What Is Biometric? The Complete 2026 Guide to Biometric Authentication & Security
Updated on December 3, 2025, by Xcitium
If you’re searching for what is biometric, you’re likely interested in one of the fastest-growing security technologies used by businesses, governments, and everyday consumers. Biometrics have rapidly become the foundation of modern authentication—powering secure access to smartphones, corporate systems, banking apps, critical infrastructure, and more. With the increasing rise of cyberattacks, identity theft, and password breaches, organizations are shifting to biometrics to strengthen access control and enhance cybersecurity.
Biometrics use a person’s unique biological or behavioral characteristics—such as fingerprints, facial structure, iris patterns, or voice—to verify identity. Unlike passwords, biometrics cannot be easily guessed, stolen, or forgotten. This makes biometric authentication essential for IT managers, cybersecurity teams, CEOs, and organizations striving for stronger digital protection.
This comprehensive guide explains what biometrics are, how biometric authentication works, its types, real-world uses, cybersecurity risks, and best practices for implementing biometric security in 2026.
What Is Biometric? (Simple Definition)
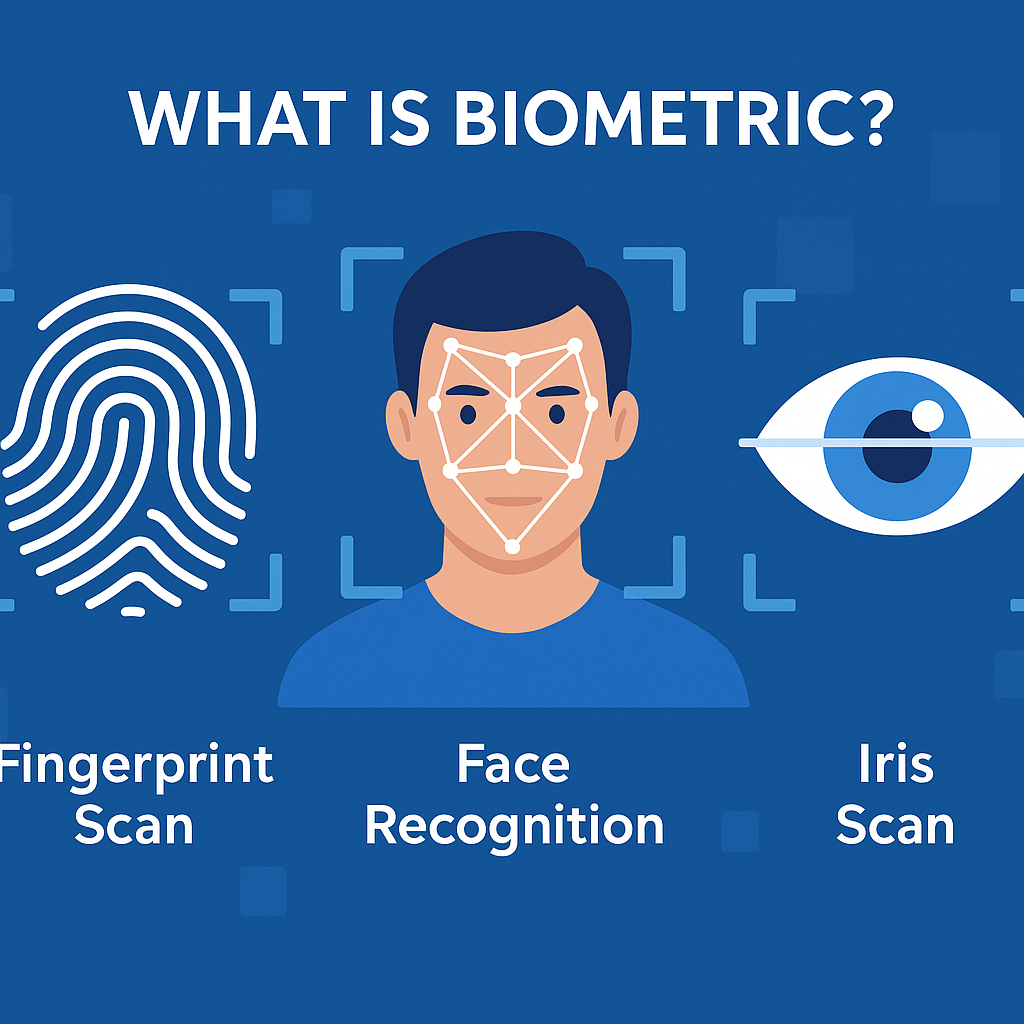
A biometric is a measurable biological or behavioral characteristic that can be used to identify or authenticate a person.
