What is a WAN? Complete Guide for IT & Security Leaders
Updated on September 1, 2025, by Xcitium

Have you ever wondered, what is a WAN and why does every enterprise depend on it? In today’s global, cloud-first world, connectivity is the lifeblood of business. Whether you’re a multinational corporation, a financial institution, or a SaaS provider, your ability to securely connect employees, applications, and data across locations determines your competitive edge.
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is the backbone that enables distributed organizations to communicate efficiently and securely. For IT managers, cybersecurity leaders, and CEOs, understanding WANs isn’t just technical—it’s mission-critical for growth, compliance, and resilience.
What is a WAN?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunications network that extends across large geographical areas, connecting multiple Local Area Networks (LANs), branch offices, data centers, and cloud platforms.
While a LAN might cover a single office building, a WAN can connect entire cities, regions, or even countries.
In simple terms:
- A LAN is your office network.
- A WAN is the corporate “superhighway” that connects all your offices, cloud services, and remote workers together.
Key Characteristics of a WAN
- Covers large geographical areas
- Uses carrier-grade circuits (MPLS, leased lines, broadband, or 5G)
- Connects LANs and remote sites together
- Relies on routers, firewalls, and WAN accelerators
- Supports enterprise collaboration, data sharing, and cloud workloads
How Does a WAN Work?
Understanding what is a WAN means looking at its components and architecture.
- Routers & Switches – Direct traffic between branch offices and data centers.
- WAN Links – Physical or virtual circuits like MPLS, broadband, or satellite connections.
- Service Providers – Telecom carriers provide the backbone infrastructure.
- Protocols & Encryption – Ensure secure communication across public networks.
- WAN Optimization – Tools like caching and compression improve performance.
Essentially, WANs stitch together multiple LANs across distance, allowing users to share resources, applications, and data as if they were on the same local network.
Types of WAN Technologies
There’s no one-size-fits-all WAN. Enterprises choose based on budget, performance, and security needs.
1. MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
- High reliability and predictable performance.
- Common in banks, healthcare, and government.
- Expensive compared to broadband.
2. Broadband Internet WAN
- Uses standard internet connections.
- Cost-effective, but less secure without additional safeguards.
3. SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)
- Virtual overlay that manages multiple connection types.
- Improves agility, cloud performance, and cost-efficiency.
- Includes intelligent routing and built-in security.
4. Cellular & Satellite WAN
- Used for remote locations (oil rigs, rural areas, defense).
- Reliable but often costly and bandwidth-limited.
WAN vs LAN: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | LAN (Local Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
| Geographic Scope | Single building/office | Multiple cities, countries |
| Speed | Very high (Gbps) | Lower, depends on carrier |
| Ownership | Owned by organization | Managed by carriers/ISPs |
| Cost | Low | Higher, recurring carrier fees |
| Security Needs | Internal security only | Strong encryption required |
👉 In short, LANs are local, WANs are global.
Why WANs Are Essential for Enterprises
So, what is a WAN used for in today’s enterprises? The answer goes far beyond simple connectivity.
1. Business Continuity & Collaboration
WANs connect global teams, enabling video conferencing, VoIP, and real-time collaboration tools.
2. Cloud & SaaS Access
Most businesses now rely on cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft 365, or Salesforce. WANs ensure secure, high-performance access.
3. Cybersecurity
WANs allow organizations to centralize firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and zero-trust architectures.
4. Scalability
As companies grow, WANs allow seamless integration of new branches, remote employees, and cloud workloads.
Security Challenges in WANs
A WAN’s strength—its distributed nature—is also its weakness.
Major WAN Security Risks:
- Data interception: Traffic across public networks can be vulnerable.
- Ransomware & malware spread: One compromised endpoint can impact the entire WAN.
- Insider threats: Remote employees may unknowingly expose systems.
