What Is a Network in Computer? A Complete Guide for Modern Businesses
Updated on February 11, 2026, by Xcitium
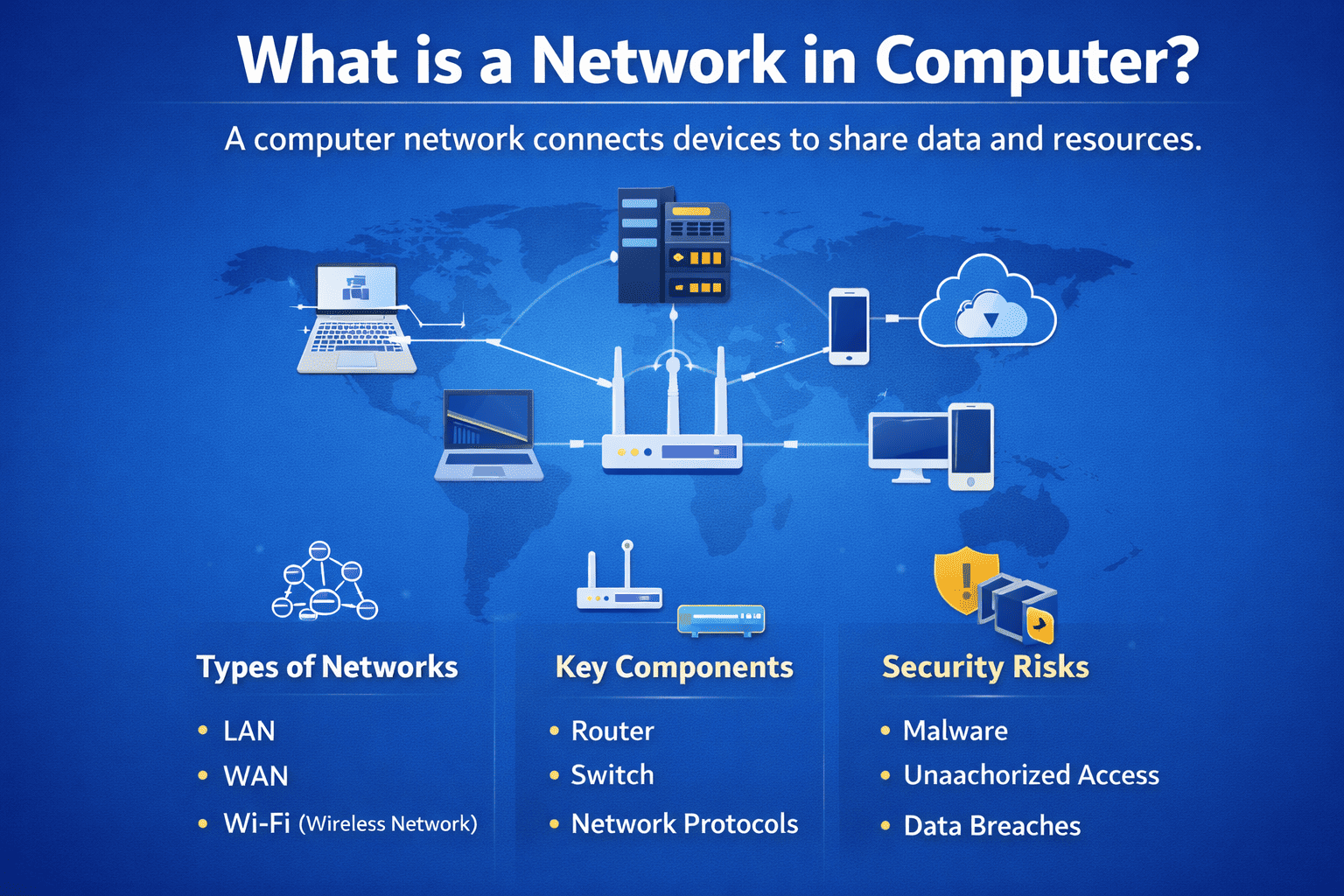
Have you ever wondered how your laptop connects to the internet, shares files with colleagues, or accesses cloud applications in seconds? The answer starts with a simple question: what is a network in computer systems?
A computer network connects devices so they can communicate, share data, and access resources efficiently. From small office setups to global enterprise infrastructures, networks are the backbone of digital operations. Understanding what is a network in computer environments is essential for IT managers, cybersecurity teams, and business leaders who rely on stable and secure connectivity.
In this guide, we’ll explore what is a network in computer systems, how it works, types of networks, key components, security risks, and best practices for building resilient and secure infrastructures.
What Is a Network in Computer?
What is a network in computer systems?
A computer network is a collection of connected devices—such as computers, servers, routers, and smartphones—that communicate and share data through wired or wireless connections.
In simple terms, a network allows devices to:
-
Share files and resources
-
Access the internet
-
Communicate through email or messaging
-
Connect to cloud services
-
Run enterprise applications
Without networks, modern business operations would stop.
Why Computer Networks Matter Today
Understanding what is a network in computer systems becomes clearer when you consider today’s digital demands.
Businesses rely on networks to:
-
Enable remote and hybrid work
-
Support cloud computing
-
Protect sensitive data
-
Connect distributed teams
-
Maintain operational continuity
Networks are no longer optional—they are mission-critical.
How Does a Computer Network Work?
To fully answer what is a network in computer systems, we must understand how it functions.
At its core, a network works by allowing devices to exchange data packets using communication protocols.
Basic networking process:
-
A device sends data
-
The data is broken into packets
-
Packets travel through routers and switches
-
The receiving device reassembles the data
This happens in milliseconds.
