How to Change Directory in CMD: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners and Pros
Updated on August 5, 2025, by Xcitium
Ever tried navigating through folders in Windows using Command Prompt and hit a wall? You’re not alone. While GUI interfaces dominate today’s OS use, knowing how to change directory in CMD (Command Prompt) remains an essential skill—especially for IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, developers, and power users. It saves time, aids automation, and is often necessary for remote admin tasks and scripting.
In this guide, we’ll break it down for all levels—whether you’re launching your first CMD window or scripting batch jobs on remote servers.
Understanding the Basics of CMD
Before diving into commands, let’s understand what CMD (Command Prompt) is:
- CMD, short for Command Prompt, is the default command-line interpreter on Windows OS.
- It allows users to interact with the system using text-based commands.
- This is especially useful for tasks like directory navigation, file manipulation, network configuration, and more.
Why You Might Need to Change Directory in CMD
Here are common use cases:
- Accessing files stored deep in subdirectories.
- Running scripts or executables located in specific folders.
- Administering remote servers.
- Troubleshooting application issues.
- Creating automation tasks or batch jobs.
Command Syntax: How to Change Directory in CMD
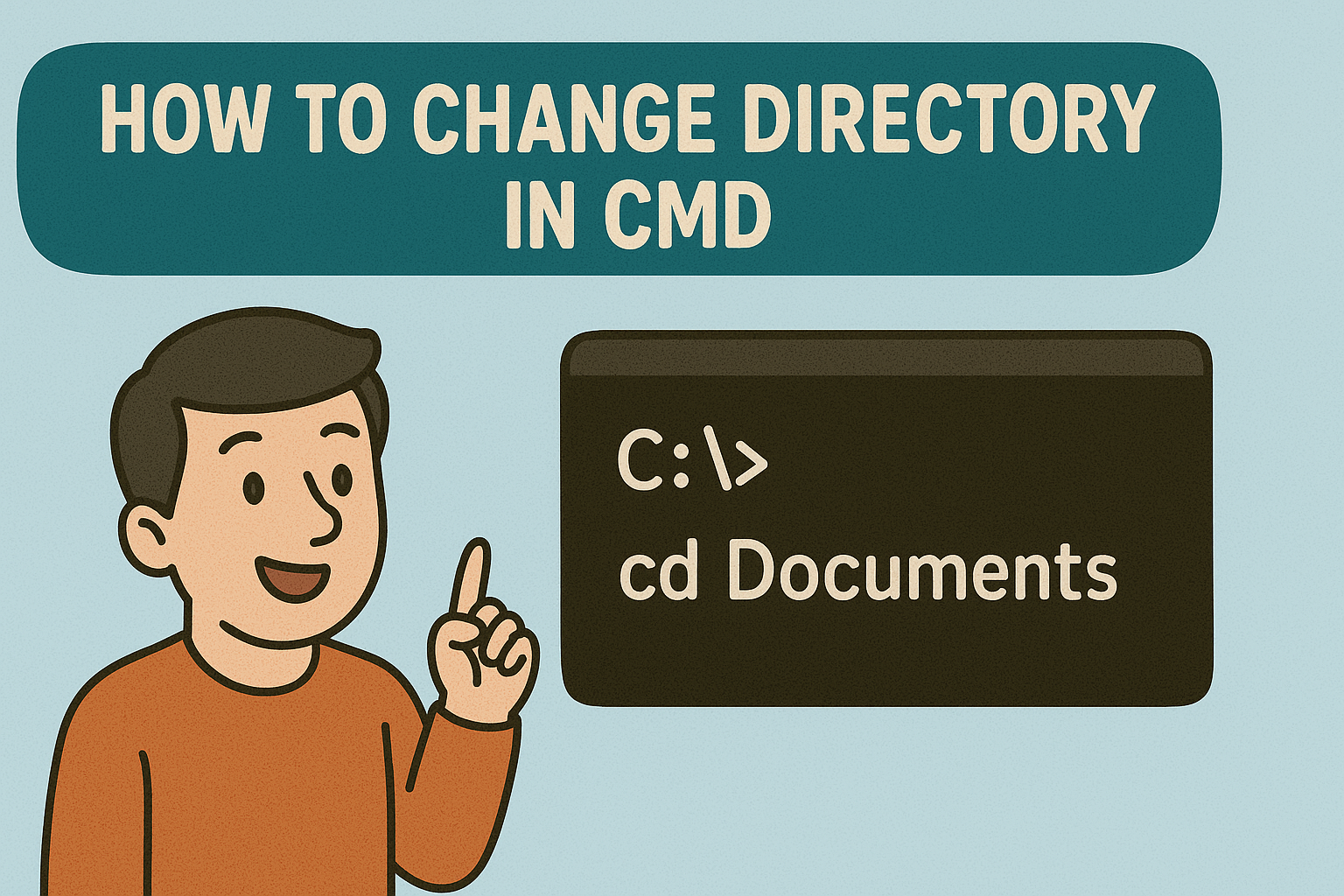
To move from one folder to another, use the cd command (short for change directory).
