What Is Digital Forensics? A Complete Guide for Cybersecurity and Business Leaders
Updated on February 5, 2026, by Xcitium
When a cyberattack occurs, how do you know what really happened?
More importantly, how do you prove it?
Understanding what is digital forensics is essential in a world where cybercrime, insider threats, and data breaches are everyday realities. Digital forensics helps organizations uncover the truth hidden inside computers, networks, and cloud environments after a security incident.
From identifying attackers to preserving legal evidence, digital forensics plays a critical role in modern cybersecurity. In this guide, we’ll explain what digital forensics is, how it works, its types, tools, real-world use cases, and why every organization should care.
What Is Digital Forensics?
What is digital forensics? Digital forensics is the process of identifying, collecting, preserving, analyzing, and presenting digital evidence from electronic devices and systems. This evidence is used to investigate cyber incidents, criminal activity, policy violations, and data breaches.
Digital forensics applies to:
-
Computers and servers
-
Mobile devices
-
Networks and firewalls
-
Cloud platforms
-
Emails, logs, and databases
The goal is to reconstruct events accurately while maintaining the integrity of the evidence.
Why Digital Forensics Is Critical in Cybersecurity
Understanding what is digital forensics becomes especially important during and after security incidents. Without forensic analysis, organizations are left with assumptions instead of facts.
Key reasons digital forensics matters:
-
Determines how an attack happened
-
Identifies affected systems and data
-
Preserves evidence for legal or regulatory use
-
Supports faster and more accurate incident response
-
Prevents repeat attacks
In cybersecurity, digital forensics turns raw data into actionable intelligence.
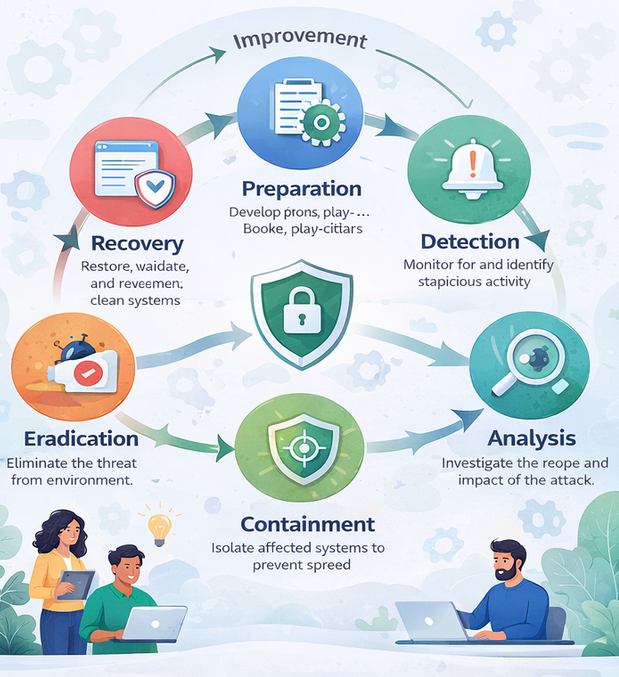
The Digital Forensics Process Explained
To fully understand what is digital forensics, it’s important to know how investigations are conducted.
The standard digital forensics process includes:
1. Identification
Recognizing potential sources of digital evidence.
2. Preservation
Securing data to prevent alteration or loss.
3. Collection
Extracting digital evidence using forensically sound methods.
4. Analysis
Examining data to uncover timelines, actions, and anomalies.
5. Documentation & Reporting
Presenting findings clearly for technical teams, executives, or legal authorities.
Each step must be performed carefully to maintain evidence integrity.