Key Components of a Computer Network
Every network includes essential components that enable communication.
1. Devices (Nodes)
Nodes are the endpoints in a network.
Examples include:
-
Computers
-
Smartphones
-
Servers
-
Printers
-
IoT devices
Each node sends and receives data.
2. Network Interface Cards (NICs)
NICs allow devices to connect to the network.
They can be:
-
Wired (Ethernet)
-
Wireless (Wi-Fi)
Without NICs, devices cannot communicate.
3. Routers
Routers direct traffic between networks.
They:
-
Connect local networks to the internet
-
Manage traffic flow
-
Assign IP addresses
Routers are essential for external connectivity.
4. Switches
Switches connect devices within a local network.
They:
-
Forward data efficiently
-
Reduce traffic collisions
-
Improve performance
Switches are critical for internal network communication.
5. Network Protocols
Protocols define communication rules.
Common protocols include:
-
TCP/IP
-
HTTP/HTTPS
-
FTP
-
DNS
Protocols ensure devices understand each other.
Types of Computer Networks
To better understand what is a network in computer systems, we must explore the different types.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN connects devices within a limited area.
Examples:
-
Office networks
-
Home networks
-
School labs
LANs offer high speed and low latency.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN connects devices across large geographic areas.
The internet is the largest WAN.
Businesses use WANs to connect branch offices globally.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN connects devices within a city or region.
It’s larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
Wireless Networks
Wireless networks use radio signals instead of cables.
Examples include:
-
Wi-Fi networks
-
Mobile networks
They provide flexibility but require strong security controls.
Network Topologies Explained
Topology describes how devices are arranged.
Common topologies:
-
Star
-
Bus
-
Ring
-
Mesh
Modern networks often use hybrid models.
What Is Computer Network Security?
Understanding what is a network in computer environments also means understanding network security.
Computer network security protects networks from unauthorized access, misuse, and cyberattacks.
Common Network Security Threats
Modern networks face constant threats.
Common threats include:
-
Malware
-
Ransomware
-
Phishing
-
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
-
Unauthorized access
Cybercriminals often target network vulnerabilities first.
Why Network Security Is Critical for Businesses
Without strong security, networks become entry points for attackers.
Consequences include:
-
Data breaches
-
Financial loss
-
Regulatory penalties
-
Reputational damage
-
Operational disruption
Network security must be proactive—not reactive.
Core Network Security Measures
Organizations protect networks using layered defenses.
Common protections include:
-
Firewalls
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
-
Encryption
-
Multi-factor authentication
-
Zero Trust architecture
Layered security reduces risk exposure.
Network Infrastructure in Cloud Environments
Modern networks extend beyond physical offices.
Cloud networks connect:
-
Remote employees
-
SaaS platforms
-
Cloud storage
-
Virtual machines
Understanding what is a network in computer systems now includes hybrid and multi-cloud models.
Network Performance and Optimization
Network performance affects productivity.
Key performance factors:
-
Bandwidth
-
Latency
-
Packet loss
-
Congestion
Optimizing network infrastructure ensures smooth operations.
Role of Networks in Cybersecurity Strategy
Networks are both enablers and targets.
Cybersecurity teams monitor networks to:
-
Detect suspicious traffic
-
Identify lateral movement
-
Block malicious domains
-
Analyze attack patterns
Strong visibility across network infrastructure improves incident response.
The Evolution of Computer Networks
Computer networks have evolved significantly.
From:
-
Basic LAN setups
To: -
Global cloud-based architectures
Modern networking integrates:
-
Software-defined networking (SDN)
-
AI-driven monitoring
-
Autonomous threat detection
The network is now intelligent.
Common Network Mistakes Businesses Make
Many organizations underestimate networking risks.
Common mistakes include:
-
Weak password policies
-
Unpatched routers
-
Flat network structures
-
Lack of monitoring
-
Ignoring insider threats
Addressing these gaps strengthens resilience.
Best Practices for Building a Secure Network
To maximize security and performance, follow best practices.
Recommended steps:
-
Implement Zero Trust principles
-
Segment networks
-
Encrypt traffic
-
Monitor continuously
-
Conduct regular audits
Proactive management reduces vulnerabilities.
Future Trends in Computer Networking
The future of networking includes:
-
AI-powered network analytics
-
5G integration
-
Edge computing
-
Automated threat containment
-
Self-healing networks
Understanding what is a network in computer systems today means preparing for tomorrow.
FAQs: What Is a Network in Computer?
1. What is a network in computer systems?
It is a group of connected devices that share data and resources.
2. What are the main types of computer networks?
LAN, WAN, MAN, and wireless networks are the most common types.
3. Why is computer network security important?
It prevents cyberattacks, data breaches, and operational downtime.
4. What devices are used in a network?
Routers, switches, servers, NICs, and endpoints.
5. Can small businesses build secure networks?
Yes. Even small networks can implement strong security practices.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding Computer Networks Matters
So, what is a network in computer systems? It is the foundation of digital communication, collaboration, and cybersecurity. Without networks, cloud computing, remote work, and global business operations would be impossible.
For IT leaders and executives, understanding network fundamentals supports smarter decisions around:
-
Security
-
Infrastructure investments
-
Business continuity
-
Compliance
Networks are not just cables and routers—they are the backbone of modern enterprise resilience.
Take the Next Step Toward Stronger Network Security
Ready to gain deeper visibility and protection across your network infrastructure?
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Discover how advanced security solutions help organizations monitor, protect, and strengthen network environments against modern cyber threats.