What Is MQTT? A Complete Guide to the MQTT Protocol
Updated on December 22, 2025, by Xcitium
In a world where billions of devices communicate every second, speed and reliability matter. But what is MQTT, and why has it become one of the most trusted communication protocols for IoT, cybersecurity, and enterprise systems? If your organization uses connected devices, cloud platforms, or real-time data streams, understanding MQTT is no longer optional—it’s essential.
The MQTT protocol is designed for lightweight, efficient communication, making it ideal for environments where bandwidth, power, and reliability are critical. For IT managers, cybersecurity teams, and executives, MQTT plays a key role in digital transformation, operational efficiency, and secure system design.
This guide explains what is MQTT, how it works, its benefits, security challenges, and why it matters across industries.
What Is MQTT? (Simple Definition)
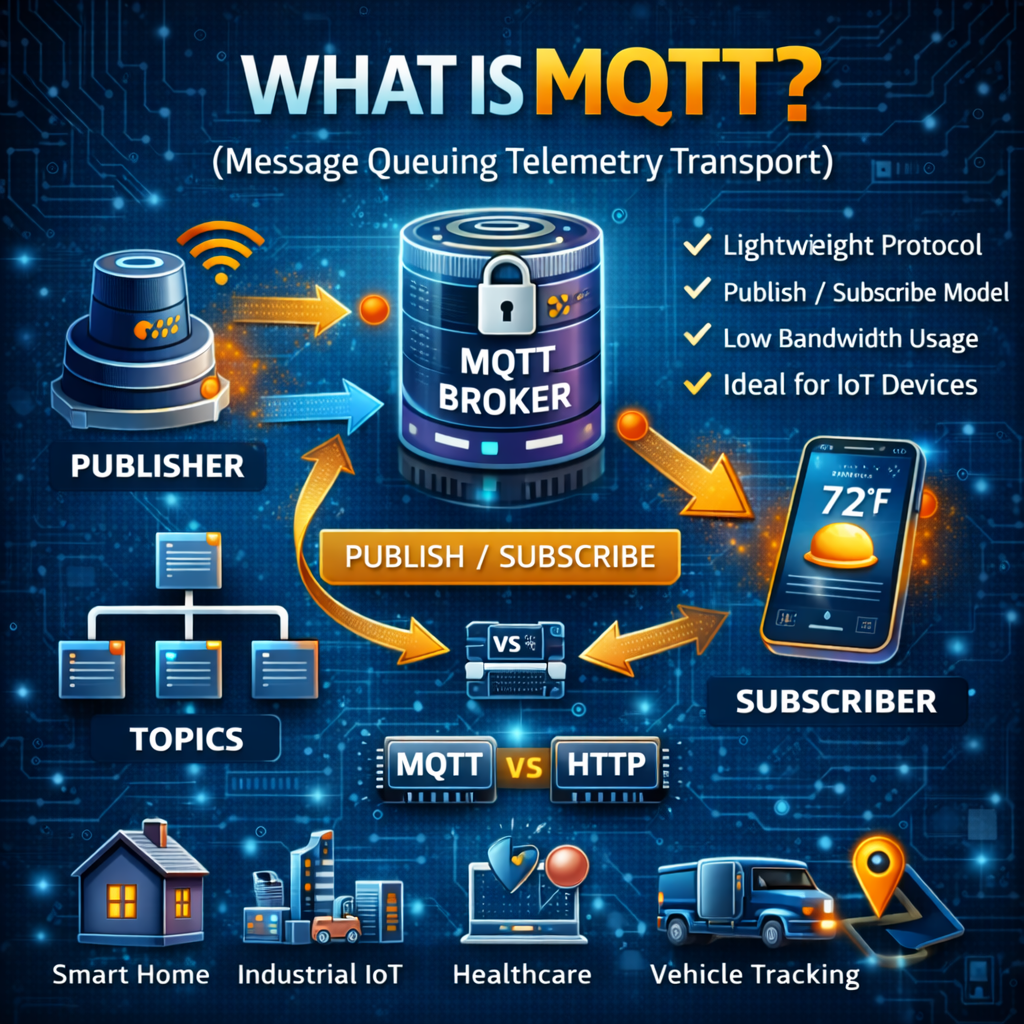
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight messaging protocol that enables devices to exchange data efficiently using a publish-subscribe model. It is designed for low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks, making it ideal for IoT and real-time communication.
Unlike traditional request-response protocols, MQTT minimizes network traffic while ensuring reliable message delivery.
Why Understanding What Is MQTT Matters Today
Understanding what is MQTT is crucial because modern systems increasingly rely on:
-
Internet of Things (IoT) devices
-
Cloud-based applications
-
Real-time monitoring and analytics
-
Distributed and remote environments
MQTT allows systems to communicate quickly while using minimal resources. For cybersecurity professionals, MQTT introduces unique security considerations that must be managed carefully.
How the MQTT Protocol Works
To fully understand what is MQTT, it’s important to examine how it operates.
