What Is Logging? A Complete Guide for Modern IT and Cybersecurity
Updated on February 5, 2026, by Xcitium
What really happens inside your systems when something goes wrong?
Without visibility, security teams are left guessing. This is exactly why understanding what is logging matters more than ever in today’s complex IT environments.
Logging is the foundation of monitoring, troubleshooting, and cybersecurity. Whether you’re investigating a breach, tracking system performance, or meeting compliance requirements, logs provide the evidence you need. In this guide, we’ll explain what logging is, how it works, why it’s critical for security teams, and how organizations can use it effectively.
What Is Logging?
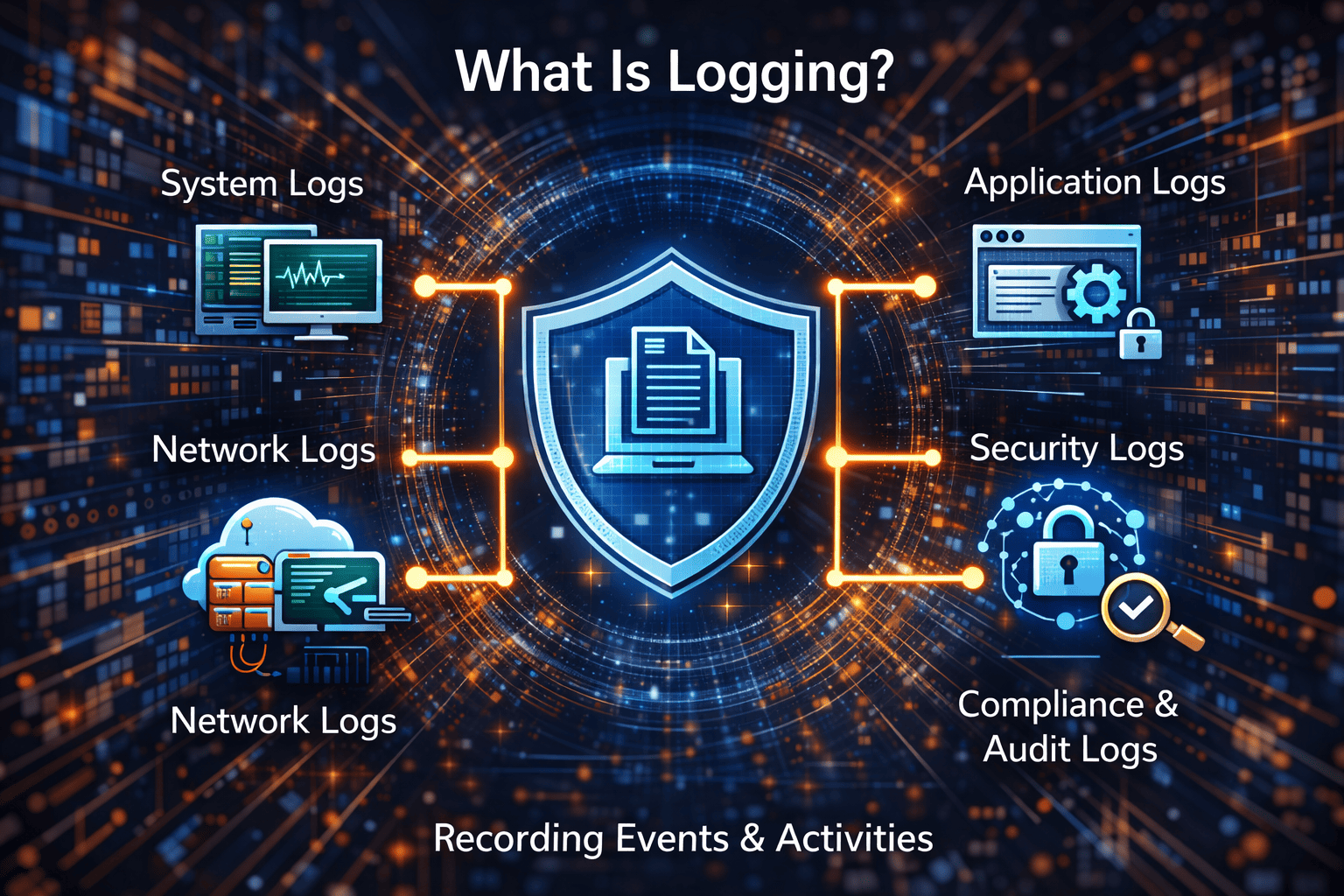
What is logging? Logging is the process of recording events, activities, and actions that occur within systems, applications, networks, and devices. These records—known as logs—capture details such as timestamps, user actions, system errors, and security events.
Logs act as a historical record of everything happening in an environment. When something breaks, slows down, or gets attacked, logs are often the first place IT and security teams look.
In cybersecurity, logging plays a vital role in detecting threats, investigating incidents, and maintaining compliance across organizations.
Why Logging Is Critical in Cybersecurity
Understanding what is logging becomes especially important when security is involved. Logs provide visibility that security tools alone cannot.
Key reasons logging is essential:
-
Detects suspicious and malicious activity
-
Helps investigate security incidents
-
Supports compliance and audits
-
Improves system reliability and uptime
-
Enables proactive threat hunting
Without proper logging, attackers can move undetected, and incidents may go unnoticed for weeks—or longer.
