What Is DSL Internet? Complete Guide for Users, IT Teams & Cybersecurity Professionals
Updated on November 27, 2025, by Xcitium
Internet technology has evolved dramatically over the years, from dial-up modems and telephone-line access to modern high-speed fiber connections. Yet one type of broadband remains widely available across homes, small businesses, and rural areas: DSL internet. If you’ve ever wondered what is DSL internet, how does it work, and is it still a good option in 2025, this guide will answer all your questions clearly and professionally.
DSL internet is still used by millions worldwide due to its reliability, affordability, and compatibility with existing telephone infrastructure. Even though faster alternatives like cable and fiber are emerging, DSL remains relevant—especially in areas where infrastructure upgrades are limited, budgets are tight, or stable connections are required for security systems and IoT devices.
This article explains everything you need to know about DSL internet—from how it works to speed limitations, benefits, security considerations, and how it compares to other technologies.
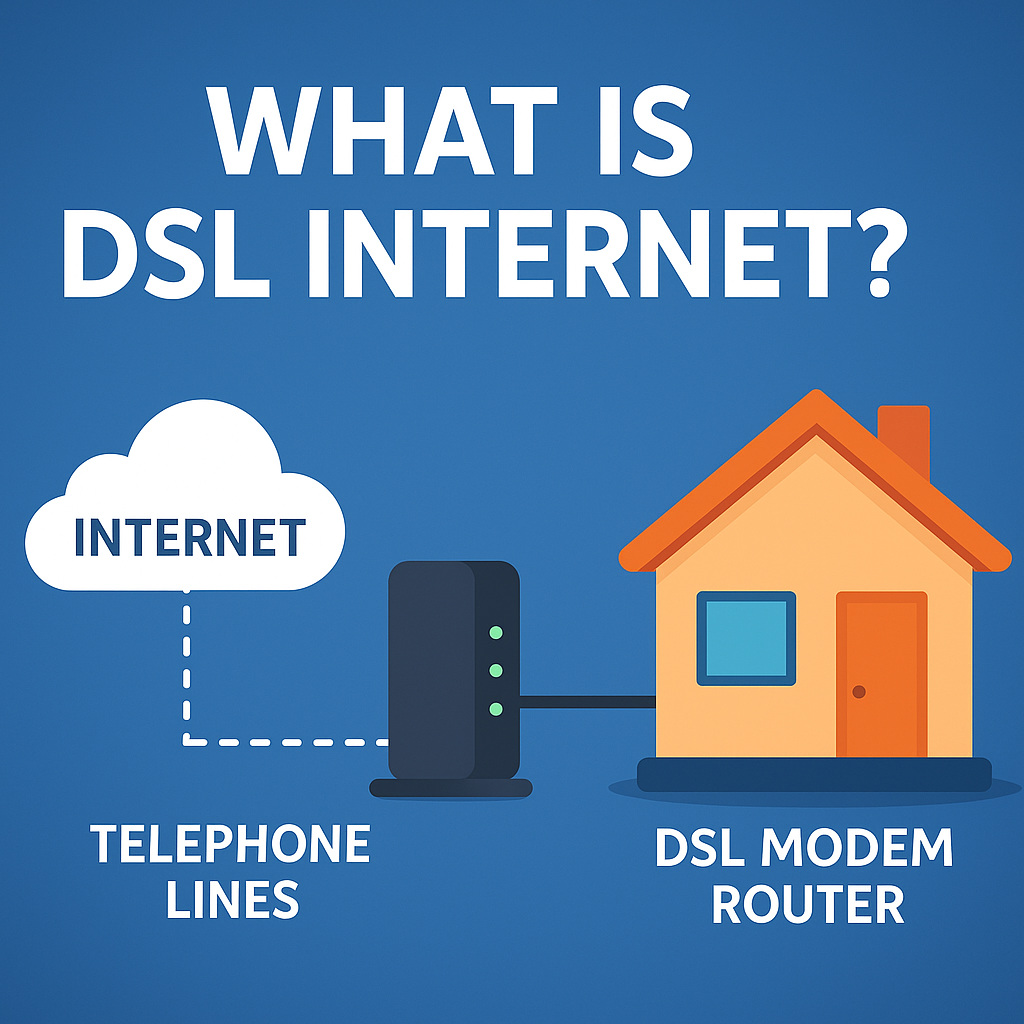
What Is DSL Internet? (Simple Definition)
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a type of broadband internet that transmits data over traditional copper telephone lines. Unlike dial-up, DSL allows you to use the internet and phone simultaneously because it uses different frequency bands.
In simple terms:
✔ DSL = Internet delivered over your phone line
✔ No interruption to voice calls
✔ Always-on connection
✔ Faster than dial-up, slower than cable and fiber
How Does DSL Internet Work?
DSL transmits digital signals over copper telephone lines without interfering with voice communication. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
1. Your home phone jack splits signals
The line carries two types of signals:
-
Voice (low frequency)
-
Internet data (high frequency)
A DSL filter or splitter separates them.
2. The DSL modem converts and manages data
Your modem receives the high-frequency digital signal and translates it into internet data your devices can use.
3. Data travels to the provider’s DSLAM
DSL Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) aggregates many customers’ DSL lines and connects them to the high-speed backbone network.
4. Your router distributes connection locally
Through Wi-Fi or Ethernet, the router sends internet access to your devices.
