What Is Data Warehouse? Complete Guide for IT, Business & Cybersecurity Leaders (2026)
Updated on December 4, 2025, by Xcitium
If you’re searching for what is data warehouse, you’re exploring one of the most important technologies in modern data management, cybersecurity, analytics, and digital transformation. Today, businesses generate more data than ever—from applications, transactions, IoT devices, security logs, cloud platforms, sales tools, and more. But raw data is not useful unless it is organized, centralized, and made ready for analysis. That is exactly what a data warehouse does.
A data warehouse stores and organizes large volumes of data from multiple sources and makes it easy to generate insights, dashboards, and business intelligence (BI). This empowers leaders, IT managers, and cybersecurity teams to make data-driven decisions with accuracy and speed.
In 2026, companies across finance, healthcare, cybersecurity, retail, transportation, energy, and government rely heavily on data warehouses to turn complex data into strategic value. This guide breaks down everything you need to know.
What Is Data Warehouse? (Simple Definition)
A data warehouse is a centralized system that stores structured data from multiple sources so it can be analyzed and used for reporting, insights, and business decision-making.
✔ In simple terms:
A data warehouse is a large, organized storage system where all company data is collected, cleaned, and optimized for analysis.
A data warehouse is built for:
-
Big data
-
Long-term storage
-
Fast queries
-
Reporting and analytics
-
Business intelligence
-
Forecasting and strategic planning
Why Data Warehouses Matter in 2026
Today, businesses depend on data warehouses more than ever because data is growing exponentially. Companies need a reliable way to:
-
Combine data from multiple systems
-
Improve decision-making
-
Ensure data accuracy
-
Maintain security and governance
-
Track business performance
-
Analyze trends and patterns
A data warehouse sits at the center of modern analytics and cybersecurity-driven operations.
How a Data Warehouse Works (Step-by-Step)
To understand what is data warehouse, let’s examine its workflow.
A typical data warehouse process involves four core stages:
1. Data Extraction (E in ETL/ELT)
Data is pulled from sources such as:
-
CRM systems
-
ERP platforms
-
Cybersecurity logs
-
Cloud applications
-
IoT devices
-
Operational databases
-
Spreadsheets
2. Data Transformation (T in ETL)
Data is cleaned, validated, and standardized:
-
Duplicate removal
-
Formatting
-
Error correction
-
Normalization
-
Aggregation
This ensures high-quality analytics.
3. Data Loading (L in ETL)
The cleaned data is loaded into the warehouse:
-
As tables
-
As partitions
-
As columnar datasets
Loading may occur in batches or in real time.
4. Querying & Analytics
Users access the transformed data using:
-
SQL
-
Business intelligence tools
-
Dashboards
-
Reporting tools
The warehouse is optimized for fast query performance across massive datasets.
Types of Data Warehouses
Data warehouses come in several types based on architecture and deployment environment.
1. Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)
A centralized, large-scale warehouse for entire organizations.
Best for:
-
Enterprises
-
Long-term analytics
-
Historical data
2. Data Mart
A smaller warehouse focused on a specific department.
Examples:
-
Marketing data mart
-
Finance data mart
-
Sales analytics mart
3. Cloud Data Warehouse
Runs on cloud infrastructure and offers:
-
Fast scalability
-
High performance
-
Lower maintenance
Popular cloud data warehouses include:
-
Snowflake
-
Amazon Redshift
-
Google BigQuery
-
Azure Synapse Analytics
4. Virtual Data Warehouse
A logical warehouse that connects data from multiple sources without physically moving it.
Data Warehouse vs Database (Key Differences)
Many people confuse data warehouses with databases, but they serve different functions:
| Feature | Database | Data Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Daily operations | Analytics & reporting |
| Data Type | Real-time transactional | Historical, aggregated |
| Speed | Optimized for small tasks | Optimized for large queries |
| Users | Applications & employees | Analysts, data teams, executives |
| Structure | Highly normalized | Denormalized for speed |
A data warehouse is ideal for long-term, strategic analysis.