Types of Logs You Should Know About
To fully understand what is logging, it’s important to know the different types of logs organizations rely on.
1. System Logs
Record operating system events such as startup, shutdown, and hardware issues.
2. Application Logs
Capture application behavior, errors, and user interactions.
3. Security Logs
Track authentication attempts, access control changes, and policy violations.
4. Network Logs
Monitor traffic flows, firewall activity, and network anomalies.
5. Audit Logs
Provide records required for compliance and governance purposes.
Each log type contributes unique insights that help teams maintain control and security.
Logging vs Monitoring: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse logging with monitoring, but they serve different purposes.
| Aspect | Logging | Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Record events | Analyze and alert |
| Data Type | Raw event data | Processed insights |
| Timing | Historical | Real-time |
| Usage | Investigation | Prevention |
Logging collects the data. Monitoring uses that data to generate alerts and actions. Together, they form a powerful security strategy.
How Logging Works in Practice
To understand what is logging in real-world environments, it helps to see how logs flow through systems.
-
Systems and applications generate logs
-
Logs are collected and centralized
-
Log data is stored securely
-
Logs are analyzed for insights and alerts
-
Teams investigate and respond to findings
Modern environments generate massive volumes of log data, making automation and centralized log management essential.
What Is Log Management?
Log management refers to the process of collecting, storing, analyzing, and retaining logs from across an organization.
Effective log management includes:
-
Centralized log collection
-
Normalization and indexing
-
Secure storage and retention
-
Search and analysis capabilities
-
Integration with SIEM tools
Without proper log management, valuable data becomes overwhelming and difficult to use.
Logging and SIEM: Why They Go Hand in Hand
A SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) platform relies heavily on logging.
How SIEM logging helps:
-
Correlates events across systems
-
Detects advanced threats
-
Provides real-time alerts
-
Supports forensic investigations
Logging supplies the raw data, while SIEM turns it into actionable intelligence. Together, they form the backbone of modern security operations.
Key Benefits of Logging for Businesses
Understanding what is logging is not just a technical concern—it’s a business advantage.
Security Benefits
-
Faster breach detection
-
Improved incident response
-
Reduced dwell time for attackers
Operational Benefits
-
Faster troubleshooting
-
Improved system performance
-
Reduced downtime
Compliance Benefits
-
Audit readiness
-
Regulatory alignment
-
Evidence-based reporting
Logging strengthens both security posture and business resilience.
Logging Best Practices Every Organization Should Follow
To get maximum value from logging, organizations should follow proven best practices.
Logging best practices include:
-
Log everything that matters—not everything possible
-
Use consistent log formats
-
Secure log storage from tampering
-
Define log retention policies
-
Regularly review and test logs
Good logging is intentional, structured, and aligned with business objectives.
Common Logging Challenges and How to Solve Them
Too Much Log Data
Use filtering and prioritization to focus on high-value events.
Lack of Visibility
Centralize logs to eliminate blind spots.
Storage Costs
Apply smart retention and compression strategies.
Alert Fatigue
Fine-tune thresholds and correlation rules.
Understanding what is logging also means understanding how to manage it effectively.
Logging in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
As organizations move to cloud and hybrid infrastructures, logging becomes more complex—but also more important.
Cloud logging considerations:
-
Distributed systems generate massive log volumes
-
Cloud-native logs differ from on-prem logs
-
Visibility must span multiple environments
Centralized log management ensures consistent visibility across cloud, hybrid, and on-prem environments.
Logging and Compliance Requirements
Many regulations explicitly require logging.
Regulations that depend on logging:
-
ISO 27001
-
SOC 2
-
PCI DSS
-
HIPAA
-
GDPR
Logs provide the evidence auditors need to verify controls, access, and incident handling.
The Future of Logging in Cybersecurity
Logging continues to evolve alongside modern threats.
Key trends shaping the future:
-
AI-driven log analysis
-
Behavioral analytics
-
Automated incident response
-
Unified security platforms
Understanding what is logging today prepares organizations for the security challenges of tomorrow.
FAQs About What Is Logging
1. What is logging in cybersecurity?
Logging in cybersecurity is the process of recording security-related events to detect threats, investigate incidents, and support compliance.
2. Why is logging important for IT teams?
Logging helps IT teams troubleshoot issues, improve performance, and maintain system reliability.
3. What is log management?
Log management involves collecting, storing, analyzing, and retaining logs from multiple sources in a centralized system.
4. How long should logs be retained?
Retention depends on compliance and business needs, but many organizations keep logs for 6–12 months or longer.
5. Can logging help prevent cyberattacks?
Yes. While logging itself is passive, it enables faster detection and response, reducing the impact of attacks.
Final Thoughts: Why Logging Is Non-Negotiable
Understanding what is logging is foundational for modern IT and cybersecurity strategies. Logs provide the visibility organizations need to detect threats, troubleshoot issues, and meet compliance requirements.
Without logging:
-
Attacks go unnoticed
-
Incidents take longer to resolve
-
Compliance becomes difficult
With effective logging, organizations gain control, clarity, and confidence.
Take the Next Step Toward Better Visibility and Security
Ready to gain deeper insight into your systems and strengthen your security posture?
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
See how advanced logging and security visibility can transform your operations.