What Are IoT Devices? Exploring the Smart World of Connected Tech
Updated on August 12, 2025, by Xcitium
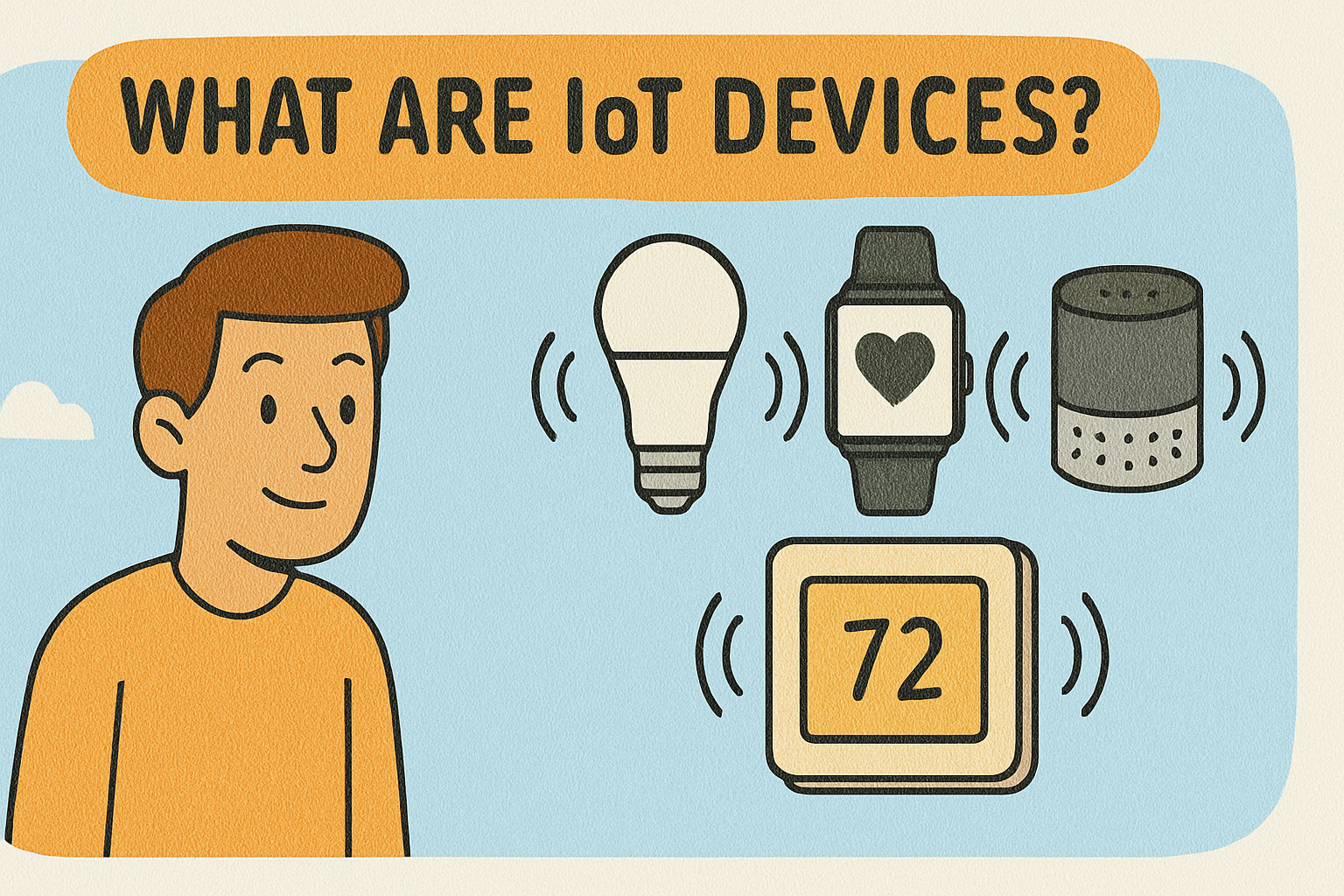
Imagine logging into a system that monitors your appliances, factory machinery, and even agricultural drones—all in real time. That’s the power of IoT devices. Simply put, IoT (Internet of Things) devices are everyday objects with built-in sensors and network connectivity that collect, exchange, and act on data. For IT and security leaders, understanding what are IoT devices is essential for smart deployments and safe implementations.