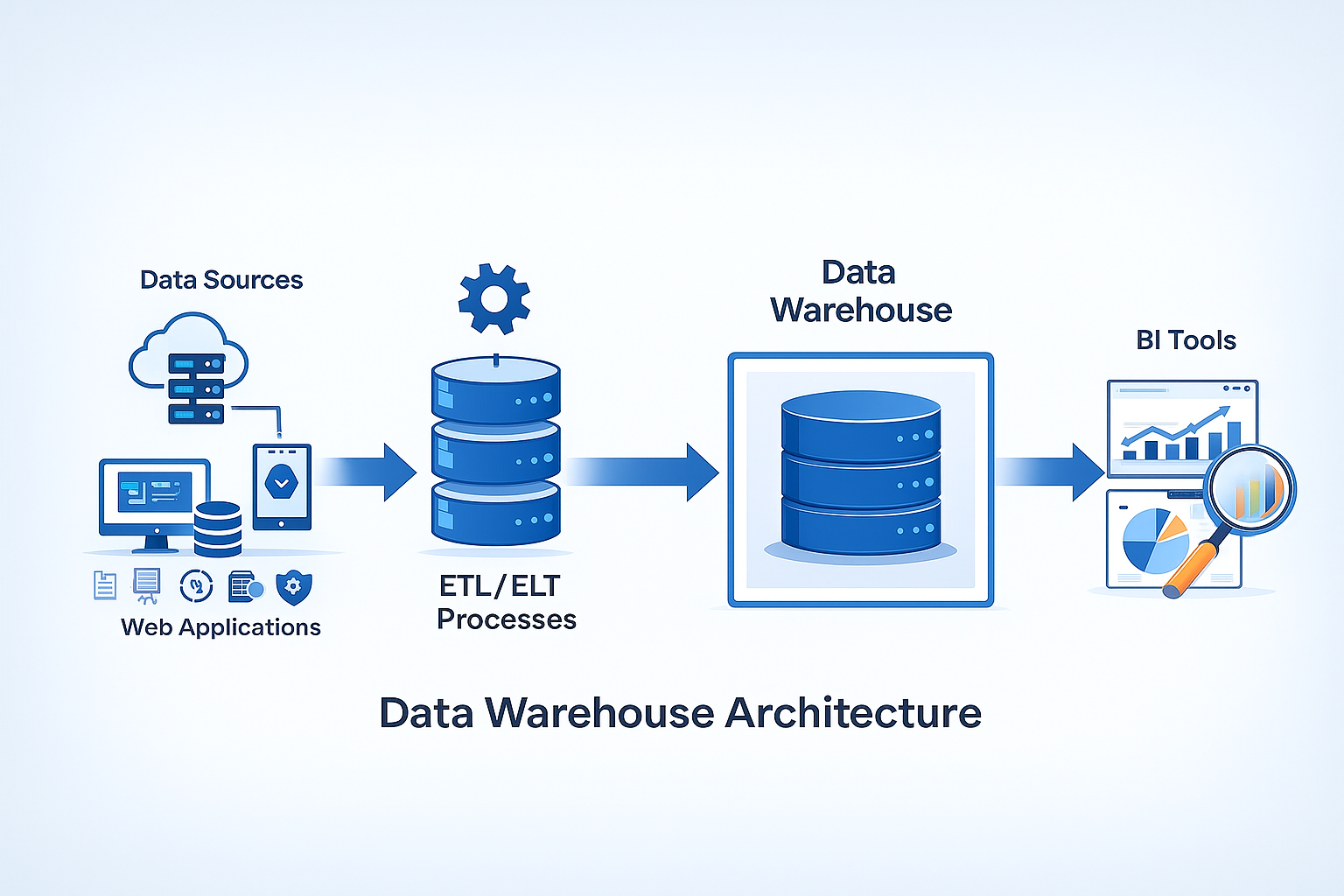
Data Warehouse Architecture (2026 Model)
A modern data warehouse typically includes several layers:
1. Data Sources Layer
Includes:
-
CRM
-
ERP
-
IoT sensors
-
Cybersecurity tools
-
Web applications
-
Databases
2. ETL/ELT Layer
Tools like:
-
Apache Airflow
-
Talend
-
dbt
-
Informatica
-
Azure Data Factory
manage the extraction, transformation, and loading pipeline.
