Shadow IT and Identity Risks
Updated on February 20, 2026, by Xcitium
Have you ever discovered a new app in your company—one that IT never approved? You’re not alone. Studies show that a significant percentage of enterprise applications are adopted without IT’s knowledge. This phenomenon, known as Shadow IT, is growing rapidly—and with it, serious identity risks.
Shadow IT and Identity Risks: While employees often adopt unsanctioned tools to boost productivity, Shadow IT opens the door to unauthorized access, credential exposure, compliance violations, and data breaches. In today’s cloud-first and remote-work environments, unmanaged apps and identities are a ticking time bomb.
In this guide, we’ll break down what Shadow IT is, how it creates identity and access management (IAM) risks, and how your organization can reduce exposure using practical, proven strategies.
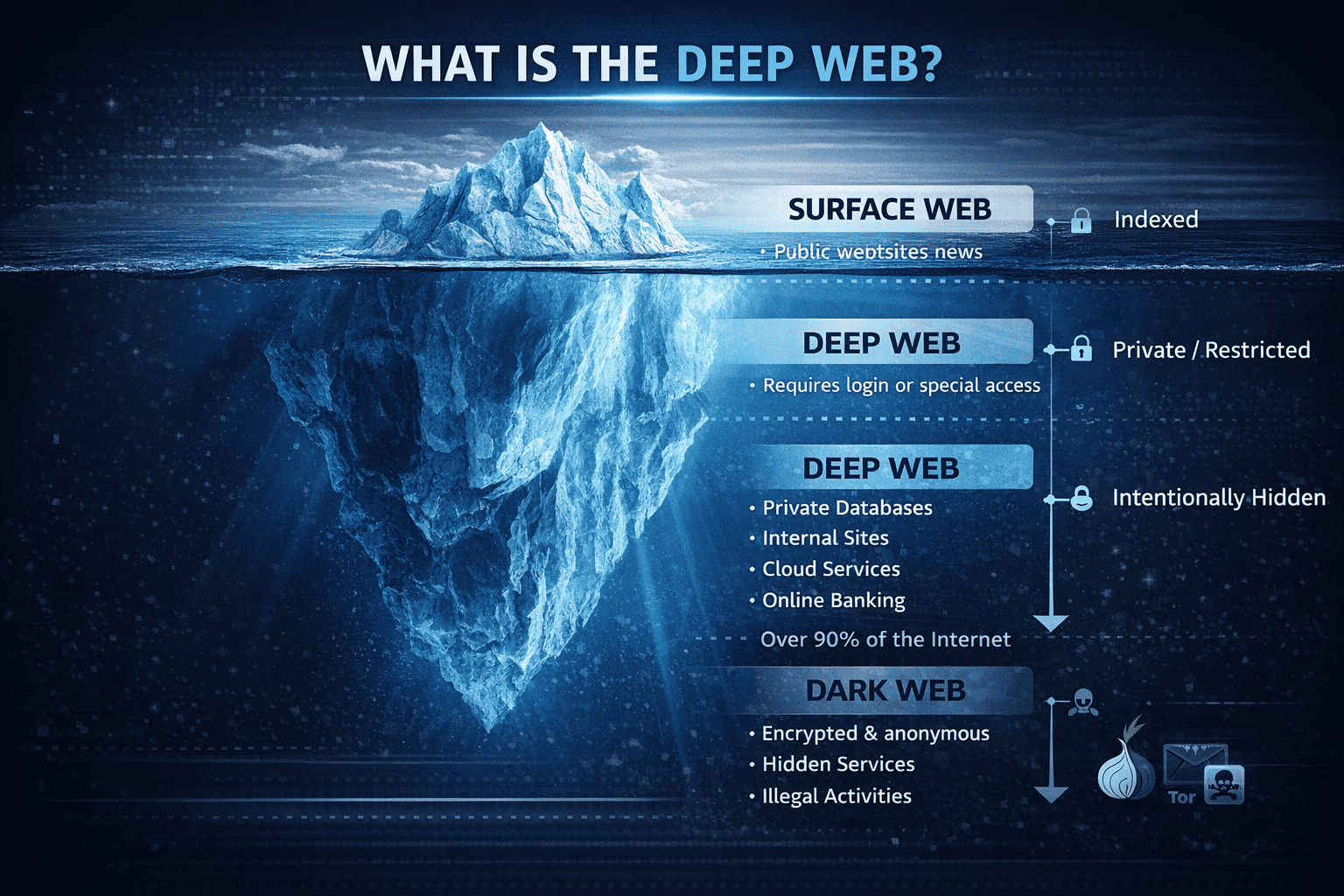
What Is Shadow IT?
Shadow IT refers to any software, hardware, cloud service, or SaaS application used within an organization without the approval or oversight of the IT department.
Common Examples of Shadow IT
-
Employees using personal file-sharing apps (e.g., unapproved cloud storage)
-
Teams adopting collaboration tools without IT review
-
Developers signing up for third-party APIs
-
Marketing teams using unauthorized analytics platforms
-
Personal devices accessing corporate networks
Shadow IT is not always malicious. Often, it starts with good intentions. However, without governance, it quickly becomes a major cybersecurity liability.
Understanding Identity Risks in Shadow IT
Modern security revolves around identity. If attackers compromise user credentials, they can bypass traditional perimeter defenses. Shadow IT significantly increases identity risk by creating unmanaged access points.