Understanding the Definition of IoT Devices
IoT devices are physical objects—like thermostats, vehicles, and industrial sensors—embedded with electronics, software, and network interfaces that enable them to connect and send data over the Internet. These objects transform into smart devices, gathering real-world information and interacting with broader systems.
Why the Business World Cares
- By 2021, over 54% of active connected devices globally were IoT-enabled.
- Applications span smart cities, manufacturing, healthcare—IoT devices drive efficiency, automation, and innovation.
- Today’s businesses rely on them for real-time data, automation, and operational intelligence.
Types of IoT Devices — From Your Living Room to the Factory Floor
IoT devices operate across different environments and use cases:
1. Consumer & Smart Home Devices
From Amazon Echo smart speakers to smart thermostats and security cameras, these gadgets improve everyday life through automation and remote control.
- Wearables & Health Tech
Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and wearable health monitors collect critical data—from steps to vitals—enabling real-time health insights and alerts.
3. Industrial & Infrastructure IoT (IIoT)
Sensors in factories monitor machine performance and trigger preventive maintenance. Smart meters for utilities transmit usage data directly to providers or centralized data systems.
4. Security & Smart Building Systems
IoT security devices like smart locks, surveillance cameras, window sensors, and alarms add automation and remote control to safety systems.
5. Urban & Agricultural Applications
IoT sensors in agriculture enable precise pesticide usage—like the Spotta system that uses sensors and AI to detect pests early. In smart cities, they manage traffic, monitor assets, and support regional infrastructure.
How IoT Devices Work
- Sensors & Data Collection: Devices sense environmental factors like motion, temperature, location, or usage.
- Connectivity: Data is transmitted over Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, Zigbee, or LoRa networks.
- Processing & Storage: Data is routed to platforms or cloud systems for analysis.
- Automation & Response: Based on analysis, IoT systems initiate actions—turning on appliances, sending alerts, or adjusting systems autonomously.
Benefits Across Industries
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation reduces errors and manual work.
- Actionable Insights: Real-time monitoring improves decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Scalability & Flexibility: IoT deployments adapt quickly across varied business contexts.
Security Challenges of IoT Devices
- Privacy Risks: Large data footprints are tempting targets for breaches.
- Unsecured Devices: Often deployed with weak credentials or outdated firmware.
- Global Risk Exposure: Talks in the UK Parliament spotlight how embedded Chinese IoT modules could disrupt critical infrastructure (like traffic lights or electric vehicles).
Industry Spotlight: Critical Threats & Opportunities
In agriculture, IoT sensors combined with AI detect pests months earlier than traditional methods—boosting crop protection and lowering chemical use. Yet at the same time, threats loom: compromised IoT systems can cascade across essential services if not secured properly.
Best Practices for IoT Deployment
- Enforce secure-by-design policies—from device procurement to deployment.
- Implement network segmentation and monitoring for IoT endpoints.
- Require strong authentication, encryption, and timely updates.
- Align technology with business goals—from automation to operational insight.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what are IoT devices—and how they operate—empowers leaders to leverage their benefits while mitigating risks. These versatile, smart-connected devices have transformed industries but require thoughtful governance and cybersecurity foresight.
Call to Action
Want to gain secure, intelligent control over your IoT ecosystem?
Request a free demo from Xcitium—see how we can protect your connected world.
FAQ: Common Questions About IoT Devices
- What defines an IoT device?
Physical devices embedded with sensors and network interfaces to collect and exchange data. - Examples of IoT devices?
Smart thermostats, wearables, factory sensors, smart meters, and home security gadgets. - How many IoT devices exist globally?
As of 2021, over 11.7 billion—making up over half of connected devices globally. - What are key risks with IoT?
Security threats, privacy exposures, and potential national infrastructure risks from compromised devices. - How can businesses secure IoT deployments?
Use secure onboarding, network segmentation, regular monitoring, and enforce authentication throughout the device lifecycle.