What Is Platform as a Service? A Friendly, Complete Guide for 2026
Updated on December 8, 2025, by Xcitium
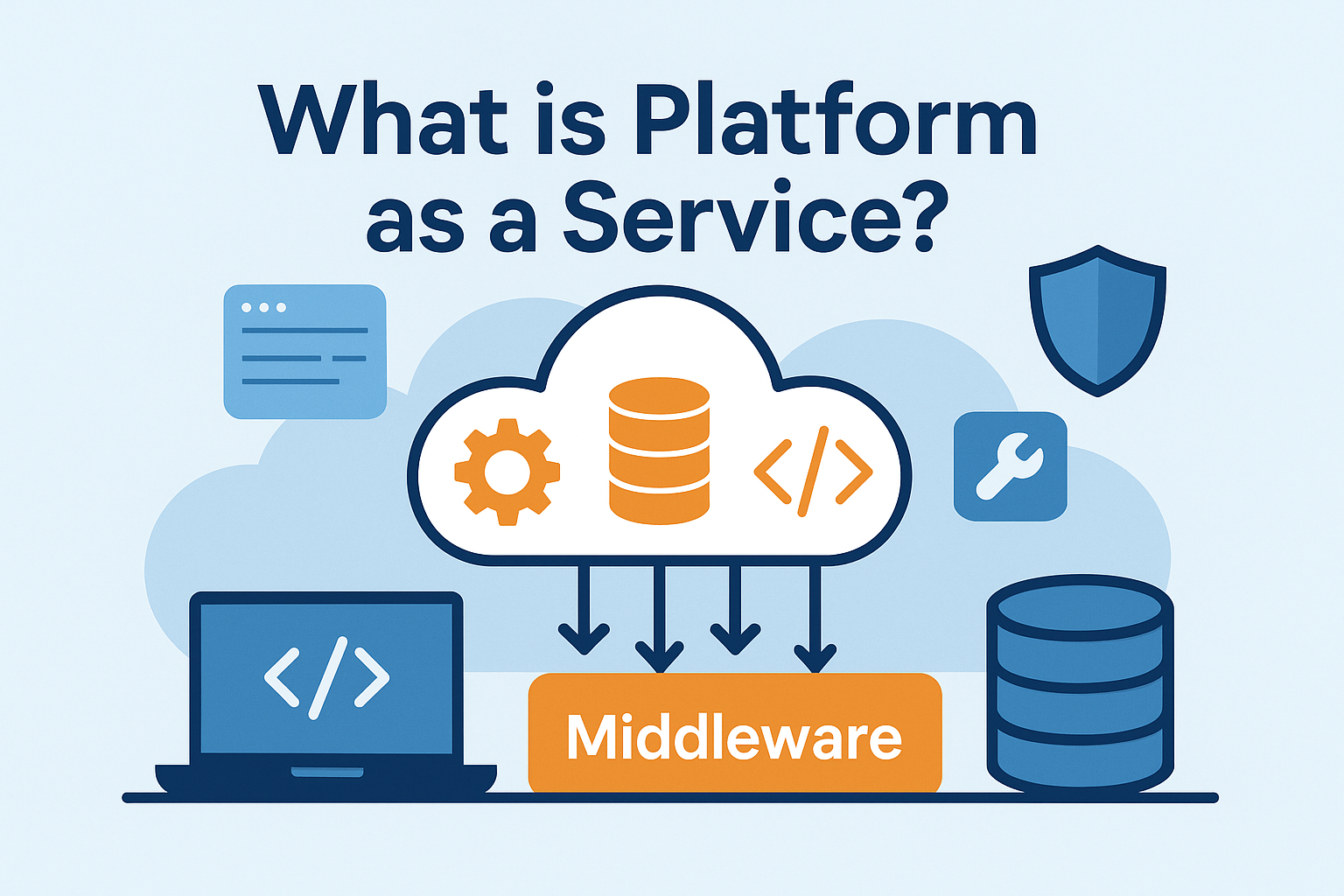
If you’ve ever wondered what is Platform as a Service and why so many businesses are moving their development operations to the cloud, you’re in the right place. PaaS has become one of the most popular cloud service models because it helps companies build, run, and scale applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Instead of buying servers, configuring networks, or maintaining hardware, organizations can focus on what matters most—creating high-quality applications faster, cheaper, and more securely. In today’s digital world, where cyber threats and downtime can cost millions, PaaS gives IT teams and developers a smarter and safer way to innovate.
Let’s break it all down in a simple, conversational way.
What Is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
So, what is Platform as a Service?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model where a provider delivers a complete development and deployment environment over the internet. This includes:
-
Servers
-
Storage
-
Databases
-
Runtime environments
-
Operating systems
-
Development tools
Instead of building and managing your own infrastructure, you use a ready-made cloud platform.
PaaS allows developers to build apps quickly without worrying about the hardware, scaling challenges, or system maintenance required behind the scenes.
How PaaS Works (Simple Explanation)
Think of PaaS as renting a fully furnished apartment.
You don’t need to buy furniture, appliances, or utilities—the landlord has already taken care of that. All you need to do is move in and start living.
With PaaS:
-
The cloud provider manages the infrastructure.
-
Developers focus on writing code and deploying apps.
-
The platform automatically handles updates, security patches, scaling, and availability.
This removes the heavy lifting from IT teams and speeds up the development lifecycle.
Key Features of Platform as a Service
1. Preconfigured Development Environments
No setup headaches—environments are ready within minutes.
