What Is Data Analysis Definition? Importance, and Business Impact
Updated on December 26, 2025, by Xcitium
What separates high-performing organizations from those that struggle to keep up? The answer often lies in how effectively they use data. Understanding what is data analysis definition is no longer just for data scientists—it’s essential for cybersecurity leaders, IT managers, and CEOs who rely on accurate insights to make critical decisions.
In its simplest form, data analysis transforms raw data into meaningful information. But in modern enterprises, it goes far beyond charts and dashboards. It drives security strategies, operational efficiency, risk mitigation, and competitive advantage.
In this guide, we’ll break down the what is data analysis definition, explore its types, tools, real-world use cases, and why it’s a strategic necessity across industries.
What Is Data Analysis? Definition Explained Simply
The what is data analysis definition refers to the process of collecting, cleaning, examining, and interpreting data to discover patterns, trends, and actionable insights that support decision-making.
In business and cybersecurity contexts, data analysis helps organizations:
-
Understand what happened
-
Identify why it happened
-
Predict what may happen next
-
Decide what actions to take
Rather than relying on intuition alone, leaders use data analysis to reduce uncertainty and improve outcomes.
Why Data Analysis Matters More Than Ever
Data is being generated at an unprecedented rate. From network logs and security alerts to customer behavior and financial metrics, organizations are drowning in information.
Key Reasons Data Analysis Is Critical Today
-
Better decision-making: Data-backed insights reduce guesswork
-
Improved security posture: Threat detection relies on data patterns
-
Operational efficiency: Identifies inefficiencies and bottlenecks
-
Strategic planning: Supports long-term business growth
For cybersecurity and IT leaders, understanding the importance of data analysis is vital for staying ahead of evolving threats.
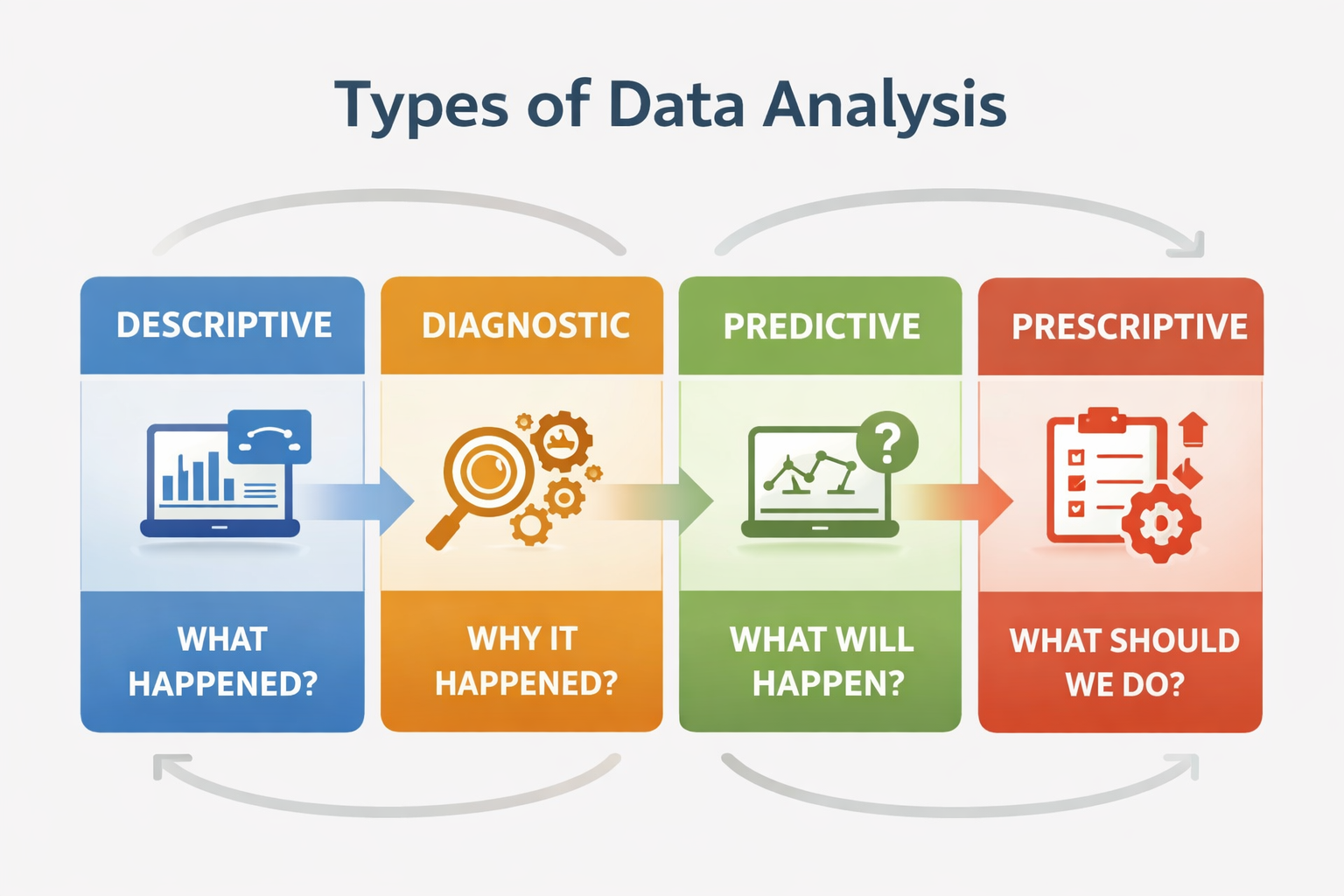
Types of Data Analysis Explained
To fully understand what is data analysis definition, it’s important to explore its core types. Each type answers a different business question.
