What Is a Local Network? A Complete Guide for Business and Cybersecurity Leaders
Updated on February 12, 2026, by Xcitium
What is a local network, and why should IT managers and CEOs care about it? Every email sent inside your office, every shared file, and every connected printer likely depends on a local network. Yet many organizations overlook how critical this internal infrastructure is to cybersecurity and performance.
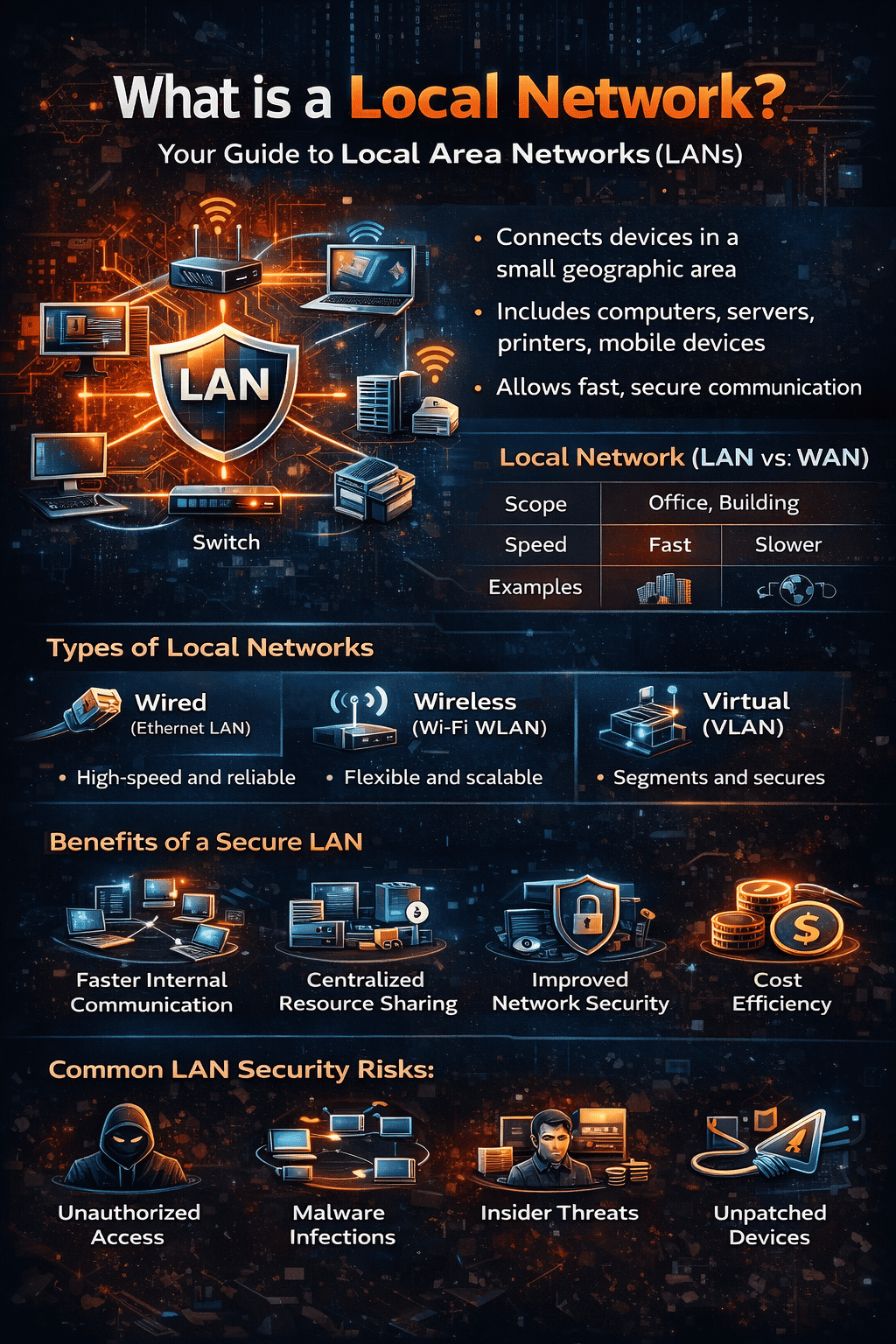
So, what is a local network in simple terms? A local network, often called a Local Area Network (LAN), connects devices within a limited geographic area such as an office, building, or campus. It allows computers, servers, mobile devices, and IoT systems to communicate securely and efficiently.
For cybersecurity professionals and business leaders, understanding what is a local network is not just technical knowledge — it’s a foundation for risk management and operational resilience.
What Is a Local Network and How Does It Work?
To fully understand what is a local network, let’s break it down into simple components.
A local network connects devices within a small physical area. Unlike a Wide Area Network (WAN), which spans cities or countries, a LAN operates in one location.
