How to Execute PowerShell Script: A Complete Guide for IT and Security Teams
Updated on January 30, 2026, by Xcitium
Have you ever tried running a script only to be blocked by Windows security warnings? Knowing how to execute PowerShell script correctly is essential for IT administrators, cybersecurity professionals, and business leaders who rely on automation. PowerShell is one of the most powerful tools in the Windows ecosystem, yet improper execution can lead to errors, security risks, or system instability.
This guide explains how to execute PowerShell script safely and efficiently, from beginner-friendly methods to enterprise-level best practices. Whether you manage endpoints, automate security workflows, or oversee IT operations, mastering PowerShell execution is a must.
What Is PowerShell and Why It Matters
PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management framework built into Windows. It combines a command-line shell with a powerful scripting language designed for system administration.
Understanding how to execute PowerShell script allows organizations to:
-
Automate repetitive administrative tasks
-
Manage systems at scale
-
Improve operational efficiency
-
Strengthen security workflows
-
Reduce human error
PowerShell is widely used in cybersecurity, cloud management, and endpoint administration because it integrates deeply with Windows and Microsoft services.
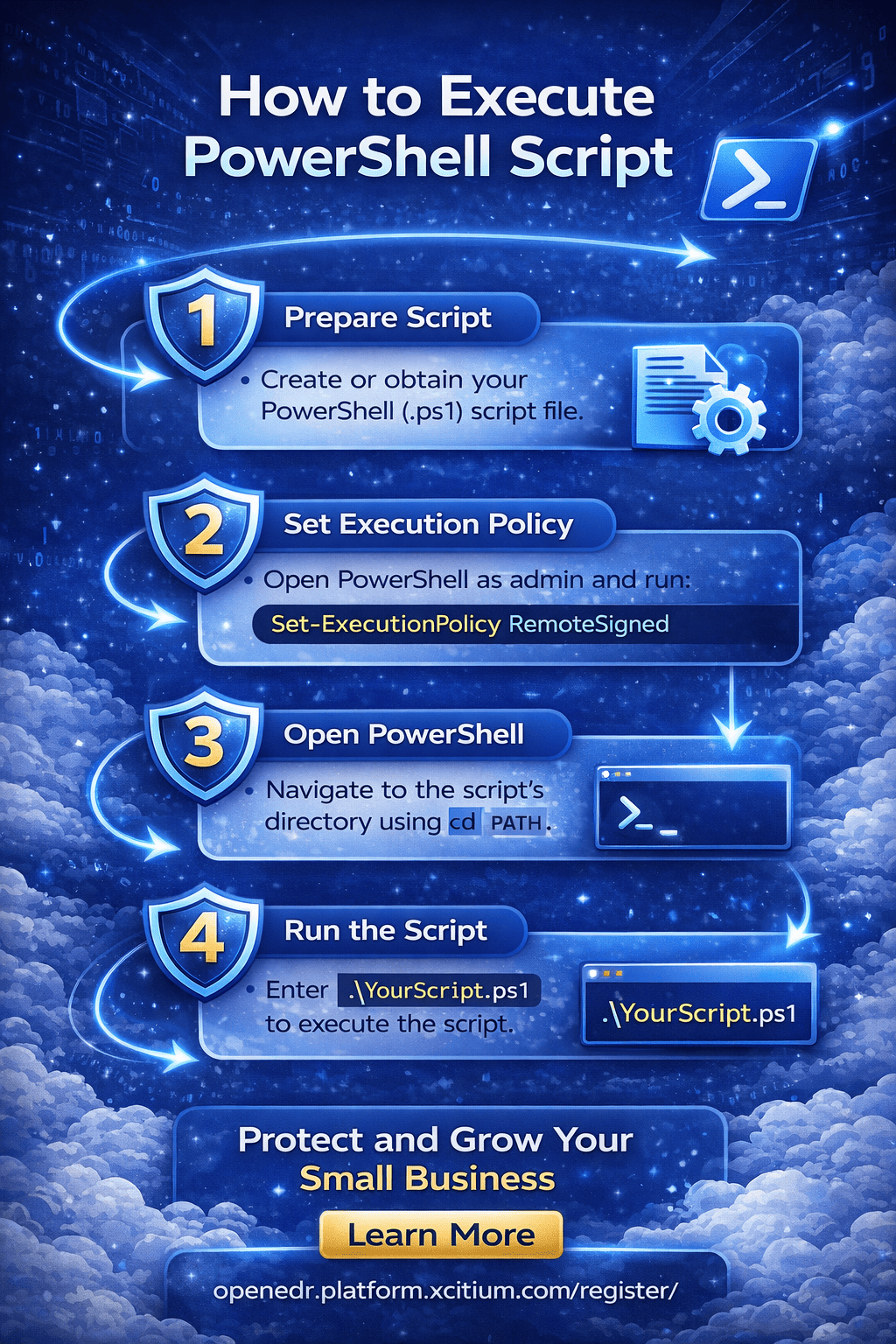
How to Execute PowerShell Script: Basic Methods
There are multiple ways to execute PowerShell script files depending on your environment and permissions.