Why DSL Is Reliable
Because DSL uses dedicated lines for each customer (unlike cable), it’s:
-
Less prone to neighborhood congestion
-
More stable during peak hours
Types of DSL Internet
There are several variations of DSL, each offering different speeds and capabilities.
1. ADSL (Asymmetric DSL) — Most common
-
Faster download speed
-
Slower upload speed
Typically used for browsing, video streaming, email, and general home use.
2. ADSL2+
Improved version of ADSL with:
-
Higher speeds
-
Better stability
-
Larger bandwidth
3. SDSL (Symmetric DSL)
-
Equal download and upload speeds
-
Used by businesses and IT teams
-
Ideal for VoIP, cloud, and video conferencing
4. VDSL (Very High Bitrate DSL)
Much faster than traditional DSL.
5. VDSL2
One of the fastest DSL technologies due to performance over short distances.
How Fast Is DSL Internet?
DSL speeds vary depending on:
-
Line quality
-
Distance from the provider
-
Type of DSL
-
Network congestion
-
Copper line age
Typical DSL Speeds (2025):
-
Download: 5–100 Mbps
-
Upload: 1–30 Mbps
VDSL/VDSL2 can reach speeds up to 100–300 Mbps in some areas.
Advantages of DSL Internet
Even with modern fiber networks, DSL still offers several benefits:
✔ 1. Affordable Pricing
Often cheaper than:
-
Cable
-
Fiber
-
Satellite
✔ 2. Wide Availability
Works almost anywhere phone lines exist, making it ideal for:
-
Rural areas
-
Older homes
-
Legacy buildings
✔ 3. Reliable & Stable
Because DSL doesn’t share bandwidth with neighbors, speed consistency is higher.
✔ 4. Easy Installation
Just plug in a DSL modem and filter. No major infrastructure changes.
✔ 5. Good for Small Businesses & Security Systems
Many organizations use DSL to support:
-
POS systems
-
Remote monitoring
-
Security cameras
-
IoT devices
Disadvantages of DSL Internet
DSL does have limitations:
❌ 1. Speed Limitations
Much slower than cable and fiber.
❌ 2. Distance Sensitivity
Performance drops dramatically if you’re far from the DSLAM.
❌ 3. Copper Line Degradation
Older infrastructure can lead to interruptions.
❌ 4. Not Ideal for Heavy Streaming or Gaming
Especially in households with multiple devices.
DSL vs Other Internet Technologies
DSL vs Cable Internet
| Feature | DSL | Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Reliability | High | Medium (shared) |
| Availability | Widespread | Limited in rural areas |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
DSL vs Fiber Internet
| Feature | DSL | Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 5–100 Mbps | 1–10 Gbps |
| Latency | Higher | Very low |
| Reliability | Medium | Very high |
| Cost | Low | Medium–High |
Fiber is better in almost every category — but not as widely available.
DSL vs Satellite Internet
| Feature | DSL | Satellite |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low | Very high |
| Speed | Moderate | Varies |
| Weather impact | Minimal | High |
| Reliability | Higher | Lower |
What Affects DSL Performance?
✔ Distance to provider
✔ Line quality
✔ Wiring interference
✔ Router capabilities
✔ Home device load
Security Considerations for DSL Internet
While DSL is stable, it’s not inherently secure.
1. DSL Modem Vulnerabilities
Outdated firmware may expose:
-
Open ports
-
Default admin credentials
-
Weak Wi-Fi encryption
2. Risks From Unsecured Networks
Always secure with:
-
WPA3/WPA2 encryption
-
Strong passwords
-
Guest networks
-
Updated firmware
3. Endpoint Protection Is Essential
Malware and phishing attacks can compromise devices on DSL connections just as easily as any other network.
4. Use Firewall & VPN Protection
A DSL connection must be paired with proper network defenses.
Who Should Use DSL Internet?
DSL is a great fit for:
-
Light internet users
-
Remote areas
-
Students
-
Small businesses
-
IoT device networks
-
Security system monitoring
-
Backup internet connections
Signs You Should Upgrade from DSL
✔ Frequent buffering
✔ Slow upload speeds
✔ Multiple users struggling
✔ Remote work performance issues
✔ Gaming lags
If available, fiber or cable is a significant upgrade.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is DSL internet?
DSL internet is a broadband connection that uses telephone lines to deliver internet access.
2. Is DSL faster than Wi-Fi?
DSL is a type of internet; Wi-Fi is a wireless distribution method.
Your Wi-Fi speed depends on your DSL speed.
3. Can I use DSL without a phone line?
You need a copper line, but you don’t need an active phone service plan.
4. Is DSL good for streaming?
Yes, but only at higher DSL speeds (15 Mbps+).
5. Is DSL going away?
Some regions are phasing out copper lines, but DSL remains active in many rural and suburban areas.
Conclusion: DSL Is Still Useful — but Know Its Limits
DSL internet may not be as fast as fiber or cable, but it remains widely available, cost-effective, and reliable. Whether you’re supporting small business systems, remote operations, IoT networks, or home internet access, DSL delivers steady performance and easy setup.
However, as cybersecurity risks increase, pairing DSL with strong network protection is essential — especially for enterprises and IT teams.
🚀 Secure Your Network with Zero-Trust Protection
Whether you use DSL, cable, or fiber, advanced threat prevention is critical.
👉 Request a Free Demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/