What Is Edge Computing? A Complete Guide for IT & Security Leaders
Updated on December 10, 2025, by Xcitium
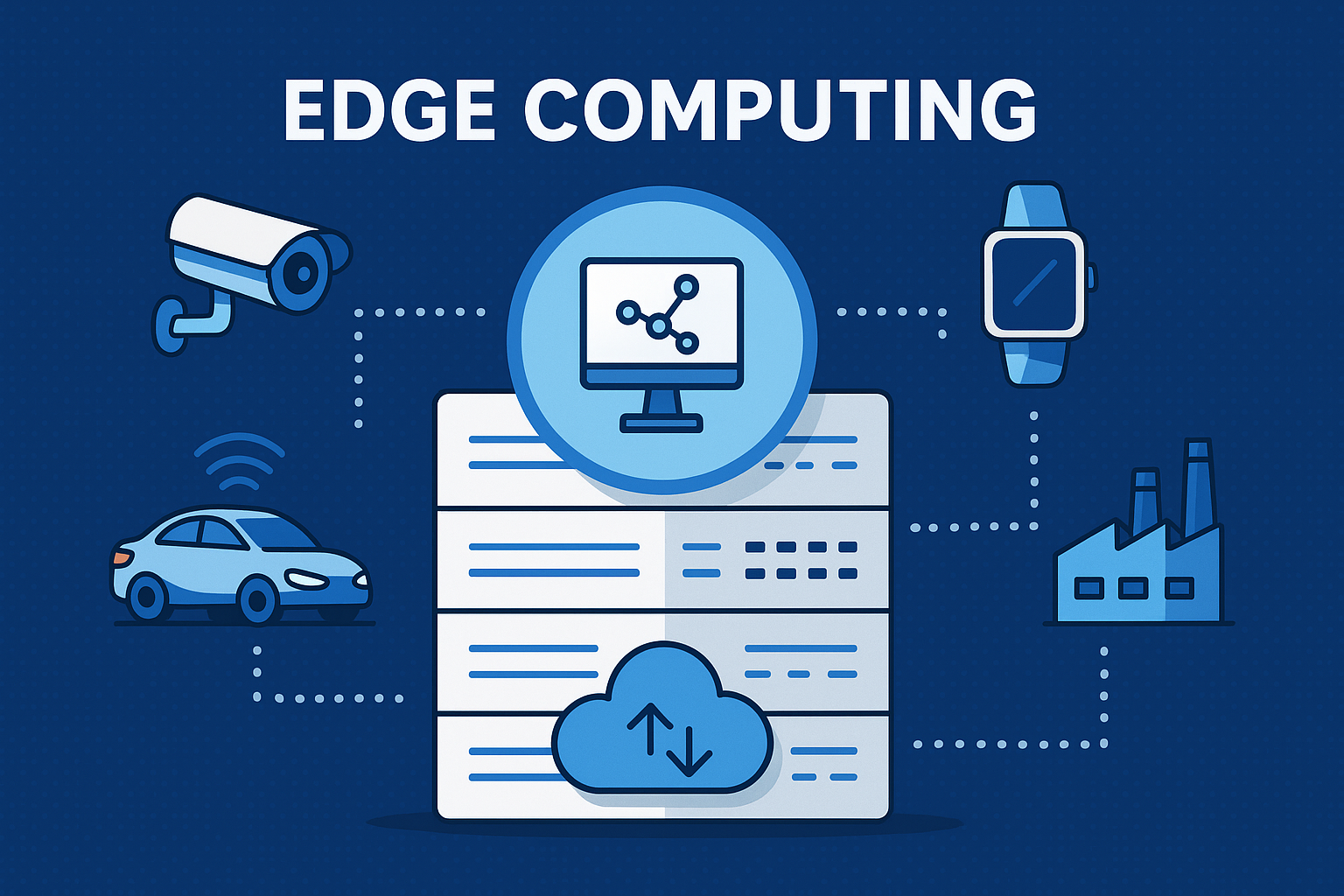
If you’ve been following digital transformation trends, you’ve probably asked yourself: what is edge computing, and why is every major industry—from cybersecurity to manufacturing—investing in it so aggressively? As data volumes explode and real-time decision-making becomes essential, traditional cloud architectures can’t always keep up. That’s exactly where edge computing comes in.
In simple terms, edge computing refers to processing data closer to its source rather than relying on a distant centralized cloud. This shift unlocks faster performance, reduced latency, and stronger security—making it a game-changer for IT managers, CISOs, cybersecurity professionals, and business leaders.
In this guide, we break down what edge computing is, how it works, why organizations are adopting it, and what risks you must prepare for.
What Is Edge Computing? (Definition & Core Concept)
Edge computing is a distributed computing model where data processing occurs at or near the source of data generation—such as IoT devices, sensors, endpoints, or local edge servers—rather than waiting for data to be sent to a centralized cloud.
This means applications make decisions locally and instantly, reducing the need for round-trip communication with the cloud. In high-security and high-performance environments, this architecture is rapidly becoming essential.
How Edge Computing Works
To understand what edge computing is, you need to see how the architecture connects devices, networks, and compute resources.
1. Data Is Generated at the “Edge”
This might happen at:
-
IoT sensors
-
Autonomous machines
-
User endpoints
-
Industrial controls
-
Healthcare devices
2. Local Processing Happens Immediately
Instead of sending raw data to the cloud:
-
Edge nodes analyze, filter, and process data
-
Only essential information is sent to the cloud
3. The Cloud Becomes a Secondary Layer
Cloud environments still provide:
-
Long-term storage
-
Analytics at scale
-
Machine learning model training
-
Centralized management
Edge ≠ Cloud Replacement
Edge enhances the cloud by reducing load and speeding up decision-making.