Method 1: Execute PowerShell Script from File Explorer
This is the simplest method, though often restricted by policy.
Steps:
-
Right-click the
.ps1file -
Select Run with PowerShell
-
Approve any security prompts
This approach is convenient but limited in enterprise environments where script execution is restricted.
Method 2: Execute PowerShell Script from PowerShell Console
This is the most common and reliable method.
Steps:
-
Open PowerShell as Administrator
-
Navigate to the script directory:
-
Run the script:
This method gives better visibility into script output and errors.
Understanding PowerShell Execution Policy
One of the most common issues when learning how to execute PowerShell script is execution policy restrictions.
What Is Execution Policy?
Execution policy controls whether scripts are allowed to run and under what conditions. It is not a security boundary but a safety feature.
Common Execution Policy Levels
-
Restricted – No scripts allowed
-
AllSigned – Only signed scripts can run
-
RemoteSigned – Local scripts allowed, downloaded scripts must be signed
-
Unrestricted – All scripts can run
Most systems default to Restricted or RemoteSigned.
How to Change Execution Policy Safely
To temporarily allow script execution:
Best practice is to change policy at the CurrentUser scope rather than system-wide.
Understanding execution policy is critical to executing PowerShell scripts securely.
How to Execute PowerShell Script with Parameters
Many scripts require parameters to function correctly.
Example:
Passing parameters improves script flexibility and reduces hardcoding, which is essential for secure automation.
How to Execute PowerShell Script Remotely
Remote execution is common in enterprise IT and security operations.
Using PowerShell Remoting
Requirements:
-
WinRM enabled
-
Proper credentials
-
Network connectivity
Example:
Remote execution allows centralized management but must be secured properly to prevent abuse.
PowerShell Script Security Best Practices
Knowing how to execute PowerShell script also means knowing how to do it securely.
Follow These Security Guidelines
-
Use script signing for production scripts
-
Avoid running scripts from unknown sources
-
Limit execution policy scope
-
Monitor PowerShell activity with logging
-
Restrict administrative privileges
PowerShell is powerful, but misuse can expose systems to risk.
PowerShell in Cybersecurity and Incident Response
PowerShell plays a major role in cybersecurity operations.
Common Security Use Cases
-
Endpoint investigation and response
-
Log collection and analysis
-
Automated remediation actions
-
Threat hunting
However, attackers also abuse PowerShell. That’s why visibility and monitoring are critical.
Modern EDR platforms track PowerShell behavior to detect malicious activity.
Common Errors When Executing PowerShell Scripts (And How to Fix Them)
Even experienced users encounter issues.
Script Is Blocked by Execution Policy
Solution: Adjust execution policy at the user scope.
“File Cannot Be Loaded” Error
Solution: Unblock the file:
Script Runs but Produces No Output
Solution: Check error handling and output commands like Write-Output.
Understanding these errors makes script execution smoother and safer.
Best Practices for Enterprise PowerShell Automation
For IT managers and executives, PowerShell should be governed, not improvised.
Enterprise Best Practices
-
Maintain a centralized script repository
-
Use version control
-
Apply least-privilege principles
-
Audit script execution regularly
-
Integrate PowerShell with security monitoring tools
Automation without governance can create hidden risks.
Measuring the Success of PowerShell Automation
Execution success isn’t just about scripts running.
Key Metrics to Track
-
Execution success rate
-
Error frequency
-
Time saved through automation
-
Security incidents linked to scripts
These metrics help justify automation investments and improve processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How to execute PowerShell script on Windows 11?
Open PowerShell as Administrator, navigate to the script location, and run it using .\scriptname.ps1.
2. Why is my PowerShell script blocked?
Execution policy restrictions or file security blocks are the most common causes.
3. Is it safe to change PowerShell execution policy?
Yes, when done at the user scope and with proper controls.
4. Can PowerShell scripts be dangerous?
Yes. Malicious scripts exist, which is why script sources and monitoring matter.
5. Do enterprises use PowerShell for automation?
Absolutely. PowerShell is widely used for IT operations, security, and cloud management.
Final Thoughts: Why PowerShell Execution Skills Matter
Understanding how to execute PowerShell script is no longer optional for modern IT and security teams. PowerShell enables automation, improves efficiency, and supports large-scale operations—but only when used responsibly.
With proper execution methods, security controls, and governance, PowerShell becomes a strategic advantage rather than a risk.
If you want deeper visibility into PowerShell activity, automated threat detection, and stronger endpoint protection:
👉 See how advanced security automation works
Request a demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/