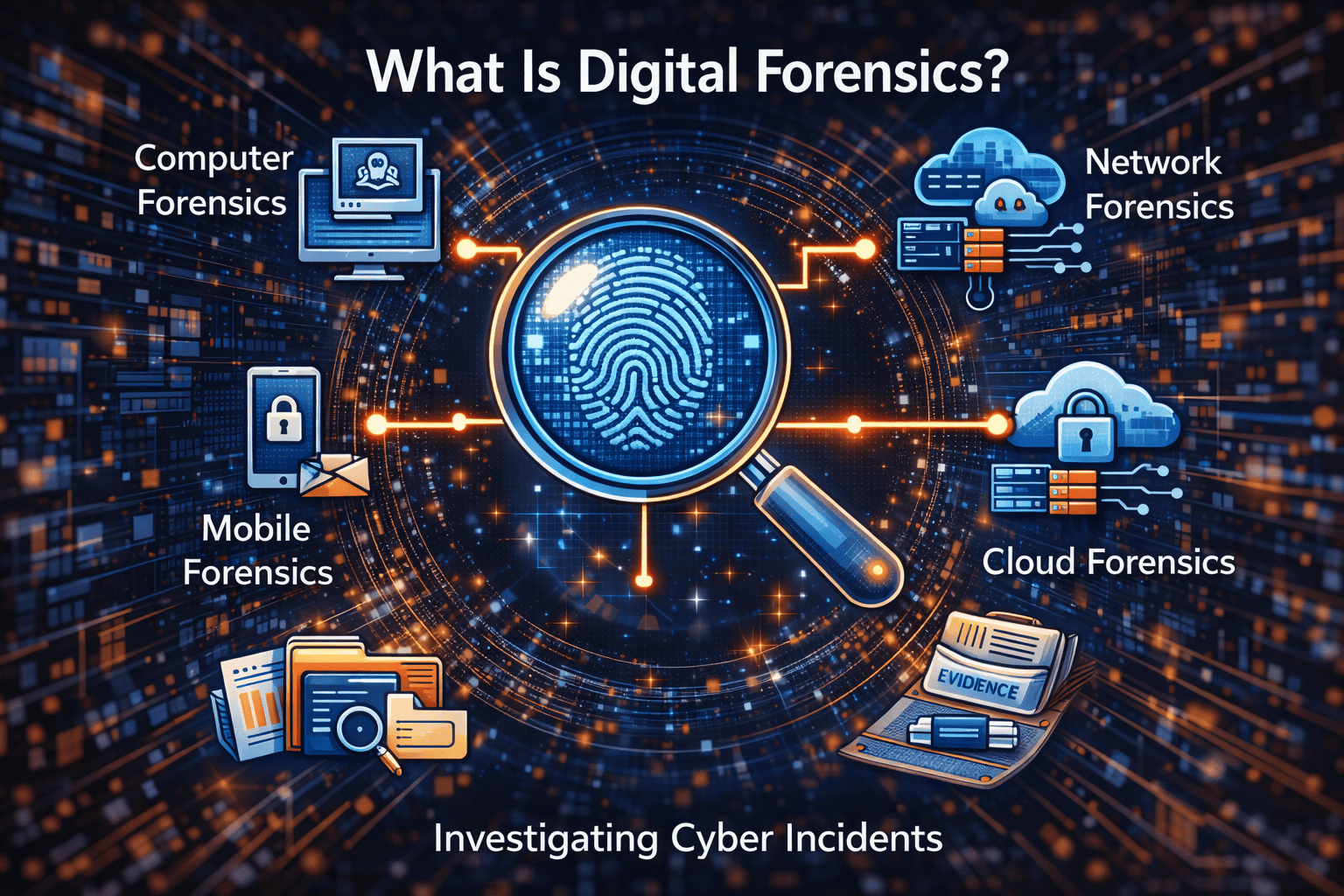
Types of Digital Forensics
Digital forensics covers multiple specialized disciplines. Understanding these areas helps clarify what digital forensics includes in practice.
Computer Forensics
Focuses on desktops, laptops, servers, and storage media.
Network Forensics
Analyzes network traffic, firewall logs, and intrusion activity.
Mobile Forensics
Extracts data from smartphones, tablets, and mobile apps.
Cloud Forensics
Investigates incidents across cloud platforms and SaaS environments.
Email and Log Forensics
Examines email headers, message content, and system logs.
Each type plays a role depending on the nature of the incident.
Digital Forensics vs Incident Response
Although closely related, digital forensics and incident response serve different purposes.
| Aspect | Incident Response | Digital Forensics |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Contain threats | Understand events |
| Focus | Speed | Accuracy |
| Timing | During attack | During & after |
| Outcome | Mitigation | Evidence & insight |
Incident response stops the bleeding. Digital forensics explains how the wound happened.
