What Is Multi Factor Authentication? A Complete Guide for Modern Security
Updated on December 15, 2025, by Xcitium

Passwords alone are no longer enough. In fact, stolen or weak credentials are responsible for the majority of data breaches worldwide. That’s why more organizations and individuals are asking a critical question: what is multi factor authentication, and why is it essential for modern cybersecurity?
Multi factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity using more than one method. Even if a password is compromised, attackers are far less likely to gain access. For IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, and business leaders, MFA is no longer a “nice to have”—it’s a foundational security control.
In this guide, we’ll explain what is multi factor authentication, how it works, common MFA methods, benefits, challenges, best practices, and how businesses can implement it effectively.
What Is Multi Factor Authentication?
Multi factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to provide two or more independent verification factors to access an account, system, or application.
Instead of relying on just a password, MFA verifies identity using a combination of factors from different categories.
The goal of MFA is simple: make unauthorized access significantly harder, even if one factor is compromised.
Why Multi Factor Authentication Is So Important Today
Understanding what is multi factor authentication also means understanding why it’s become critical.
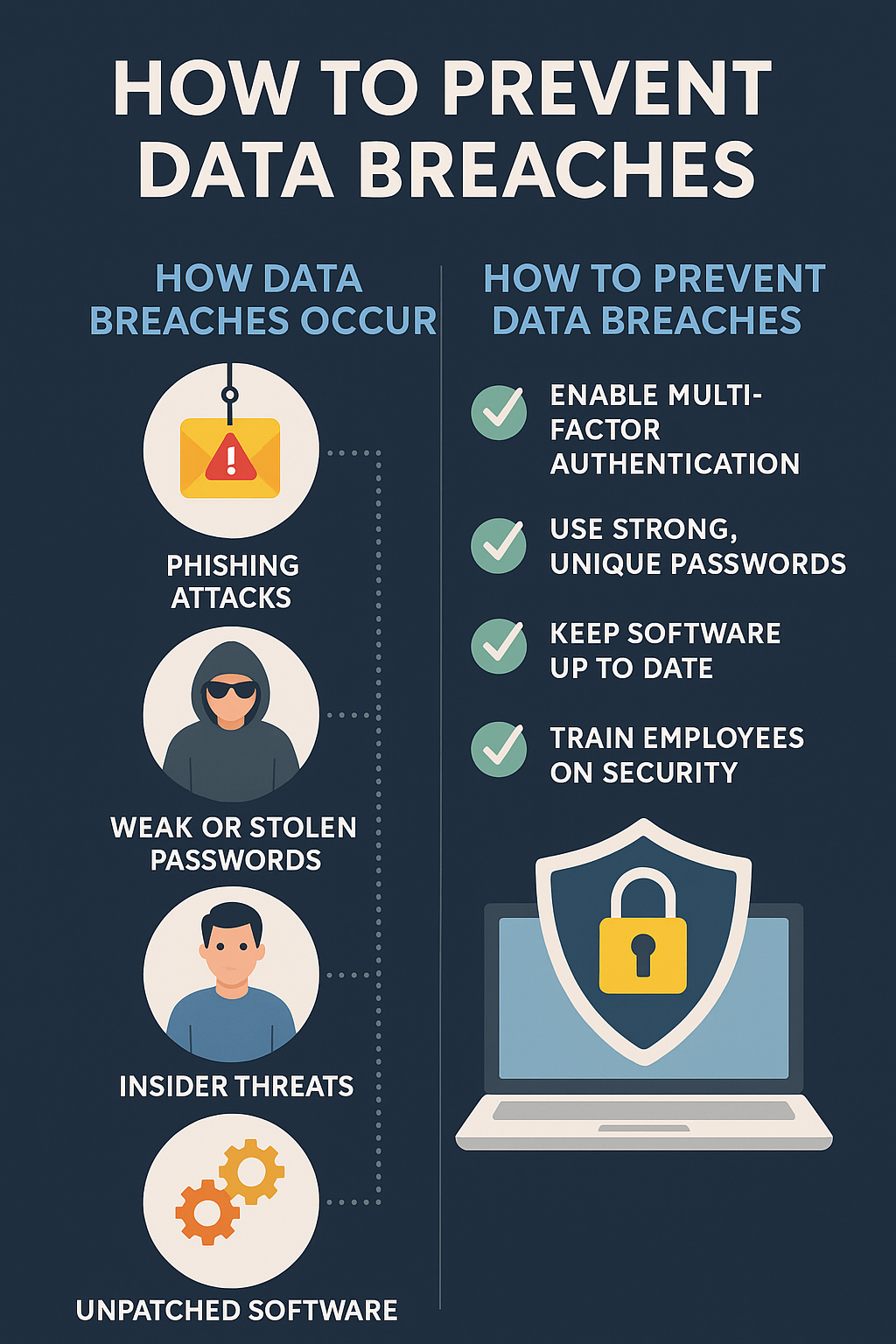
1. Passwords Are Easily Compromised
Passwords can be:
-
Phished
-
Reused
-
Brute-forced
-
Leaked in data breaches
MFA reduces the risk dramatically.