1. Descriptive Data Analysis
Descriptive analysis answers: What happened?
It summarizes historical data using:
-
Reports
-
Dashboards
-
Metrics
-
Visualizations
Example: Monthly security incident reports showing the number of detected threats.
2. Diagnostic Data Analysis
Diagnostic analysis answers: Why did it happen?
It digs deeper into data to identify root causes by:
-
Comparing trends
-
Analyzing correlations
-
Investigating anomalies
Example: Identifying why phishing attacks increased during a specific period.
3. Predictive Data Analysis
Predictive analysis answers: What is likely to happen next?
It uses:
-
Historical data
-
Statistical models
-
Machine learning
Example: Predicting potential ransomware attacks based on past threat behavior.
4. Prescriptive Data Analysis
Prescriptive analysis answers: What should we do about it?
It provides recommendations using:
-
Optimization algorithms
-
AI-driven insights
-
Scenario modeling
Example: Recommending automated containment actions for detected threats.
The Data Analysis Process: Step-by-Step
Understanding the data analysis process helps organizations apply it consistently and effectively.
Step 1: Data Collection
Data is gathered from various sources such as:
-
Security logs
-
Applications
-
Sensors
-
User activity
Quality data collection is the foundation of accurate analysis.
Step 2: Data Cleaning
Raw data is often messy. Cleaning involves:
-
Removing duplicates
-
Fixing errors
-
Handling missing values
This step ensures reliability and accuracy.
Step 3: Data Exploration
Analysts examine the data to:
-
Identify trends
-
Detect outliers
-
Understand distributions
Visualization tools are often used here.
Step 4: Data Analysis & Modeling
This is where insights are generated using:
-
Statistical methods
-
Machine learning models
-
Pattern recognition
Step 5: Interpretation & Decision-Making
Results are translated into business actions, strategies, or policies.
This step bridges the gap between data and leadership decisions.
Tools Commonly Used in Data Analysis
Modern data analysis relies on a combination of tools and platforms.
Popular Data Analysis Tools
-
Excel & spreadsheets
-
SQL databases
-
Python and R
-
BI tools (Power BI, Tableau)
-
Security analytics platforms
For cybersecurity teams, specialized tools analyze vast datasets in real time to detect threats before damage occurs.
Data Analysis in Cybersecurity: A Strategic Advantage
In cybersecurity, data analysis isn’t optional—it’s foundational.
How Data Analysis Supports Cybersecurity
-
Detects abnormal behavior across systems
-
Identifies early indicators of compromise
-
Reduces false positives
-
Improves incident response times
Security operations centers (SOCs) depend on continuous data analysis to maintain visibility and control.
Data Analysis for IT Managers and Executives
For IT managers and business leaders, understanding what is data analysis definition helps bridge the gap between technical teams and strategic goals.
Executive-Level Benefits
-
Data-driven budgeting decisions
-
Better risk management
-
Improved compliance reporting
-
Clearer ROI on technology investments
Data analysis empowers leaders to make confident, informed decisions.
Common Challenges in Data Analysis
Despite its value, data analysis comes with challenges.
Key Obstacles Organizations Face
-
Poor data quality
-
Data silos across departments
-
Lack of skilled personnel
-
Overreliance on manual analysis
Addressing these challenges requires the right tools, processes, and leadership support.
Best Practices for Effective Data Analysis
To maximize value, organizations should follow proven best practices.
Actionable Tips
-
Define clear objectives before analyzing data
-
Automate data collection and processing
-
Use real-time analytics where possible
-
Combine human expertise with AI-driven insights
-
Continuously refine models and assumptions
These practices ensure data analysis delivers measurable results.
The Future of Data Analysis
Data analysis is evolving rapidly with advancements in AI and automation.
Key Trends Shaping the Future
-
Real-time analytics
-
Predictive and prescriptive intelligence
-
AI-powered anomaly detection
-
Integrated security and business analytics
Organizations that embrace these trends gain a competitive edge.
FAQ: Data Analysis Explained
1. What is data analysis definition in simple terms?
Data analysis is the process of examining data to discover useful information, draw conclusions, and support decision-making.
2. Why is data analysis important for cybersecurity?
It helps detect threats, identify abnormal behavior, and respond to incidents faster and more accurately.
3. What are the main types of data analysis?
The four main types are descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive data analysis.
4. Who should understand data analysis?
IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, executives, and decision-makers all benefit from understanding data analysis.
5. Can small businesses benefit from data analysis?
Yes. Even basic data analysis improves efficiency, security, and strategic planning for businesses of any size.
Final Thoughts: Turning Data Into Decisions
Understanding what is data analysis definition is no longer a technical luxury—it’s a business necessity. In a world driven by data, organizations that fail to analyze it effectively risk falling behind.
For cybersecurity leaders, IT managers, and executives, data analysis provides clarity, confidence, and control in an increasingly complex digital environment.
If your organization is still relying on reactive tools and fragmented data, it’s time to modernize your approach.
👉 Discover how Xcitium’s advanced, data-driven security platform delivers real-time insights and proactive protection.
Request a demo today: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/