Examples include:
-
Fingerprints
-
Face recognition
-
Iris and retina patterns
-
Voice characteristics
-
Hand geometry
-
Behavioral traits (typing rhythm, walking patterns, etc.)
✔ In simple terms:
Biometrics are physical or behavioral features used for identity verification.
Biometric authentication uses these features to confirm someone’s identity, usually for security purposes.
Why Biometrics Matter More Than Ever
Cybercrime is increasing at an alarming rate:
-
80% of data breaches involve stolen or weak passwords
-
Identity theft rose over 30% in the last two years
-
Organizations lose billions annually due to unauthorized access
Passwords alone are no longer enough.
Biometrics provide:
-
Stronger authentication
-
Faster access
-
Less user friction
-
Higher identity accuracy
This is why biometrics are used everywhere—phones, airports, banking, corporate networks, and critical infrastructure.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work? (Step-by-Step)
Biometric authentication has four main stages:
1. Data Capture
A biometric sensor (camera, fingerprint reader, microphone) captures a user’s biological trait.
2. Feature Extraction
The biometric system analyzes the captured data and extracts unique identifiers, such as:
-
Fingerprint patterns
-
Facial points
-
Iris textures
-
Voice frequency patterns
3. Template Creation
The system converts extracted features into a secure digital template (mathematical representation).
❗ Important:
Biometric systems do NOT store actual images—only encrypted templates.
4. Matching / Verification
During authentication:
-
The new biometric sample is compared to the stored template
-
If they match → access is granted
-
If not → access is denied
Biometrics can be used for authentication (1:1 match) or identification (1:many match).
Types of Biometrics (2026 Overview)
Biometrics are divided into two major categories:
1. Physiological Biometrics (Physical Traits)
These measure physical characteristics that are unique and stable.
Examples:
-
Fingerprint recognition (most common form of biometric security)
-
Facial recognition
-
Iris scanning
-
Retina scanning
-
Hand geometry
-
DNA analysis
These are widely used due to high accuracy.
2. Behavioral Biometrics
These measure behavioral patterns unique to each individual.
Examples:
-
Voice recognition
-
Keystroke dynamics
-
Gait analysis (walking pattern)
-
Mouse movement
-
Signature recognition
Behavioral biometrics are often used as complementary authentication.
Most Common Types of Biometric Authentication
Let’s break down the most widely used methods worldwide:
1. Fingerprint Recognition
Used in:
-
Smartphones
-
Laptops
-
Access control
-
Time-tracking systems
Accurate, fast, and cost-effective.
2. Facial Recognition
Used in:
-
Phones and laptops
-
Airports
-
Banking apps
-
Public security systems
Powered by AI and 3D-mapping.
3. Iris Recognition
Ultra-secure and extremely accurate.
Used in:
-
Border control
-
Defense industries
-
High-security facilities
4. Voice Recognition
Common in:
-
Call centers
-
Smart assistants
-
Banking verification
5. Retina Scanning
Highly accurate but used in niche high-security environments.