3. Data Storage Layer
Stores structured, cleaned data in:
-
Columnar tables
-
Partitions
-
Data marts
4. Metadata Layer
Tracks:
-
Data lineage
-
Data ownership
-
Schema definitions
-
Business rules
5. Access Layer
BI tools access warehouse data:
-
Power BI
-
Tableau
-
Looker
-
QlikView
This layer delivers insights through dashboards and reports.
Benefits of a Data Warehouse
A well-built data warehouse delivers immense value.
1. Better Decision Making
Executives rely on accurate, consolidated data.
2. Faster Query Performance
Warehouses are optimized for analytics, not transactions.
3. Improved Data Quality
Cleaning and standardization ensure accurate reporting.
4. Advanced Analytics
Supports:
-
Predictive analytics
-
Machine learning
-
Trend forecasting
5. Strong Security & Governance
Data warehouses enforce:
-
Access controls
-
Encryption
-
Data privacy compliance
-
User activity monitoring
6. Scalability
Cloud warehouses scale up or down based on usage.
Data Warehouse in Cybersecurity
A data warehouse is essential for cybersecurity teams because it can store and analyze:
-
SIEM logs
-
Threat intelligence feeds
-
Endpoint activity
-
Firewall logs
-
Identity access logs
-
Incident records
Cybersecurity analysts use warehouse data to:
-
Detect anomalies
-
Investigate attacks
-
Identify insider threats
-
Improve threat intelligence
Common Data Warehouse Challenges
Even the best data warehouses face obstacles.
1. Complex ETL Pipelines
Large data volumes require advanced processing frameworks.
2. High Cost Without Optimization
Cloud compute can become expensive without proper planning.
3. Data Integration Issues
Legacy and modern systems often conflict.
4. Real-Time Data Latency
Some warehouses are not designed for instant analytics.
5. Skill Gaps
Data engineers and warehouse architects are in high demand.
Best Practices for Data Warehouse Success
Follow these guidelines for best performance:
✔ 1. Use a Cloud-First Approach
Cloud warehouses offer agility and scalability.
✔ 2. Optimize ETL Pipelines
Use incremental loading and automation.
✔ 3. Implement Strong Security
-
Encryption
-
Role-based access
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
-
Audit logs
✔ 4. Maintain Data Quality
Use validation rules and monitoring.
✔ 5. Track Data Lineage
Ensures transparency on where data comes from.
✔ 6. Use BI Tools Effectively
Dashboards help leaders make better decisions.
Future of Data Warehousing (2025–2030)
The next decade will transform data warehousing with:
✔ AI-driven ETL optimization
✔ Serverless data warehouses
✔ Real-time streaming data
✔ Data mesh and data fabric architectures
✔ Quantum-resilient encryption
✔ Fully automated cloud warehouses
Data warehouses will become more intelligent, automated, and secure.
FAQs: What Is Data Warehouse?
1. What is data warehouse used for?
A data warehouse is used for analytics, reporting, and business intelligence.
2. What is the difference between a database and a data warehouse?
Databases handle day-to-day operations; warehouses handle long-term analytics.
3. Is a data warehouse part of big data?
Yes, it plays a major role in big data analytics.
4. What industries use data warehouses?
Finance, cybersecurity, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, government, and more.
5. What tools are used to build a data warehouse?
ETL tools like Airflow, Informatica, dbt, and cloud platforms such as Redshift, BigQuery, Snowflake, and Azure Synapse.
Conclusion
Understanding what is data warehouse is essential for business leaders, IT teams, and cybersecurity professionals in 2026. As data continues to grow, the need for centralized, secure, and high-performance analytics infrastructure becomes more critical than ever.
A data warehouse empowers organizations to:
-
Consolidate data
-
Improve decision-making
-
Enhance security
-
Support BI and forecasting
-
Drive innovation
🚀 Strengthen Your Data & Security Architecture Today
👉 Request a Demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/