Common Use Cases for Digital Forensics
Organizations across industries rely on digital forensics for many scenarios.
Cyberattack Investigations
Identify attackers, attack vectors, and affected assets.
Insider Threat Investigations
Detect unauthorized access or data misuse by employees.
Data Breach Analysis
Determine what data was accessed or exfiltrated.
Compliance and Audits
Provide evidence for regulatory inquiries.
Legal and Law Enforcement Support
Preserve admissible digital evidence.
Understanding what is digital forensics helps organizations respond with confidence instead of uncertainty.
Digital Forensics Tools and Technologies
Modern digital forensics relies on specialized tools to handle large volumes of data.
Common digital forensics tools include:
-
Disk and memory analysis tools
-
Log and SIEM analysis platforms
-
Network traffic analyzers
-
Email forensic tools
-
Cloud forensic frameworks
Automation and AI are increasingly used to speed up analysis without sacrificing accuracy.
Digital Forensics and Logs: A Powerful Combination
Logs are often the most valuable source of forensic evidence.
Why logs matter in digital forensics:
-
Provide timelines of activity
-
Show authentication and access attempts
-
Reveal lateral movement and persistence
-
Support attribution and root cause analysis
Strong logging practices dramatically improve digital forensics outcomes.
Digital Forensics in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Cloud adoption has changed how digital forensics works.
Cloud forensic challenges include:
-
Shared responsibility models
-
Limited access to underlying infrastructure
-
Distributed and ephemeral workloads
To address this, digital forensics now relies on:
-
Cloud-native logging
-
API-based evidence collection
-
Centralized forensic visibility
Understanding what is digital forensics today means understanding cloud environments as well.
Best Practices for Digital Forensics Readiness
Organizations should prepare for forensic investigations before incidents occur.
Best practices include:
-
Enable comprehensive logging
-
Centralize log management
-
Define evidence handling procedures
-
Train incident response teams
-
Use automated forensic tools
Preparation reduces investigation time and improves accuracy when incidents happen.
Digital Forensics and Compliance Requirements
Many regulations require forensic-ready environments.
Compliance frameworks that depend on digital forensics:
-
ISO 27001
-
SOC 2
-
PCI DSS
-
HIPAA
-
GDPR
Digital forensics provides the proof needed to demonstrate compliance and due diligence.
Challenges in Digital Forensics and How to Overcome Them
Data Volume
Use automation and filtering to focus on relevant evidence.
Encryption
Leverage key management and memory analysis techniques.
Skill Gaps
Combine expert services with advanced forensic platforms.
Time Sensitivity
Preserve evidence immediately to prevent loss.
Knowing what is digital forensics also means understanding how to overcome these challenges.
The Future of Digital Forensics
Digital forensics continues to evolve alongside cyber threats.
Emerging trends include:
-
AI-assisted forensic analysis
-
Faster incident reconstruction
-
Cloud-native forensic tooling
-
Integrated XDR and forensic platforms
As attacks grow more advanced, digital forensics becomes even more critical.
FAQs About What Is Digital Forensics
1. What is digital forensics in cybersecurity?
Digital forensics in cybersecurity involves collecting and analyzing digital evidence to investigate cyber incidents and breaches.
2. Is digital forensics only used after an attack?
No. It’s also used proactively for threat hunting, compliance audits, and readiness planning.
3. What is the difference between computer forensics and digital forensics?
Computer forensics focuses on computers, while digital forensics covers all digital systems, including networks and cloud platforms.
4. How long does a digital forensics investigation take?
It depends on the scope, but investigations can range from hours to several weeks.
5. Can digital forensics evidence be used in court?
Yes. When properly collected and preserved, digital evidence is legally admissible.
Final Thoughts: Why Digital Forensics Matters More Than Ever
Understanding what is digital forensics is no longer optional for modern organizations. When incidents occur, digital forensics provides clarity, accountability, and proof.
Without digital forensics:
-
Attacks go unexplained
-
Evidence is lost
-
Compliance becomes risky
With digital forensics:
-
Incidents are understood
-
Lessons are learned
-
Security posture improves
Take the Next Step Toward Stronger Incident Visibility
Ready to gain deeper insight into security incidents and strengthen your investigation capabilities?
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
See how advanced visibility and forensic-ready security can transform your response strategy.