Core Components of a Local Network
A standard local network includes:
-
Switches – Connect devices within the network
-
Routers – Connect the LAN to the internet
-
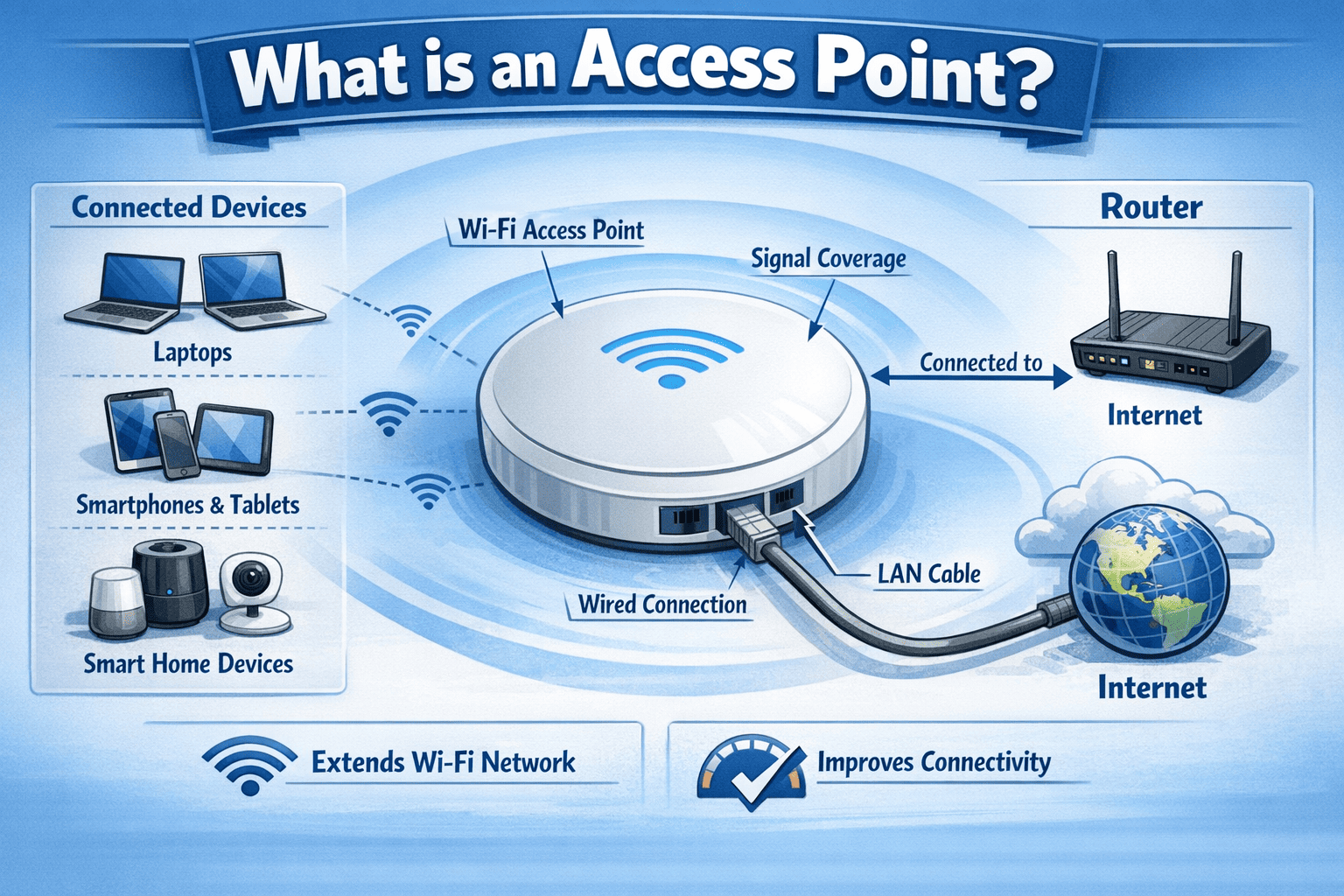
Access points – Provide wireless connectivity
-
Ethernet cables – Enable wired connections
-
Servers – Store files, applications, or databases
When someone asks, what is a local network, the answer includes both hardware and software working together to allow internal communication.
How Data Moves Inside a LAN
When a device sends data:
-
The data is broken into packets.
-
The switch identifies the destination.
-
The packets are delivered within milliseconds.
-
If external access is needed, the router forwards traffic to the internet.
Because everything stays within a confined area, LAN communication is typically faster and more secure than internet-based traffic.
Types of Local Networks Businesses Use
Understanding what is a local network also means knowing its variations.
1. Wired Local Network (Ethernet LAN)
-
Uses physical cables
-
High speed and reliability
-
Ideal for data-heavy environments
2. Wireless Local Network (WLAN)
-
Uses Wi-Fi access points
-
Flexible and scalable
-
Supports mobile devices and remote work
3. Virtual LAN (VLAN)
-
Segments networks logically
-
Improves security and performance
-
Common in enterprise network security setups
For modern enterprises, VLANs help separate departments, restrict access, and reduce internal threats.
Why Local Networks Matter for Cybersecurity
Now that we’ve defined what is a local network, let’s examine its security impact.
