Prefer
rmdirwhen possible -
Avoid
rm -rf /or root-level commands -
Keep regular backups
These habits protect both systems and careers.
Final Thoughts: Mastering Directory Removal in Linux
Knowing how to remove directory in Linux is a foundational skill for system administrators, developers, and cybersecurity professionals. While Linux gives powerful tools, it also demands discipline and awareness.
Whether you’re cleaning up test environments or managing enterprise systems, safe directory removal practices help maintain stability, security, and compliance.
Take the Next Step Toward Secure System Management
Linux expertise is critical—but so is securing your endpoints and infrastructure against modern threats.
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How to remove directory in Linux if it is not empty?
Use the command rm -r directory_name to remove directories that contain files and subdirectories.
2. What is the safest way to delete a directory in Linux?
Use rmdir for empty directories or rm -ri to confirm deletions interactively.
3. Can I undo a directory deletion in Linux?
No. Linux does not have a built-in undo feature. Always back up important data before deletion.
4. What does rm -rf mean in Linux?
It forcefully and recursively deletes directories without confirmation. Use with extreme caution.
5. Why does Linux deny permission when deleting a directory?
The directory may belong to another user or require elevated privileges. Use sudo or adjust permissions.