What Is SDLC Life Cycle? A Complete Guide for Secure Software Development
Updated on February 3, 2026, by Xcitium
What is SDLC life cycle, and why does it matter so much in today’s security-driven digital world? Every application—whether a mobile app, enterprise platform, or cloud service—follows a structured journey from idea to deployment. The SDLC life cycle provides that structure, ensuring software is built efficiently, securely, and with minimal risk.
For cybersecurity professionals, IT managers, and business leaders, understanding what is SDLC life cycle is essential. A poorly executed SDLC leads to insecure applications, project delays, and rising costs. This guide explains the SDLC life cycle in simple terms, its phases, models, security implications, and best practices for modern organizations.
What Is SDLC Life Cycle?
What is SDLC life cycle? SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle. It is a systematic process used to design, develop, test, deploy, and maintain software applications. The SDLC life cycle breaks software development into well-defined phases to improve quality, predictability, and security.
Instead of building software in an unstructured way, SDLC ensures every stage is planned and reviewed. This reduces errors, controls costs, and improves collaboration between development, security, and business teams.
In today’s threat landscape, SDLC is no longer just a development framework—it’s a security requirement.
Why the SDLC Life Cycle Is Important for Businesses
The SDLC life cycle plays a critical role in both operational success and risk management.
Key reasons SDLC matters include:
-
Predictable project timelines
-
Reduced development costs
-
Improved software quality
-
Better security integration
-
Clear accountability at each stage
For executives and IT leaders, a strong SDLC life cycle means fewer surprises and more reliable outcomes.
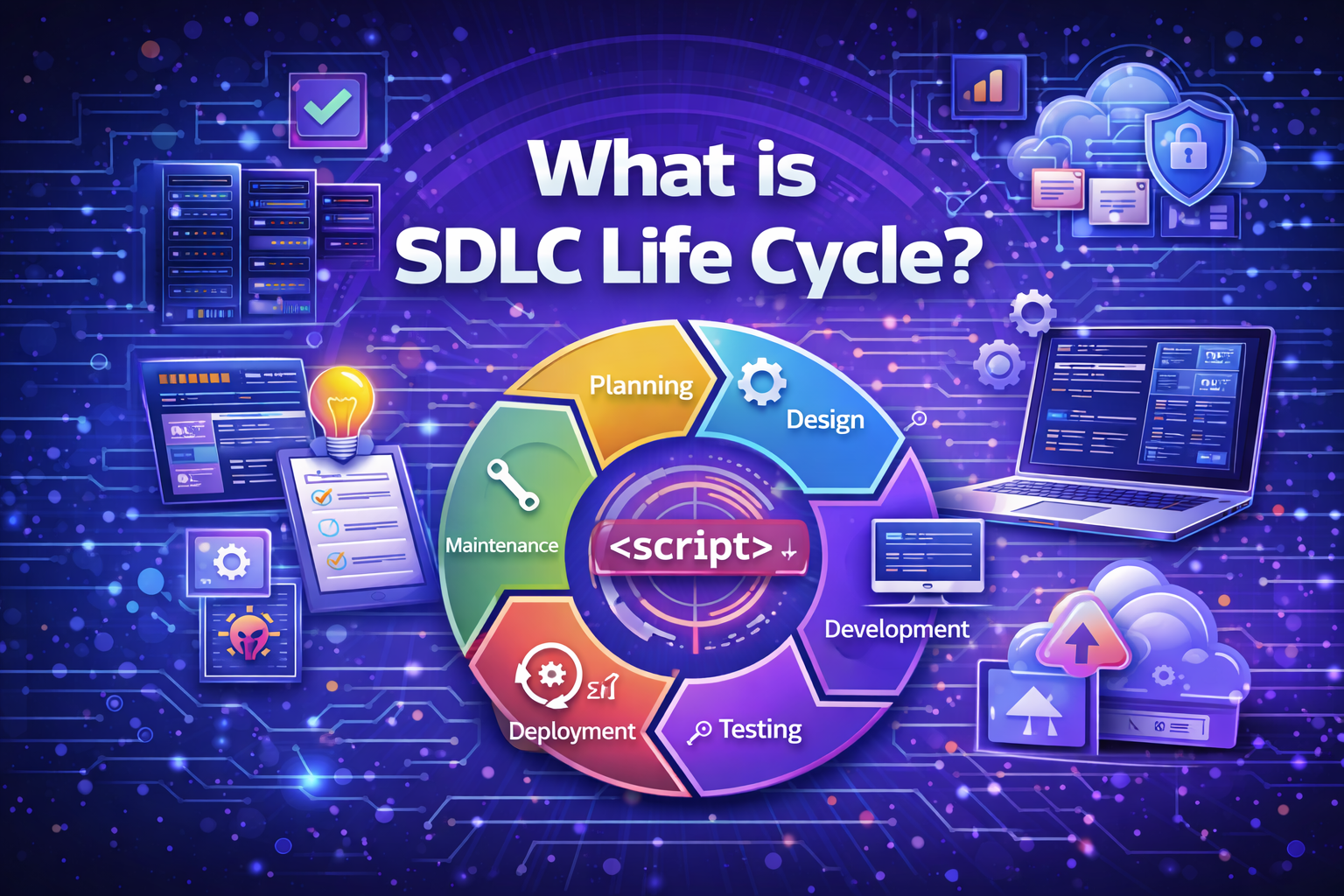
The Key Phases of the SDLC Life Cycle
Understanding what is SDLC life cycle requires a clear look at its core phases. While names may vary slightly, the structure remains consistent.