Your local network is often the first line of defense. If compromised, attackers can:
-
Access sensitive data
-
Move laterally across systems
-
Deploy ransomware
-
Exfiltrate confidential information
Common LAN Security Risks
-
Unauthorized access
-
Malware spreading internally
-
Insider threats
-
Weak password policies
-
Unpatched devices
A secure local network design reduces these risks significantly.
What Is a Local Network in Enterprise Environments?
In large organizations, a local network becomes more complex.
Enterprise LANs often include:
-
Multiple switches and routers
-
Segmented VLANs
-
Network access control (NAC)
-
Endpoint detection systems
-
Firewalls and intrusion prevention systems
When IT leaders evaluate what is a local network in business terms, they must consider scalability, redundancy, and cybersecurity posture.
LAN vs WAN: Understanding the Difference
A common question tied to what is a local network is how it compares to a WAN.
| Feature | Local Network (LAN) | Wide Area Network (WAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Scope | Small area | Large area |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Security Control | Higher internal control | More external exposure |
| Example | Office network | Internet |
While WAN connects offices globally, LAN connects devices locally. Both require strong cybersecurity measures.
Benefits of a Secure Local Network
Understanding what is a local network becomes strategic when you look at its benefits.
1. Faster Communication
Internal data transfer is rapid. Teams can collaborate efficiently without relying on external servers.
2. Centralized Resource Sharing
Employees can share:
-
Printers
-
Files
-
Applications
-
Databases
3. Improved Cybersecurity Control
Security teams can:
-
Monitor traffic
-
Restrict access
-
Deploy network segmentation
-
Enforce security policies
4. Cost Efficiency
Local networks reduce bandwidth costs by keeping internal traffic off the internet.
How Hackers Exploit Local Networks
Cybercriminals often target weak LAN configurations.
Common Attack Methods
-
ARP spoofing
-
Man-in-the-middle attacks
-
Lateral movement after phishing
-
Rogue device insertion
-
IoT vulnerabilities
Once attackers gain access, they move across the local network to escalate privileges.
That’s why understanding what is a local network must include understanding how it can be attacked.
Best Practices to Secure a Local Network
If you manage IT infrastructure, here are actionable steps to protect your LAN.
1. Use Network Segmentation
Separate sensitive systems using VLANs. Limit access between departments.
2. Deploy Strong Authentication
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
-
Role-based access control
-
Strong password policies
3. Install Enterprise-Grade Firewalls
Monitor incoming and outgoing traffic.
4. Keep Systems Updated
Unpatched devices are easy entry points.
5. Monitor Network Activity
Use network monitoring tools to detect unusual behavior.
Encryption, endpoint protection, and managed detection services further strengthen security.
Local Networks and Remote Work Challenges
Hybrid work environments changed how we define what is a local network.
Today:
-
Employees access LAN resources remotely
-
VPNs extend network boundaries
-
Cloud integration blurs traditional network edges
This increases risk.
Remote endpoints can introduce threats into internal systems if not properly secured.
Zero Trust security models now treat every device as untrusted — even inside the local network.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Healthcare
Hospitals rely on local networks for patient data systems and connected medical devices. Security failures can disrupt care.
Financial Services
Banks use secure LANs to protect transaction systems and internal records.
Manufacturing
Industrial control systems often operate within isolated local networks. A breach can halt production.
SaaS and Tech Companies
Development teams rely on LAN speed and secure access to internal servers.
For executives, understanding what is a local network means understanding operational continuity.
The Role of Managed Cybersecurity in LAN Protection
Managing a secure local network requires continuous monitoring.
Organizations often benefit from:
-
24/7 threat detection
-
Incident response teams
-
Endpoint protection platforms
-
Network behavior analytics
Cyber threats evolve rapidly. Internal network protection must evolve as well.
Even the most advanced local network can be compromised without proper security oversight.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a local network in simple terms?
What is a local network? It is a system that connects devices within a limited area like an office or building, allowing them to share data and resources.
2. Is a Wi-Fi network a local network?
Yes. A wireless network (WLAN) is a type of local network that connects devices using Wi-Fi instead of cables.
3. How secure is a local network?
A local network can be very secure if properly configured with firewalls, encryption, access controls, and monitoring tools.
4. What is the difference between LAN and internet?
A LAN connects devices locally. The internet is a global network connecting millions of LANs and WANs.
5. Why do businesses need a secure local network?
Businesses depend on local networks to run operations. A breach can disrupt services, expose data, and cause financial loss.
Final Thoughts: Why Your Local Network Is a Critical Asset
So, what is a local network? It’s the backbone of your organization’s daily operations. It connects your devices, stores your data, and powers collaboration.
However, it is also a primary target for cyberattacks.
Understanding what is a local network is just the first step. Securing it requires proactive monitoring, endpoint protection, network segmentation, and rapid incident response.
If your organization wants to strengthen its internal network security and prevent modern cyber threats, it’s time to take action.
👉 See how Xcitium helps businesses protect their endpoints, networks, and internal infrastructure with advanced cybersecurity solutions.
Request a personalized demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Your local network is too important to leave unprotected.