2. Phishing Attacks Are More Sophisticated
Attackers now use:
-
AI-generated emails
-
Fake login pages
-
SMS and voice phishing
MFA helps stop these attacks from succeeding.
3. Remote and Cloud Work Increase Risk
Employees access systems from:
-
Home networks
-
Personal devices
-
Public Wi-Fi
MFA helps verify identity regardless of location.
4. Compliance Requirements
Many regulations require strong authentication for sensitive systems.
5. Identity Is the New Perimeter
Modern security focuses on verifying users—not just networks.
The Three Main Authentication Factors
To fully answer what is multi factor authentication, you need to understand authentication factors.
1. Something You Know
This includes:
-
Passwords
-
PINs
-
Security questions
These are the weakest factors on their own.
2. Something You Have
This includes:
-
Smartphones
-
Hardware security keys
-
Smart cards
-
One-time password (OTP) tokens
Attackers must physically possess the device.
3. Something You Are
This includes biometric data such as:
-
Fingerprints
-
Facial recognition
-
Retina or iris scans
Biometrics are difficult to replicate.
MFA combines two or more of these factors, significantly improving security.
Multi Factor Authentication vs Two Factor Authentication
Many people confuse MFA and 2FA.
Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
-
Uses exactly two authentication factors
Multi Factor Authentication (MFA)
-
Uses two or more factors
-
More flexible and scalable
In practice, 2FA is a subset of MFA.
How Multi Factor Authentication Works
Here’s a simple example of how MFA works in real life.
Step-by-step process:
-
User enters username and password
-
System verifies credentials
-
System prompts for an additional factor
-
User provides second factor (OTP, biometric, etc.)
-
Access is granted only if all factors are verified
Even if attackers steal a password, they’re stopped at step three.
Common Types of Multi Factor Authentication Methods
There are many ways to implement MFA.
1. SMS-Based One-Time Passwords
Users receive a temporary code via text message.
Pros: Easy to use
Cons: Vulnerable to SIM swapping and phishing
2. Authenticator Apps
Apps generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP).
Pros: More secure than SMS
Cons: Requires smartphone access
3. Push Notifications
Users approve login attempts via a mobile app.
Pros: User-friendly
Cons: Vulnerable to push fatigue attacks
4. Hardware Security Keys
Physical devices that must be plugged in or tapped.
Pros: Very secure, phishing-resistant
Cons: Additional cost
5. Biometric Authentication
Fingerprint or facial recognition verification.
Pros: Convenient and secure
Cons: Privacy and hardware dependency concerns
Benefits of Multi Factor Authentication
Organizations adopt MFA for several strong reasons.
1. Strong Protection Against Account Takeovers
MFA stops most credential-based attacks.
2. Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
Even stolen credentials don’t guarantee access.
3. Improved Compliance
Supports standards like:
-
GDPR
-
HIPAA
-
PCI DSS
-
ISO 27001
4. Enhanced User Trust
Customers feel safer when strong security is in place.
5. Lower Incident Response Costs
Preventing breaches is cheaper than fixing them.
