What Is IPv4? A Complete Guide for Modern Networks
Updated on January 9, 2026, by Xcitium
How does your device know where to send data on the internet? Every website you visit, email you send, or application you use relies on a unique addressing system. To understand how this works, you first need to know what is IPv4.
IPv4, or Internet Protocol version 4, is the foundational technology that allows devices to communicate across networks. Despite the rise of newer standards, IPv4 still powers much of today’s internet. For IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, and business leaders, understanding IPv4 is essential for managing networks, security, and digital infrastructure.
What Is IPv4?
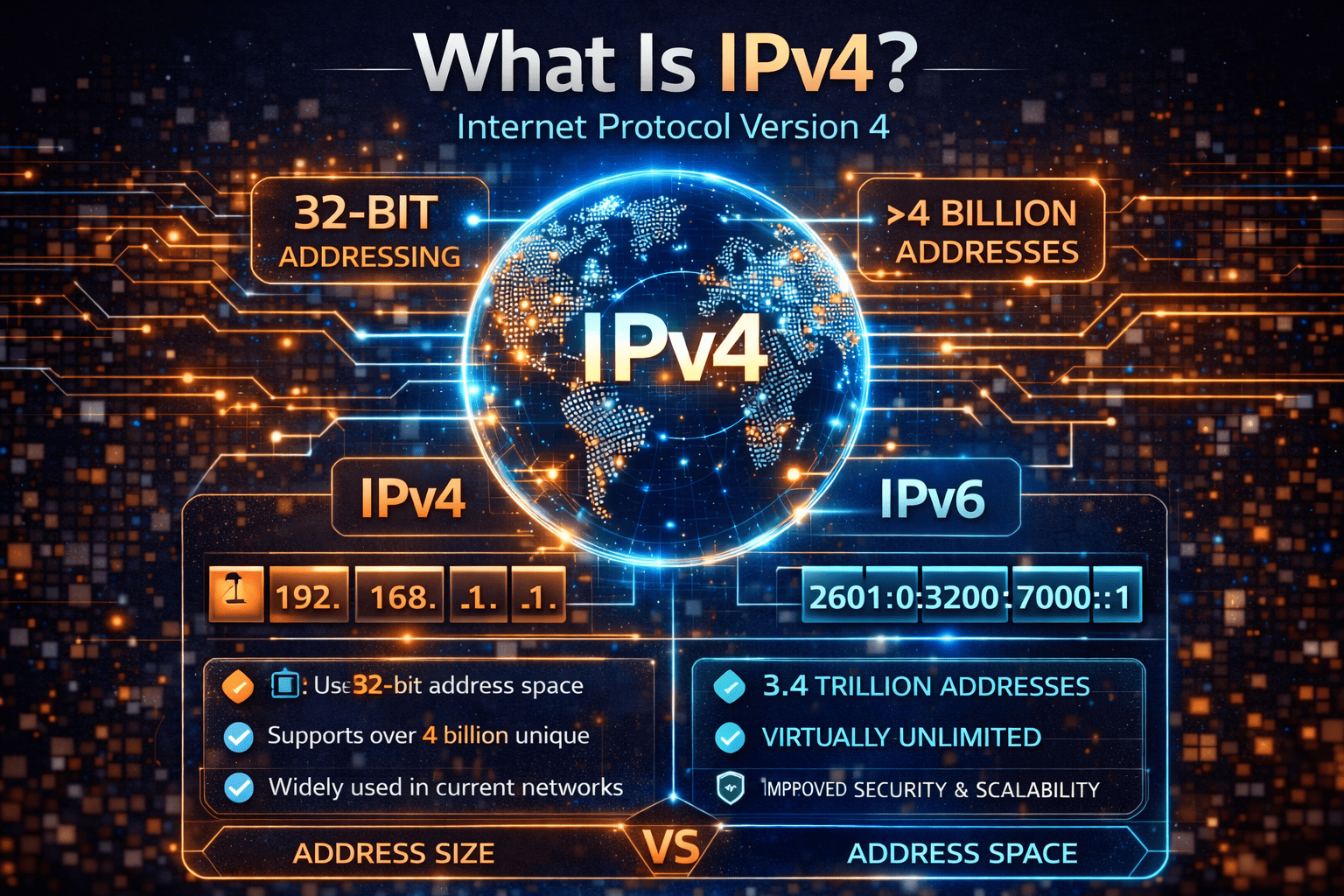
What is IPv4? IPv4 stands for Internet Protocol version 4. It is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol and the most widely used method for identifying devices on a network.
IPv4 assigns a unique numerical address to every device connected to a network. These addresses allow data packets to be routed correctly from one system to another.
An IPv4 address is a 32-bit number written in decimal format, divided into four sections separated by dots.
Example of an IPv4 address:
Understanding what is IPv4 helps explain how devices communicate across local networks and the global internet.
How IPv4 Addresses Work
To fully understand what is IPv4, it’s important to see how IPv4 addresses function behind the scenes.
Each IPv4 address consists of four numbers called octets. Each octet ranges from 0 to 255. Together, these values create more than 4 billion possible unique addresses.