6. Behavioral Biometrics
Increasingly used in cybersecurity for:
-
Fraud detection
-
Continuous authentication
-
Insider threat monitoring
Biometrics vs. Passwords: Why Biometrics Are Better
Passwords Are Weak Because:
-
They can be hacked
-
Users reuse passwords
-
People choose weak passwords
-
Passwords can be shared or stolen
Biometrics Are Strong Because:
-
Unique to each person
-
Hard to fake
-
Convenient and fast
-
Cannot be “forgotten”
-
Enable multi-factor authentication
Thus, biometrics provide a stronger identity layer for cybersecurity.
Where Biometrics Are Used (Real-World Applications)
✔ 1. Smartphones & Consumer Devices
Face ID, Touch ID, Android biometrics.
✔ 2. Enterprise Security
Secure login to corporate systems.
✔ 3. Finance & Banking
Biometric login, voice verification, fraud detection.
✔ 4. Healthcare
Patient identity, secure medical records.
✔ 5. Government Agencies
-
Border protection
-
ePassports
-
National identity programs
✔ 6. Airports & Travel
Faster identity checks and boarding.
✔ 7. E-Commerce & Payments
Biometric payment authorization.
Advantages of Biometrics
Biometrics offer several benefits over traditional authentication:
1. Increased Security
Harder to spoof than passwords.
2. Faster Access
Instant login with a touch or glance.
3. Convenience
Users do not need to remember anything.
4. Reduced Fraud
Biometrics prevent impersonation and unauthorized access.
5. Higher Accuracy
Each biometric trait is unique.
Challenges & Risks of Biometrics
Despite the benefits, biometrics have challenges worth noting.
1. Privacy Concerns
Biometric data is sensitive.
If compromised, it cannot be “reset” like a password.
2. False Positives / False Negatives
Accuracy varies by system and environment.
3. Spoofing Risks
Although difficult, advanced attackers can attempt:
-
Deepfake voice
-
Face manipulation
-
Fake fingerprints
4. Data Storage Risks
Biometric data must be securely encrypted.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Organizations must follow:
-
GDPR
-
CCPA
-
HIPAA
-
Biometric privacy laws
Best Practices for Biometric Security (For Organizations)
To use biometrics safely, organizations should follow these practices:
✔ 1. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Biometrics + password + token is ideal.
✔ 2. Encrypt Biometric Templates
Never store raw biometric data.
✔ 3. Use Liveness Detection
Ensures that biometrics come from a real person, not a spoof.
✔ 4. Implement Zero-Trust Security
Continuously validate identity.
✔ 5. Limit Biometric Data Access
Only authorized personnel should access templates.
✔ 6. Follow Global Compliance Standards
Avoid legal risks.
✔ 7. Regularly Update Sensors & Algorithms
Improves accuracy and security.
Future of Biometrics (2025–2030)
Biometrics will evolve dramatically in the coming years.
Emerging Trends:
-
AI-powered adaptive biometrics
-
Multi-modal biometric systems
-
Continuous authentication
-
Biometric cryptography
-
Touchless biometrics (face, iris, gait)
-
Quantum-safe biometric encryption
Biometrics will become a core layer of cybersecurity for enterprises worldwide.
FAQs: What Is Biometric?
1. What is biometric authentication?
It’s a security method that verifies identity using unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial features.
2. What are examples of biometrics?
Fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, voice ID, hand geometry, and behavioral biometrics.
3. Are biometrics safer than passwords?
Yes—biometrics are harder to forge and more convenient, though they must be securely stored.
4. What is the difference between biometric and authentication?
Biometrics are the traits; biometric authentication is the process of using those traits for verification.
5. Can biometric data be hacked?
Yes, but with strong encryption, liveness detection, and zero-trust systems, risks can be minimized.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what biometrics are is essential as organizations transition to stronger, more modern authentication methods. Biometrics provide a powerful, convenient, and secure way to verify identity—helping companies reduce fraud, streamline access, and enhance cybersecurity.
In a world where cyberattacks continue to grow in complexity, biometrics offer a critical layer of protection that password-only systems simply cannot provide.
🚀 Strengthen Your Authentication & Cybersecurity with Advanced Protection
👉 Request a Demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/