Challenges and Limitations of MFA
While powerful, MFA is not perfect.
1. User Resistance
Some users see MFA as inconvenient.
2. MFA Fatigue Attacks
Attackers bombard users with push requests.
3. Legacy System Compatibility
Older systems may not support MFA easily.
4. Cost and Management
Hardware keys and platforms require investment.
5. MFA Bypass Techniques
Sophisticated attackers may exploit:
-
Session hijacking
-
Token theft
-
Social engineering
This is why MFA must be part of a layered security strategy.
Best Practices for Implementing Multi Factor Authentication
To get the most value from MFA, follow these best practices.
1. Apply MFA Everywhere
Protect:
-
VPNs
-
Cloud apps
-
Email
-
Admin accounts
2. Prioritize Strong MFA Methods
Prefer:
-
Authenticator apps
-
Hardware security keys
Avoid SMS when possible.
3. Protect MFA Itself
Secure MFA systems against:
-
Token theft
-
Push abuse
-
Admin misuse
4. Use Conditional Access
Trigger MFA based on:
-
Location
-
Device risk
-
User behavior
5. Educate Users
Training reduces MFA fatigue and phishing success.
Multi Factor Authentication and Zero Trust Security
Modern security strategies rely heavily on Zero Trust.
Zero Trust assumes:
-
No user or device is trusted by default
-
Continuous verification is required
MFA is a core pillar of Zero Trust, ensuring identities are validated before access is granted.
Why MFA Alone Is Not Enough
While essential, MFA should not be the only defense.
MFA does not:
-
Stop malware execution
-
Detect lateral movement
-
Contain compromised endpoints
That’s why organizations pair MFA with:
-
Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
-
Behavior-based monitoring
-
Zero Trust containment
Role of Endpoint Security Alongside MFA
Many attacks bypass MFA by compromising endpoints directly.
Advanced endpoint security helps by:
-
Detecting malicious behavior
-
Isolating compromised systems
-
Preventing lateral movement
-
Containing unknown threats
Solutions like Xcitium OpenEDR® stop threats even when credentials are compromised—without disrupting business operations.
Multi Factor Authentication in Different Industries
MFA is now standard across many sectors.
Healthcare
Protects patient records and clinical systems.
Finance
Secures transactions and customer accounts.
Government
Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
Retail and E-Commerce
Reduces account takeover fraud.
Technology and SaaS
Protects cloud platforms and developer access.
Future Trends in Multi Factor Authentication
MFA continues to evolve.
Emerging trends include:
-
Passwordless authentication
-
Biometric-first security
-
Phishing-resistant MFA standards (FIDO2)
-
Risk-based authentication
-
Continuous identity verification
Passwords are slowly being phased out in favor of stronger identity controls.
Common Myths About Multi Factor Authentication
Myth 1: MFA Is Too Complicated
Reality: Modern MFA is user-friendly and fast.
Myth 2: MFA Is Only for Enterprises
Reality: Individuals and small businesses benefit just as much.
Myth 3: MFA Makes Systems Unhackable
Reality: MFA reduces risk but must be layered with other controls.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is multi factor authentication?
Multi factor authentication is a security method that requires two or more verification factors to confirm a user’s identity.
2. Is MFA the same as two factor authentication?
Two factor authentication is a type of MFA that uses exactly two factors.
3. Is SMS-based MFA secure?
It’s better than passwords alone but less secure than app-based or hardware MFA.
4. Can MFA be hacked?
MFA can be bypassed in rare cases, which is why layered security is essential.
5. Should businesses require MFA for all users?
Yes. Especially for email, cloud apps, VPNs, and admin accounts.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is multi factor authentication is fundamental to protecting modern digital environments. MFA dramatically reduces the risk of account compromise and is one of the most effective security controls available today.
However, MFA works best when combined with endpoint visibility, behavioral monitoring, and Zero Trust principles. In an era where attackers constantly adapt, layered security is the key to staying ahead.
👉 Want to stop threats even when credentials are compromised?
Request a demo of Xcitium OpenEDR® today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/