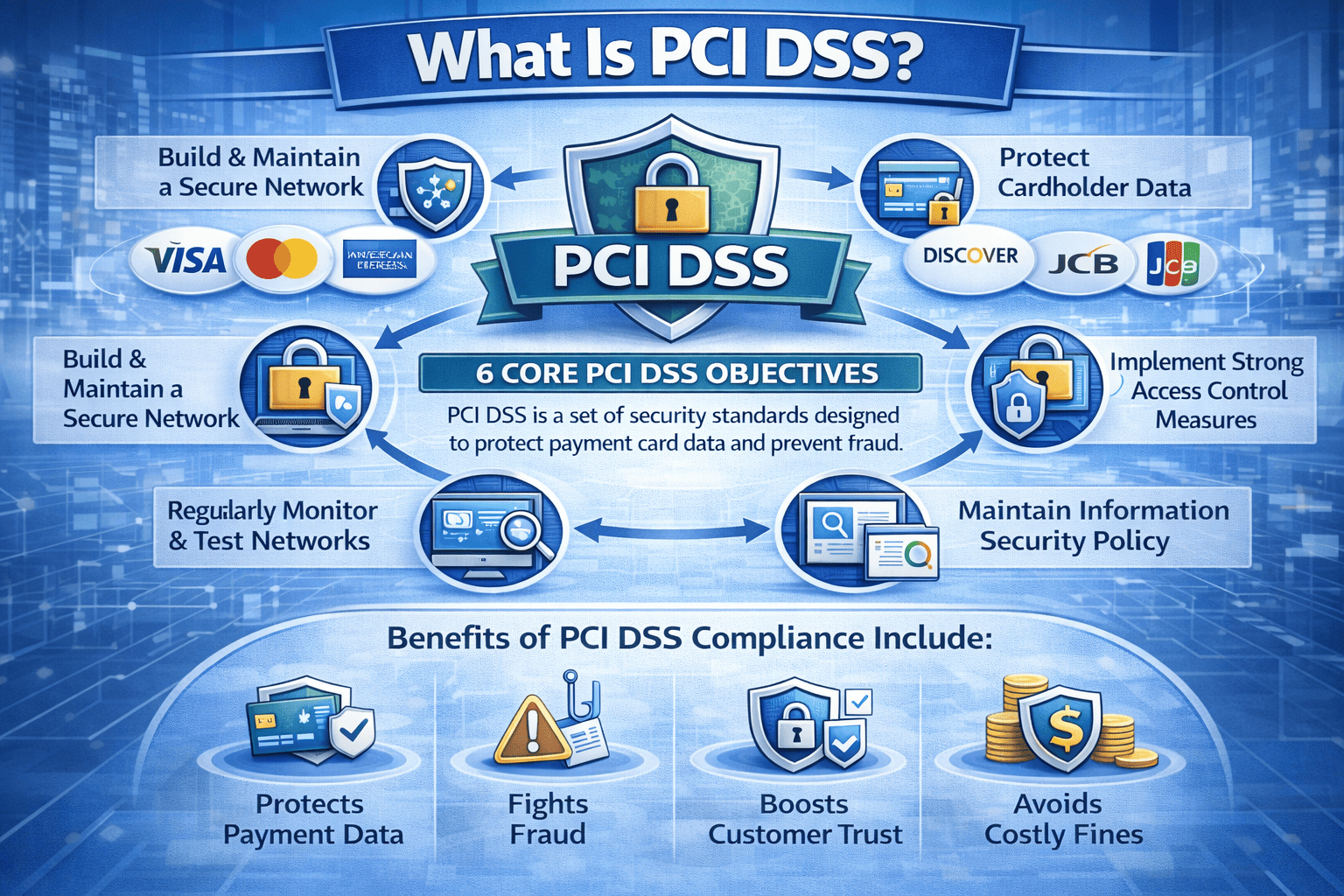
- Compliance risks: Finance and healthcare industries must meet strict standards (PCI-DSS, HIPAA).
Best Practices for WAN Security
- Deploy end-to-end encryption for all traffic.
- Implement Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).
- Use next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) at WAN edges.
- Adopt SD-WAN with built-in security.
- Continuously monitor with SIEM platforms.
Benefits of a Well-Designed WAN
When IT leaders ask what is a WAN, they really want to know: Why invest in one?
Business Benefits:
- Reduced downtime and better business continuity.
- Seamless collaboration across geographies.
- Faster cloud adoption.
IT Benefits:
- Centralized monitoring and control.
- Simplified compliance reporting.
- Lower operational costs with SD-WAN.
Security Benefits:
- Stronger defense against cyberattacks.
- Easier policy enforcement across locations.
- Secure remote work enablement.
Industry Use Cases of WANs
WANs power mission-critical operations across industries:
- Financial Services: Secure interbank transactions, fraud monitoring.
- Healthcare: Real-time access to patient data across hospitals.
- Retail: Connecting point-of-sale systems with headquarters.
- Manufacturing: Linking IoT devices and remote plants.
- Government & Defense: Encrypted communication across regions.
Each case shows that WANs are strategic enablers of business and security.
The Future of WAN: From Hardware to Cloud
WANs are evolving rapidly to meet new demands.
- SD-WAN growth: By 2026, 65% of enterprises will adopt SD-WAN (Gartner).
- 5G integration: Ultra-low latency for IoT and edge computing.
- Zero Trust WANs: Security-first design for hybrid environments.
- AI-driven optimization: Predictive traffic routing and anomaly detection.
👉 Tomorrow’s WANs will be cloud-native, software-defined, and AI-enhanced.
FAQs on WANs
Q1: What is a WAN in simple terms?
A WAN is a network that connects multiple LANs across large areas, allowing organizations to share data securely.
Q2: How is a WAN different from the internet?
The internet is public, while a WAN is a private, enterprise-grade network often built on top of internet or carrier infrastructure.
Q3: Why is WAN security important?
WANs carry sensitive business data. Without encryption and monitoring, they’re vulnerable to breaches, ransomware, and compliance violations.
Q4: What is SD-WAN and why is it popular?
SD-WAN is a modern, software-driven approach that improves WAN performance, reduces costs, and enhances security.
Q5: Who needs a WAN?
Any organization with multiple locations, remote employees, or cloud-based applications relies on WANs.
Conclusion: Why WANs Are the Backbone of Modern Enterprises
To sum it up, what is a WAN? It’s the digital bridge connecting people, applications, and data worldwide. Without WANs, global business, cloud adoption, and secure remote work would be impossible.
For IT managers, CEOs, and cybersecurity leaders, building a secure, scalable, and resilient WAN should be a top priority in 2025 and beyond.
👉 Ready to secure your enterprise WAN with cutting-edge protection? Request a Demo with Xcitium