2. Built-In Middleware
PaaS includes software components required to connect apps, databases, and services.
3. Automated Scaling
The platform automatically adds or removes resources based on demand.
4. Database Management
No installation required—just choose a database engine and go.
5. Security & Patching
Providers take care of OS updates, monitoring, and foundational security.
6. Collaboration Tools
Multiple developers can work in the same environment seamlessly.
7. DevOps Support
CI/CD pipelines, testing frameworks, and automation tools are often included.
8. Multi-Platform Support
Build and run applications for web, mobile, and IoT.
Benefits of PaaS for Businesses
Here’s why businesses of all sizes—from startups to enterprise teams—choose Platform as a Service.
1. Faster Development Cycles
Teams can launch apps faster without infrastructure delays.
2. Reduced Costs
You pay only for what you use. No costly hardware upfront.
3. Enhanced Scalability
Apps scale automatically during high usage.
4. Easy Maintenance
The provider handles updates, patches, and routine system tasks.
5. Supports Remote & Global Teams
Cloud access allows development from anywhere.
6. Encourages Innovation
Teams can test new ideas quickly using pre-built components.
7. Better Security Baseline
Cloud platforms provide strong built-in controls, monitoring, and access management.
PaaS vs IaaS vs SaaS (Clear Breakdown)
To understand PaaS better, it’s helpful to compare it to the other major cloud models.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
You manage:
-
Apps
-
Middleware
-
Runtime
-
OS
Provider manages:
-
Servers & networking
Best for:
Highly customized environments.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
You manage:
-
Apps & data only
Provider manages:
-
Infrastructure
-
OS
-
Middleware
-
Runtime
-
Scaling
Best for:
Developers who want speed, scalability, and managed environments.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
You use a fully built application over the internet.
Best for:
Businesses who want ready-made tools (email, CRM, HR software).
Common Use Cases of PaaS
PaaS shines in several popular business scenarios:
1. Application Development & Deployment
Build apps with minimal setup and maintenance.
2. Microservices Architecture
PaaS is ideal for containerized or modular systems.
3. DevOps Automation
CI/CD pipelines streamline deployments.
4. API Development
Easily build, publish, and scale APIs.
5. Big Data Analytics
PaaS platforms include built-in analytics engines.
6. IoT Applications
Connect devices and process telemetry at scale.
7. Mobile App Development
Includes SDKs, testing tools, and compatibility setups.
Popular PaaS Providers
Some of the biggest names in PaaS include:
-
Google App Engine
-
Microsoft Azure App Service
-
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
-
IBM Cloud Foundry
-
Red Hat OpenShift
-
Heroku
Each platform offers different features, pricing, and strengths depending on your application needs.
Security Considerations in PaaS
Although PaaS improves security in many ways, it does not eliminate risks entirely. Understanding your responsibilities is crucial.
1. Shared Responsibility Model
The provider secures the infrastructure; you secure the apps and data.
2. Data Protection
You must ensure strong encryption, access controls, and secure storage.
3. Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Role-based access is a must to limit insider threats.
4. Compliance Requirements
Not all PaaS platforms meet every industry standard by default.
5. Third-Party Integrations
APIs and external services can increase your attack surface.
Why this matters
Attackers often target misconfigurations, vulnerable code, or weak authentication—things the business must control, not the PaaS provider.
Challenges & Limitations of PaaS
While PaaS is powerful, it does come with challenges.
1. Vendor Lock-In
Moving applications to a new provider may be difficult.
2. Limited Customization
You don’t control the infrastructure layer.
3. Performance Variability
Resource sharing can impact speeds.
4. Compliance Gaps
Some industries require strict controls that certain PaaS platforms do not offer.
5. Security Misconfigurations
Developers may unintentionally expose services or APIs.
How to Choose the Right PaaS Platform
Here’s a simple checklist to help your team pick the best PaaS solution:
1. Identify your development goals
Web apps? APIs? Machine learning? Microservices?
2. Assess pricing structure
Compare per-use, subscription, or instance-based models.
3. Evaluate deployment flexibility
Make sure it supports your preferred languages and frameworks.
4. Check compliance compatibility
Does the provider meet standards like PCI DSS, SOC 2, HIPAA, or GDPR?
5. Review built-in security tools
Look for IAM, encryption, monitoring, and network controls.
6. Understand scalability features
Your app should grow without rearchitecting.
7. Test with a free trial
Hands-on experience is the best way to evaluate usability.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is Platform as a Service helps you make smarter decisions for your business’s development and cloud strategy. PaaS simplifies app building, reduces costs, strengthens security, and empowers developers to innovate faster.
But remember—while PaaS strengthens infrastructure-level security, businesses still need strong application and endpoint protection. Cybercriminals target users, code, and endpoints just as often as cloud systems.
To build a stronger security foundation for your apps and devices:
👉 Request a demo of enterprise-grade protection from Xcitium:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Platform as a Service in simple terms?
PaaS is a cloud platform that provides all the tools needed to build and deploy applications without managing hardware.
2. What is the main purpose of PaaS?
To simplify development by providing ready-to-use environments, tools, and infrastructure.
3. Is PaaS the same as SaaS?
No—SaaS delivers ready-to-use apps, while PaaS provides a platform to build your own apps.
4. What companies use PaaS?
Developers, startups, enterprises, and IT teams building web, mobile, or cloud applications.
5. Is PaaS secure?
Yes, but security depends on shared responsibilities. The provider secures the platform; you must secure your application and data.