1. Planning and Requirement Analysis
This phase defines the project’s scope, goals, and feasibility.
Activities include:
-
Business requirement gathering
-
Risk assessment
-
Cost and timeline estimation
A strong planning phase prevents scope creep and misaligned expectations.
2. System Design
During system design, requirements are transformed into technical specifications.
This includes:
-
Architecture design
-
Data flow diagrams
-
Technology stack selection
Security design decisions made here significantly affect future risk.
3. Development (Implementation)
This is where actual coding takes place. Developers build the software based on design specifications.
Best practices include:
-
Secure coding standards
-
Version control
-
Code reviews
Following secure SDLC principles during development reduces vulnerabilities.
4. Testing
Testing ensures the application works as expected and is free from defects.
Common testing types:
-
Functional testing
-
Performance testing
-
Security testing
Security testing is critical to identify vulnerabilities before release.
5. Deployment
Once tested, the application is deployed to production.
Deployment activities include:
-
Environment configuration
-
Release management
-
Monitoring setup
A controlled deployment process minimizes downtime and errors.
6. Maintenance and Support
After release, the application enters the maintenance phase.
This includes:
-
Bug fixes
-
Updates and patches
-
Performance optimization
Maintenance ensures the application remains secure and reliable over time.
Popular SDLC Life Cycle Models
Different projects require different SDLC models. Understanding these models helps teams choose the right approach.
Waterfall Model
A linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before moving on.
Best for:
-
Stable requirements
-
Low complexity projects
Limitations include inflexibility and late testing.
Agile Model
Agile focuses on iterative development and continuous feedback.
Best for:
-
Dynamic requirements
-
Fast-changing environments
Agile supports continuous improvement and faster delivery.
DevOps Model
DevOps integrates development and operations for faster, automated delivery.
Key benefits:
-
Continuous integration and deployment
-
Improved collaboration
-
Faster incident response
DevOps works well with modern cloud environments.
Spiral Model
The Spiral model combines iterative development with risk analysis.
Best for:
-
Large, high-risk projects
-
Security-sensitive applications
It emphasizes early identification of risks.
SDLC Life Cycle and Cybersecurity
Security is no longer optional in software development. The SDLC life cycle provides the ideal framework for integrating security from the start.
What Is Secure SDLC?
Secure SDLC (SSDLC) embeds security controls into every phase of development.
Key security practices include:
-
Threat modeling during design
-
Secure coding standards
-
Regular vulnerability testing
-
Continuous monitoring
Security flaws are far cheaper to fix early in the SDLC than after deployment.
Common Challenges in the SDLC Life Cycle
Even with a defined SDLC, organizations face challenges.
Typical Issues Include:
-
Poor requirement clarity
-
Lack of security expertise
-
Insufficient testing
-
Weak communication between teams
Addressing these challenges requires governance, training, and automation.
Best Practices for an Effective SDLC Life Cycle
Organizations can strengthen their SDLC life cycle with proven best practices.
Actionable Best Practices
-
Involve security teams early
-
Automate testing and code scanning
-
Use standardized documentation
-
Enforce change management
-
Continuously review and improve processes
These steps improve both quality and security.
SDLC Life Cycle for IT Managers and Executives
For leadership teams, SDLC is a strategic tool—not just a technical process.
Executive Benefits of a Strong SDLC
-
Predictable delivery timelines
-
Lower long-term costs
-
Reduced security incidents
-
Improved regulatory compliance
Understanding what is SDLC life cycle helps leaders make informed technology decisions.
Measuring the Success of the SDLC Life Cycle
You can’t improve what you don’t measure.
Key Metrics to Track
-
Defect rates
-
Development cycle time
-
Security vulnerabilities detected
-
Cost overruns
-
Post-release incidents
These metrics provide insight into SDLC effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is SDLC life cycle in simple terms?
The SDLC life cycle is a step-by-step process for building, testing, deploying, and maintaining software.
2. Why is SDLC important for security?
SDLC integrates security early, reducing vulnerabilities and lowering breach risk.
3. Which SDLC model is best?
It depends on project needs. Agile and DevOps are popular for modern applications.
4. Can SDLC reduce development costs?
Yes. Early planning and testing prevent expensive fixes later.
5. Is SDLC used only in large organizations?
No. SDLC benefits organizations of all sizes across industries.
Final Thoughts: Why SDLC Life Cycle Matters More Than Ever
Understanding what is SDLC life cycle is essential in today’s fast-paced and threat-heavy digital environment. A well-implemented SDLC ensures software is reliable, secure, and aligned with business goals.
For organizations focused on long-term success, SDLC is not just a framework—it’s a competitive advantage.
If you want better visibility into development risks, stronger security controls, and protection across your digital ecosystem:
👉 Strengthen your security posture today
Request a demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/