What Is SAN Storage? A Complete Guide for Modern IT & Security Leaders
Updated on January 27, 2026, by Xcitium
If you manage enterprise infrastructure or oversee cybersecurity strategy, you’ve likely asked: what is SAN storage, and why is it critical for modern businesses? As data volumes explode and uptime becomes non-negotiable, traditional storage models often fall short.
Understanding what is SAN storage helps organizations achieve high performance, scalability, and reliability—while maintaining strong security controls. From financial services to healthcare and SaaS environments, SAN storage remains a foundational technology for mission-critical workloads.
In this guide, we’ll explain what is SAN storage, how it works, its benefits, security implications, and when businesses should deploy it.
What Is SAN Storage?
To start simply, what is SAN storage?
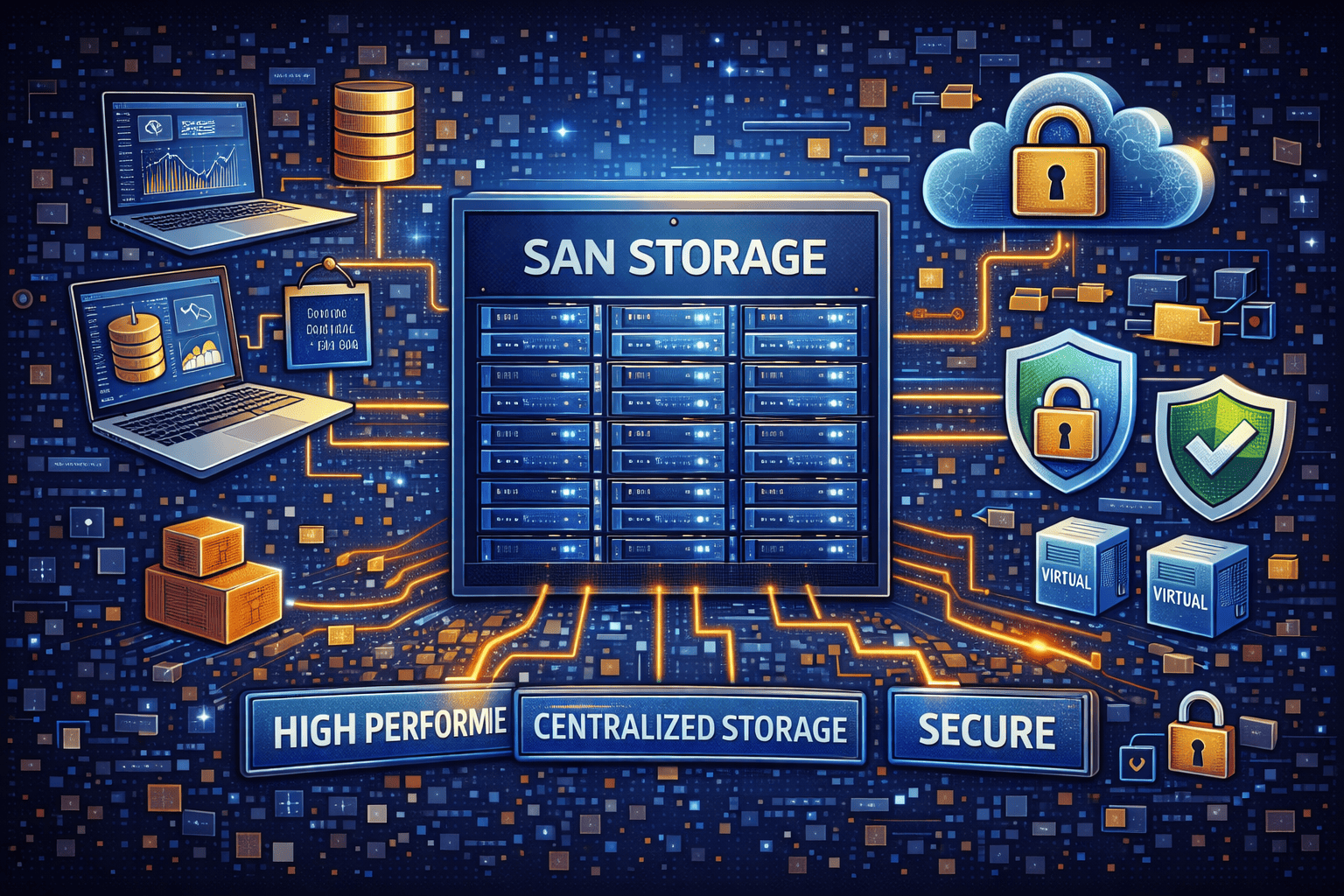
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a high-speed, dedicated network that provides access to consolidated block-level storage. Unlike direct-attached storage (DAS), SAN storage separates storage resources from servers and makes them available over a specialized network.
This architecture allows multiple servers to access shared storage as if it were locally attached, delivering exceptional speed and reliability.
Why SAN Storage Exists
Before SANs, storage was tightly coupled to individual servers. This created limitations in:
-
Scalability
-
Performance
-
High availability
-
Disaster recovery
By centralizing storage, SAN storage solves these problems while improving manageability and resilience.
How SAN Storage Works
To fully understand what is SAN storage, it helps to break down its components.
Core SAN Components
-
Storage arrays – Disk or flash systems holding data
-
SAN switches – Specialized network switches
-
Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) – Connect servers to the SAN
-
Cabling and protocols – Fibre Channel, iSCSI, or FCoE
Data is transferred at the block level, which is ideal for databases, virtual machines, and transactional systems.