Key components of an IPv4 address:
-
Network portion: Identifies the network
-
Host portion: Identifies the device on that network
Routers use IPv4 addresses to determine where data packets should be sent. Without IPv4, devices would not know how to find each other.
Types of IPv4 Addresses
IPv4 addresses are divided into different categories based on their purpose.
1. Public IPv4 Addresses
Public IPv4 addresses are assigned by internet service providers. These addresses are visible on the internet and identify your network globally.
2. Private IPv4 Addresses
Private addresses are used within internal networks and are not routable on the public internet.
Common private IPv4 ranges include:
-
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
-
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
-
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
Understanding what is IPv4 includes knowing when addresses are public versus private.
IPv4 Address Classes Explained
Originally, IPv4 addresses were divided into classes to support networks of different sizes.
IPv4 address classes:
-
Class A: Very large networks
-
Class B: Medium-sized networks
-
Class C: Small networks
-
Class D: Multicast addresses
-
Class E: Experimental use
While modern networking uses CIDR instead of classes, this classification still helps explain IPv4 structure.
Why IPv4 Is Still Widely Used
Despite its age, IPv4 remains the dominant protocol on the internet. Understanding what is IPv4 also means understanding why it hasn’t disappeared.
Reasons IPv4 is still popular:
-
Massive existing infrastructure
-
Compatibility with legacy systems
-
Lower transition costs
-
Simpler configuration for many environments
For many organizations, replacing IPv4 entirely is neither quick nor simple.
Limitations of IPv4
One of the biggest challenges when discussing what is IPv4 is address exhaustion.
IPv4 supports approximately 4.3 billion addresses. With billions of devices now connected to the internet, IPv4 addresses have largely run out.
Key IPv4 limitations:
-
Limited address space
-
Increased reliance on NAT
-
Reduced end-to-end connectivity
These limitations led to the development of IPv6.
IPv4 vs IPv6: What’s the Difference?
Understanding IPv4 vs IPv6 is critical for future-ready network planning.
Key differences:
-
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses
-
IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses
-
IPv6 supports virtually unlimited devices
-
IPv6 improves efficiency and security
However, IPv4 remains deeply embedded in global networks, which is why both protocols coexist today.
IPv4 and Network Security
From a cybersecurity perspective, understanding what is IPv4 is vital. Many attacks exploit weaknesses in network configuration rather than the protocol itself.
Common IPv4 security risks:
-
IP spoofing
-
DDoS attacks
-
Misconfigured firewalls
-
Exposed public IPs
Security teams must monitor IPv4 traffic closely and apply layered defenses.
Role of IPv4 in Enterprise Networks
Enterprise environments rely heavily on IPv4 for internal communication, cloud access, and endpoint connectivity.
IPv4 supports:
-
Internal LAN communication
-
VPN connections
-
Firewall and access control rules
-
Log correlation and monitoring
For IT managers, IPv4 knowledge remains essential for daily operations.
How IPv4 Impacts Business Operations
Understanding what is IPv4 goes beyond technical knowledge. It directly affects business continuity and performance.
Business implications include:
-
Network scalability limitations
-
Security exposure
-
ISP dependency
-
Cloud architecture decisions
Executives and founders must account for IPv4 when planning digital growth strategies.
Best Practices for Managing IPv4 Networks
Effective IPv4 management reduces risk and improves reliability.
Actionable best practices:
-
Regularly audit IP address usage
-
Segment networks using subnets
-
Secure public IPv4 addresses
-
Monitor traffic and logs
-
Plan gradual IPv6 adoption
These steps help organizations maintain control while preparing for the future.
The Future of IPv4
Although IPv6 adoption continues to grow, IPv4 is not disappearing anytime soon.
Experts predict:
-
Long-term coexistence of IPv4 and IPv6
-
Continued use in legacy systems
-
Increased IPv4 address trading
Understanding what is IPv4 remains relevant for years to come.
Final Thoughts: Why IPv4 Still Matters
Knowing what is IPv4 is foundational for anyone working with networks, security, or digital infrastructure. IPv4 continues to support the majority of internet traffic despite its limitations.
For IT leaders, cybersecurity professionals, and business decision-makers, IPv4 knowledge supports smarter planning, stronger security, and smoother operations.
Take the Next Step Toward Secure Network Visibility
Understanding IP addressing is only part of protecting your infrastructure. Modern threats require modern visibility and control.
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is IPv4 in simple terms?
IPv4 is a system that assigns unique addresses to devices so they can communicate over the internet or local networks.
2. Why is IPv4 still used today?
IPv4 remains widely used because of existing infrastructure, compatibility, and the cost of migrating fully to IPv6.
3. What does an IPv4 address look like?
An IPv4 address consists of four numbers separated by dots, such as 192.168.1.1.
4. Is IPv4 secure?
IPv4 itself is not insecure, but improper configuration can expose networks to attacks.
5. Will IPv4 be replaced by IPv6?
IPv6 is gradually replacing IPv4, but both protocols will coexist for many years.