Why Identity Is the New Attack Surface
In cloud and SaaS environments:
-
Users log in from anywhere
-
Applications store sensitive data externally
-
Credentials unlock multiple services
-
Single sign-on (SSO) integrations expand access scope
When IT lacks visibility into these tools, identity security weakens.
How Shadow IT Creates Identity and Access Risks
1. Unmanaged User Accounts
Employees often create accounts using corporate email addresses. When they leave the company, these accounts may remain active—creating orphaned identities.
Risk Impact:
-
Former employees retain access
-
Password reuse across platforms
-
Increased insider threat exposure
2. Weak or Reused Credentials
Shadow apps often lack enforced security policies such as:
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
-
Strong password requirements
-
Conditional access policies
This makes them prime targets for credential stuffing and phishing attacks.
3. Lack of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Approved enterprise systems follow structured identity and access management (IAM) protocols. Shadow IT tools rarely integrate with corporate RBAC frameworks.
Consequences:
-
Excessive user privileges
-
No least-privilege enforcement
-
Inconsistent access permissions
4. No Centralized Monitoring
Security teams cannot monitor what they cannot see. Without centralized logging and audit trails:
-
Suspicious activity goes unnoticed
-
Breaches are detected late
-
Compliance audits fail
Business Impacts of Shadow IT and Identity Risks
Shadow IT is more than a technical issue—it’s a business risk.
Data Breaches and Financial Loss
Unsecured SaaS tools can expose sensitive data such as:
-
Customer records
-
Financial information
-
Intellectual property
-
Employee data
The average cost of a data breach runs into millions of dollars—not including reputational damage.
Compliance Violations
Industries subject to regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, etc.) must control data access and processing. Shadow IT undermines these controls.
Failure to manage identities properly can result in:
-
Regulatory fines
-
Legal consequences
-
Loss of certifications
Reduced Visibility and Security Gaps
Without visibility into cloud usage, organizations lose:
-
Control over authentication policies
-
Consistency in identity governance
-
Accurate risk assessment
This fragmented environment makes cyberattacks easier to execute.
How to Mitigate Shadow IT Identity Risks
Eliminating Shadow IT entirely is unrealistic. Instead, organizations must focus on visibility, governance, and identity protection.
Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
A centralized IAM solution helps control and secure user access across approved and discovered applications.
Key IAM Best Practices:
-
Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA)
-
Use single sign-on (SSO) with security controls
-
Apply least-privilege access policies
-
Automate user provisioning and deprovisioning
-
Conduct regular access reviews
IAM ensures every identity is verified and monitored.
Deploy Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
A CASB solution provides visibility into cloud application usage and helps detect unauthorized SaaS tools.
Benefits include:
-
Shadow IT discovery
-
Risk scoring of applications
-
Policy enforcement
-
Data loss prevention (DLP)
Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model
Zero Trust assumes no user or device should be trusted by default.
Core Zero Trust Principles:
-
Verify every access request
-
Enforce least privilege
-
Continuously monitor behavior
-
Segment network access
By validating identity continuously, organizations reduce exposure from unmanaged apps.
Educate Employees About Security Risks
Shadow IT often grows due to convenience. Training employees on secure alternatives reduces risky behavior.
Focus on:
-
Recognizing phishing attempts
-
Using approved collaboration tools
-
Reporting new software needs
-
Understanding identity security risks
Security awareness strengthens your human firewall.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Identity-based threats evolve quickly. Security teams must monitor for:
-
Anomalous login patterns
-
Unusual privilege escalation
-
Suspicious third-party app integrations
-
Credential compromise indicators
Automated threat detection tools improve response time and reduce dwell time.
Building a Culture That Reduces Shadow IT
Technical controls are essential, but culture matters just as much.
Encourage Transparent IT Collaboration
Instead of blocking tools outright:
-
Create a fast approval process
-
Offer secure alternatives
-
Involve teams in tool selection
When IT becomes an enabler rather than a gatekeeper, Shadow IT naturally declines.
The Future of Identity Security in a Cloud-First World
As organizations continue adopting SaaS, hybrid work, and third-party integrations, identity will remain the primary attack vector.
Emerging trends include:
-
Identity threat detection and response (ITDR)
-
Passwordless authentication
-
Adaptive access policies
-
AI-driven anomaly detection
Companies that prioritize identity security now will stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main risk of Shadow IT?
The biggest risk is unmanaged identities. Unauthorized apps create blind spots, making it easier for attackers to compromise credentials and access sensitive data.
2. How does Shadow IT affect compliance?
Shadow IT bypasses established security controls, leading to improper data handling and potential violations of regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
3. Can Shadow IT ever be beneficial?
It can highlight productivity gaps. However, without governance and identity management controls, the security risks outweigh the benefits.
4. How can organizations detect Shadow IT?
Using tools like CASB, network monitoring, and identity analytics solutions helps identify unauthorized applications and risky access behaviors.
5. What role does Zero Trust play in reducing identity risks?
Zero Trust ensures every access request is verified and continuously monitored, minimizing the impact of compromised credentials or unmanaged apps.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Identity Before It’s Too Late
Shadow IT is not just an IT problem—it’s an identity security challenge that affects your entire organization. As SaaS adoption grows, unmanaged applications multiply, and cybercriminals target identities more aggressively than ever.
The good news? With strong identity and access management, Zero Trust architecture, continuous monitoring, and employee awareness, you can dramatically reduce exposure.
Don’t wait for a breach to reveal your blind spots.
👉 Strengthen your identity security and eliminate Shadow IT risks today.
Request a demo and see how advanced cybersecurity solutions can protect your organization:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Secure your identities. Protect your data. Stay ahead of threats.