SAN Storage Protocols Explained
SAN storage relies on high-performance protocols designed for speed and reliability.
Common SAN Protocols
-
Fibre Channel (FC) – Ultra-low latency, enterprise-grade
-
iSCSI – Runs over standard Ethernet
-
FCoE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet) – Combines FC and Ethernet
Each protocol offers different trade-offs between cost, complexity, and performance.
What Is SAN Storage Used For?
Organizations invest in SAN storage for workloads where performance and uptime matter most.
Common SAN Storage Use Cases
-
Databases (SQL, Oracle, NoSQL)
-
Virtualized environments (VMware, Hyper-V)
-
Enterprise applications (ERP, CRM)
-
High-transaction workloads
-
Business-critical systems
SAN storage excels when milliseconds matter.
Key Benefits of SAN Storage
Understanding what is SAN storage means understanding why enterprises still rely on it.
1. High Performance
SAN storage delivers low latency and high throughput, especially with Fibre Channel or NVMe-over-Fabrics.
2. Scalability
Storage capacity can grow independently of compute resources.
3. High Availability
SAN architectures support redundancy, failover, and fault tolerance.
4. Centralized Management
Administrators manage storage from a single platform.
5. Improved Disaster Recovery
SAN storage simplifies replication and backup strategies.
SAN Storage vs NAS: What’s the Difference?
A common follow-up to what is SAN storage is how it compares to NAS.
| Feature | SAN Storage | NAS |
|---|---|---|
| Data Access | Block-level | File-level |
| Performance | Very high | Moderate |
| Use Cases | Databases, VMs | File sharing |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Complexity | High | Low |
SAN storage is designed for performance-critical workloads, while NAS is better for shared files.
SAN Storage and Virtualization
SAN storage plays a major role in modern virtualized environments.
Why SAN Storage Works Well with VMs
-
Fast disk access for multiple VMs
-
Live migration support
-
Snapshot and cloning features
-
Centralized storage pools
Virtualization platforms often rely on SAN storage for predictable performance.
Security Considerations in SAN Storage
For cybersecurity leaders, what is SAN storage also raises important security questions.
Key SAN Security Concerns
-
Unauthorized access
-
Data interception
-
Misconfiguration risks
-
Insider threats
SAN networks must be secured just like any other critical infrastructure.
Best Practices for Securing SAN Storage
To protect SAN environments, organizations should implement:
-
Network segmentation
-
Strong access controls
-
Zoning and LUN masking
-
Encryption at rest and in transit
-
Continuous monitoring
Security missteps in SAN storage can expose massive volumes of sensitive data.
SAN Storage and Zero Trust Architecture
SAN storage aligns well with Zero Trust principles when configured correctly.
Zero Trust in SAN Environments
-
Authenticate every connection
-
Limit access by role
-
Monitor all activity
-
Assume breach readiness
Treating SAN access as untrusted by default reduces attack surfaces.
SAN Storage in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
While cloud storage dominates headlines, SAN storage still plays a role.
Hybrid SAN Models
-
On-prem SAN for performance-critical data
-
Cloud storage for scalability and backup
-
Replication between environments
Many enterprises combine SAN storage with cloud infrastructure for flexibility.
Costs and Challenges of SAN Storage
Despite its benefits, SAN storage is not for everyone.
Common Challenges
-
High upfront cost
-
Specialized skills required
-
Complex configuration
-
Ongoing maintenance
Organizations should evaluate workloads carefully before deployment.
When SAN Storage Makes Sense
SAN storage is ideal when:
-
Performance is mission-critical
-
Downtime is unacceptable
-
Large databases are involved
-
Virtualization is core to operations
For less demanding workloads, alternatives may suffice.
SAN Storage vs DAS (Direct-Attached Storage)
Another common comparison related to what is SAN storage is DAS.
| Feature | SAN | DAS |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | High | Low |
| Performance | High | Moderate |
| Management | Centralized | Local |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
SAN storage offers long-term flexibility that DAS cannot.
Future of SAN Storage
SAN storage continues to evolve with:
-
NVMe-over-Fabrics
-
Software-defined storage
-
Automation and AI-driven management
These innovations keep SAN storage relevant in modern data centers.
Actionable Tips for Choosing SAN Storage
If you’re considering SAN storage, ask these questions:
-
What workloads need the highest performance?
-
What are uptime requirements?
-
How will security be enforced?
-
Can staff support SAN complexity?
Planning reduces costly mistakes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is SAN storage in simple terms?
SAN storage is a high-speed network that connects servers to shared storage as if it were local.
2. Is SAN storage better than NAS?
For performance-critical workloads, yes. For file sharing, NAS is simpler and cheaper.
3. Is SAN storage secure?
Yes, when properly configured with zoning, encryption, and monitoring.
4. Is SAN storage still relevant in the cloud era?
Absolutely. Many enterprises use SAN storage alongside cloud services.
5. Who should use SAN storage?
Organizations with high-performance, mission-critical workloads.
Final Thoughts: Why SAN Storage Still Matters
Understanding what is SAN storage helps organizations build resilient, high-performance infrastructures that support business growth and security objectives. While not every workload needs SAN storage, for the right use cases it delivers unmatched reliability and speed.
As data threats grow and uptime expectations rise, securing storage infrastructure is more important than ever.
👉 See how advanced cybersecurity solutions protect critical infrastructure like SAN storage.
Request a personalized demo today.
🔗 Request a demo:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/