MQTT Uses a Publish-Subscribe Model
Instead of devices talking directly to each other, MQTT relies on a broker.
Here’s how it works:
-
Publishers send messages to a topic
-
The broker receives and filters messages
-
Subscribers receive messages for topics they follow
This architecture decouples devices, improving scalability and reliability.
Core Components of MQTT
1. MQTT Broker
The central server that manages messages, topics, and client connections.
2. MQTT Clients
Devices or applications that publish or subscribe to messages.
3. Topics
Hierarchical labels that organize messages (e.g., factory/sensor/temperature).
4. Messages
Lightweight data packets sent between clients via the broker.
Each component plays a vital role in efficient data transmission.
Key Features of the MQTT Protocol
Understanding what is MQTT also means recognizing what makes it unique.
Lightweight Design
MQTT uses minimal overhead, making it ideal for constrained devices.
Reliable Message Delivery
Supports multiple Quality of Service (QoS) levels.
Low Bandwidth Usage
Optimized for slow or unstable networks.
Asynchronous Communication
Devices communicate without waiting for direct responses.
MQTT Quality of Service (QoS) Levels Explained
MQTT offers three QoS levels to control message reliability:
-
QoS 0 – At most once
Messages are sent once with no confirmation. -
QoS 1 – At least once
Messages are guaranteed to arrive but may be duplicated. -
QoS 2 – Exactly once
Ensures messages arrive only once (highest reliability).
These options allow businesses to balance performance and reliability.
Common MQTT Use Cases
Once you understand what is MQTT, its widespread adoption becomes clear.
IoT and Smart Devices
-
Smart homes
-
Industrial sensors
-
Wearable devices
Industrial Automation
-
Equipment monitoring
-
Predictive maintenance
-
SCADA systems
Healthcare Systems
-
Remote patient monitoring
-
Medical device telemetry
Automotive and Transportation
-
Fleet tracking
-
Vehicle diagnostics
Financial and Enterprise Systems
-
Real-time alerts
-
Event-driven applications
MQTT vs HTTP: What’s the Difference?
A common question when learning what is MQTT is how it compares to HTTP.
| Feature | MQTT | HTTP |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Model | Publish/Subscribe | Request/Response |
| Bandwidth Usage | Very low | Higher |
| Ideal For | IoT, real-time data | Web applications |
| Connection | Persistent | Stateless |
| Latency | Low | Higher |
MQTT excels where efficiency and speed are critical.
Security Challenges in MQTT
From a cybersecurity perspective, understanding what is MQTT also means recognizing its risks.
Common MQTT Security Risks
-
Unauthorized device access
-
Data interception
-
Weak authentication
-
Misconfigured brokers
-
Lack of encryption
Because MQTT was designed for efficiency, security must be implemented correctly.
Best Practices for Securing MQTT
To protect MQTT environments, organizations should follow these best practices:
Actionable Security Tips
-
Use TLS encryption for data in transit
-
Enforce strong authentication (certificates, tokens)
-
Restrict topic access with access control lists (ACLs)
-
Monitor traffic for anomalies
-
Segment MQTT networks
Zero Trust security principles are especially effective for MQTT deployments.
Benefits of Using MQTT
Understanding what is MQTT helps organizations unlock significant benefits.
Key Advantages
-
Reduced network traffic
-
Improved scalability
-
Faster data delivery
-
Reliable communication
-
Lower operational costs
These benefits make MQTT a preferred choice for large-scale deployments.
Industries That Rely on MQTT
MQTT is widely used across industries, including:
-
Manufacturing
-
Healthcare
-
Energy and utilities
-
Retail
-
Smart cities
-
Transportation
Each industry benefits from MQTT’s lightweight and scalable nature.
MQTT and the Future of IoT
As IoT adoption grows, MQTT continues to evolve.
Emerging Trends
-
MQTT 5.0 enhancements
-
Integration with cloud-native platforms
-
AI-driven monitoring and analytics
-
Increased focus on security and compliance
For business leaders, MQTT supports digital transformation initiatives.
FAQs: What Is MQTT?
1. What is MQTT used for?
MQTT is used for efficient, real-time communication between devices, especially in IoT environments.
2. Is MQTT secure?
MQTT can be secure when properly configured with encryption, authentication, and access controls.
3. What is an MQTT broker?
An MQTT broker is a server that manages message distribution between publishers and subscribers.
4. How is MQTT different from HTTP?
MQTT uses a publish-subscribe model and consumes far less bandwidth than HTTP.
5. Why is MQTT important for cybersecurity?
MQTT connects many devices, making it critical to secure against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Final Thoughts: Why MQTT Matters for Modern Organizations
So, what is MQTT in today’s connected world? It is a foundational protocol that enables efficient, scalable, and real-time communication across devices and systems. For IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, and executives, MQTT offers powerful capabilities—but only when secured properly.
As digital ecosystems expand, MQTT will continue to play a vital role in operational resilience and innovation.
Secure Your Connected Systems Today
Protect MQTT-based environments with advanced cybersecurity solutions designed for modern enterprises.
👉 Request a personalized demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/