The Key Benefits of Edge Computing
Organizations exploring what edge computing is usually focus on its transformative benefits. Here are the most impactful advantages:
1. Ultra-Low Latency
Since data is processed locally, decisions happen in milliseconds.
Perfect for industries where timing is critical:
-
Cyber defense automation
-
Healthcare monitoring
-
Smart factory operations
-
Autonomous vehicles
2. Reduced Bandwidth & Cloud Costs
Not all data needs to go to the cloud.
By processing locally:
-
You minimize transmission costs
-
You avoid cloud overconsumption
-
You reduce storage overhead
3. Improved Data Security & Privacy
One of the biggest misconceptions is that edge computing is “less secure.”
In reality, it enhances privacy when implemented correctly.
-
Sensitive data stays local
-
Lower exposure to cloud breaches
-
Encrypted transmission of only essential data
4. Better Reliability
Edge systems continue working—even if the cloud goes down.
This independence is vital for:
-
Hospitals
-
Manufacturing plants
-
National security systems
-
Energy grids
5. Scalability for Distributed Environments
As organizations expand geographically, edge nodes can be deployed anywhere without requiring major infrastructure overhauls.
Top Edge Computing Use Cases by Industry
Understanding what edge computing is becomes easier when you see how industries use it.
1. Cybersecurity & Endpoint Protection
Edge computing allows real-time detection and response at the device level.
Examples:
-
Zero Trust host-based decisions
-
Local malware detection
-
Network segmentation enforcement
-
AI-driven anomaly detection
2. Manufacturing & Industry 4.0
Smart factories depend on instant processing:
-
Equipment failure prediction
-
Robotic automation
-
Computer vision systems
-
Inventory tracking
3. Healthcare
Edge computing reduces risks and latency in:
-
Remote patient monitoring
-
Surgical robotics
-
Diagnostic imaging
-
Medical IoT devices
4. Transportation & Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars cannot wait for cloud round trips.
They process data on-board for:
-
Collision detection
-
Navigation
-
Traffic decisions
5. Retail & Smart Stores
Retailers use edge systems for:
-
Personalized in-store experiences
-
Real-time inventory tracking
-
Self-checkout automation
-
Loss prevention analytics
Cybersecurity Risks in Edge Computing
While the benefits are significant, expanding the edge also increases the attack surface. Every device becomes a potential entry point.
Major security risks include:
1. Physical Device Attacks
Edge devices operate outside data centers, making them easier to:
-
Tamper with
-
Steal
-
Reverse engineer
2. Device Misconfigurations
Weak or default settings on IoT/edge devices create vulnerabilities.
3. Lack of Centralized Security
Distributed nodes can be challenging to monitor consistently.
4. Unsecured Communication Channels
If encryption is not enforced, attackers may intercept:
-
Telemetry
-
Sensor data
-
Commands
5. Supply Chain Risks
Compromised firmware or third-party components can infect the entire edge ecosystem.
Best Practices for Securing the Edge
If you’re deploying edge architecture, adopt these security best practices:
1. Implement Zero Trust Everywhere
Never trust a device just because it sits inside your network perimeter.
Zero Trust ensures:
-
Continuous verification
-
Least-privilege access
-
Identity-based controls
2. Harden All Devices
-
Disable unused ports
-
Enforce strong authentication
-
Apply firmware integrity checks
-
Remove default credentials
3. Encrypt Data at Every Layer
Both data in transit and data at rest must be protected with strong encryption protocols such as TLS 1.3.
4. Automate Threat Detection
Use AI-driven endpoint tools capable of:
-
Behavioral analysis
-
Instant isolation
-
Local remediation
5. Centralize Monitoring
Even though compute is distributed, visibility must remain unified.
Use:
-
Central SOC dashboards
-
SIEM event correlation
-
Automated response orchestration
Edge vs. Cloud vs. Fog Computing
Many professionals ask how edge computing differs from cloud or fog models. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing | Fog Computing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Location | At device/source | Centralized data centers | Between edge + cloud |
| Latency | Lowest | Highest | Medium |
| Security | High (local control) | Shared model | High |
| Best for | Real-time apps | Large-scale analytics | Distributed IoT |
Future Trends: Where Edge Computing Is Headed
Edge computing is still evolving, but several trends are shaping its future:
1. AI at the Edge (Edge AI)
Devices will run on-device machine learning for:
-
Threat detection
-
Predictive maintenance
-
Real-time decision-making
2. 5G-Driven Edge Expansion
5G provides the bandwidth and speed required for massive, distributed edge networks.
3. Hyper-Automation
Edge + AI + automation = fully intelligent systems.
4. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Converging networking and security at the edge.
5. Explosion of IoT Devices
More devices = more data = greater need for local processing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is edge computing in simple terms?
Edge computing is processing data near the source instead of sending everything to a distant cloud.
2. Why is edge computing important?
It reduces latency, improves security, enables real-time decisions, and lowers cloud dependence.
3. Is edge computing replacing cloud computing?
No. Edge and cloud work together. Edge handles real-time tasks; the cloud manages storage and large-scale analytics.
4. What industries use edge computing the most?
Cybersecurity, manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and retail rely heavily on edge solutions.
5. What are the biggest security risks in edge computing?
Device tampering, weak configurations, insecure communication, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what edge computing is is essential for modern organizations trying to stay ahead in performance, security, and innovation. As data generation accelerates, businesses that adopt edge strategies will enjoy faster decision-making, improved reliability, and stronger defenses against cyber threats.
If your company is exploring how edge computing fits into your cybersecurity roadmap, now is the time to take action.
👉 Ready to strengthen your security posture and integrate next-gen edge protection?
Request a demo today: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/