1. Basic Syntax
cd foldername
Example:
cd Documents
This changes the working directory to Documents, provided it’s a subfolder of your current directory.
2. Navigating to Another Drive
To switch from drive C: to D: and then access a folder:
D:
cd Games
First, switch drives, then run cd for the target folder.
3. Go Up One Level
cd ..
.. tells CMD to go one directory level up.
4. Access a Full Path
cd C:\Users\YourUsername\Downloads
This accesses a directory regardless of your current location.
5. Using Quotation Marks for Folders with Spaces
cd “My Documents”
CMD requires quotes when directory names include spaces.
6. Clear the Screen
cls
Not related to directory navigation, but useful for cleaning up your workspace.
Common Directory Navigation Scenarios
Use Case 1: Navigating to a System Folder
cd C:\Windows\System32
Used by admins to access system utilities.
Use Case 2: Launching a Script in a Deep Folder
cd “C:\Users\Admin\Documents\Scripts”
run_script.bat
Run automation scripts after navigation.
Useful CMD Shortcuts for Power Users
| Shortcut | Action |
| Tab | Auto-complete folder name |
| Arrow ↑↓ | Navigate command history |
| Ctrl + C | Cancel command |
| Alt + Enter | Toggle full-screen CMD |
Troubleshooting Tips
1. “The system cannot find the path specified”
- Check spelling.
- Ensure the folder exists.
- Wrap folder names with spaces in quotes.
2. “Access is denied”
- Try opening CMD with admin privileges.
- Ensure your user account has required permissions.
Use Cases in Cybersecurity & DevOps
- Penetration testers use CMD to navigate to exploit tools.
- IT admins rely on it for scripts and user account management.
- Developers use CMD to compile and run code from specific directories.
Best Practices
- Keep folder names simple and lowercase.
- Avoid spaces; use underscores or hyphens.
- Set environment variables for frequently used paths.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How do I change to another drive in CMD?
Use the drive letter followed by a colon. For example, D: switches you to drive D.
2. How do I open Command Prompt in a specific directory?
Shift + Right-click in the folder → “Open PowerShell window here” or type cmd in the folder’s address bar.
3. What does cd .. do in CMD?
It moves you up one level in the directory structure.
4. How can I check my current directory in CMD?
Type cd and press Enter. It will show your current path.
5. How do I list contents of a directory in CMD?
Use the dir command to list all files and folders in the current directory.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to change directory in CMD is a foundational skill for anyone in IT, cybersecurity, and system administration. It opens the door to advanced scripting, automation, and system configuration. With just a few keystrokes, you can boost your workflow speed and become more efficient in Windows environments.
Ready to Supercharge Your Cybersecurity Operations?
Experience the next level of endpoint protection, threat detection, and automation with Xcitium.