What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? The Complete Conversational Guide for 2026
Updated on November 20, 2025, by Xcitium
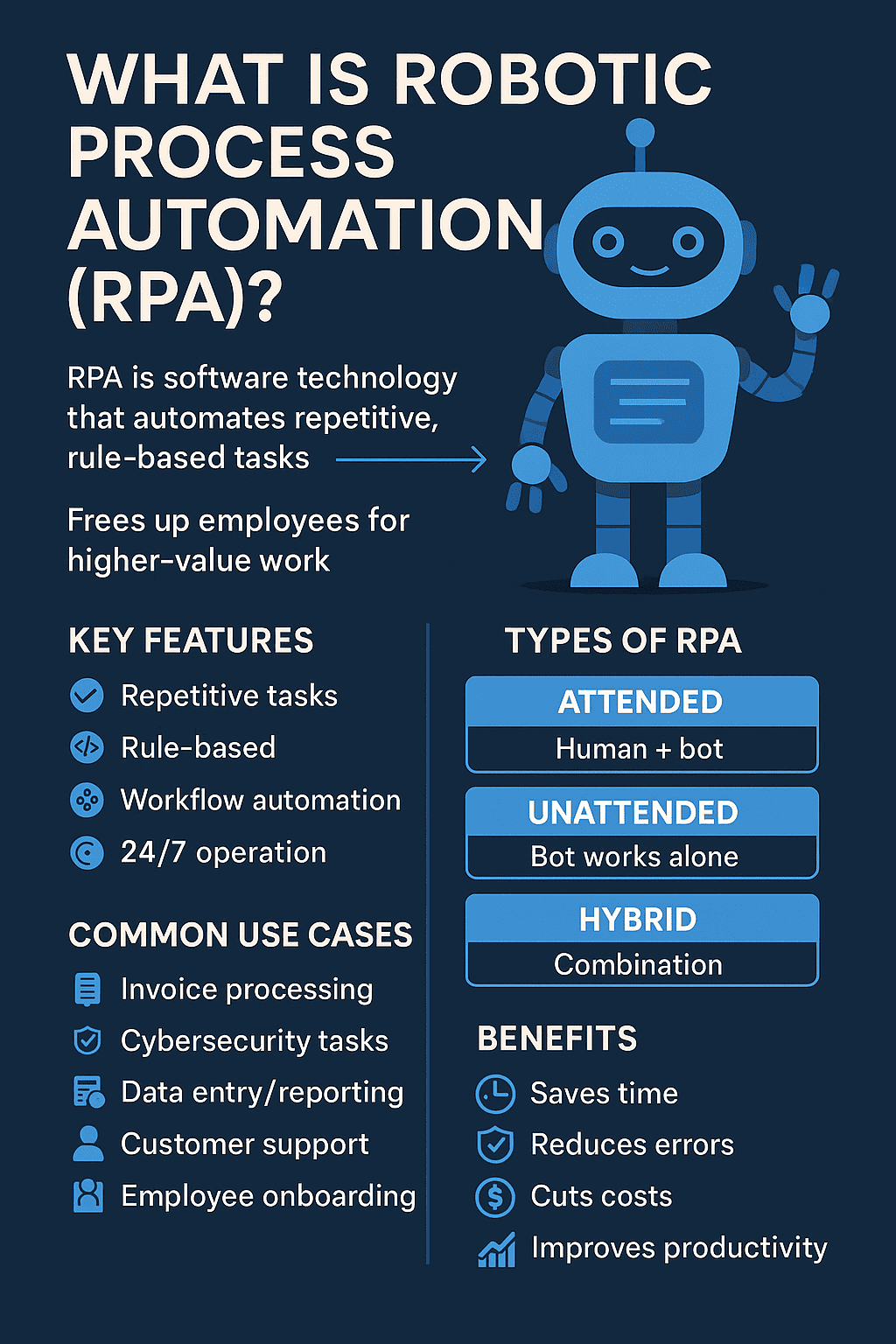
Have you ever wished you could hand off boring, repetitive computer tasks to a robot so you could focus on the work that really matters? Good news — that’s exactly what RPA (Robotic Process Automation) does for businesses today. If you’re wondering what is robotic process automation RPA, how it works, or why so many organizations are adopting it, you’re in the right place.
RPA has become one of the fastest-growing technologies in digital transformation. From finance and healthcare to cybersecurity, IT management, and enterprise operations, RPA bots are taking over repetitive tasks and helping teams work smarter, faster, and more efficiently. In fact, over 70% of global organizations plan to adopt or scale RPA by the end of 2025, proving that automation is no longer a “nice-to-have” — it’s a necessity.
In this in-depth yet conversational guide, we’ll break down exactly what RPA is, why it matters, how it works, and how businesses use it to save time, reduce costs, and eliminate human error.
Let’s dive in.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? (Simple Definition)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots — “bots” — to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that humans normally perform on computers.
Think of RPA bots as digital workers. They don’t look like mechanical robots — instead, they run on your computer or server and perform tasks like:
-
Copying and pasting data
-
Filling out forms
-
Moving files
-
Extracting information
-
Processing transactions
-
Sending emails
-
Reading documents
In simple terms:
👉 RPA automates boring, repetitive tasks so humans can focus on higher-value work.
It’s fast, affordable, and scalable — which is why companies across all industries are adopting it.
⭐ Why RPA Matters for Businesses in 2026
RPA is growing rapidly because modern businesses need:
-
Faster processes
-
Lower operational costs
-
Fewer human errors
-
Stronger compliance
-
More efficient workflows
-
Better customer experiences
Here’s the big reason RPA matters:
✔ It allows your team to work smarter, not harder.
Instead of spending hours on manual tasks, employees can focus on planning, strategy, analysis, and innovation.
RPA helps solve these common problems:
-
Excessive manual data entry
-
Slow processing times
-
Compliance challenges
-
High operational costs
-
Workforce shortages
-
Human errors in repetitive tasks
Today’s organizations need speed and accuracy — and RPA delivers both.
🧩 How RPA Works (Explained Simply)
RPA bots can:
-
Observe how users perform a task
-
Learn the steps
-
Repeat them automatically
-
Run tasks 24/7 without breaks
-
Work across multiple applications
Here’s how it works behind the scenes:
1. The bot records your actions
You perform a task once — like downloading a report or updating a spreadsheet.
2. The bot converts your actions into steps
RPA software uses screen scraping, computer vision, rules, and scripts.
3. The bot repeats the process whenever needed
It runs silently in the background, just like a digital assistant.
4. The bot handles exceptions (or alerts you)
If something goes wrong, it notifies the user.
5. The bot scales easily
You can deploy dozens or hundreds of bots instantly.
RPA can automate simple and complex tasks, depending on the company’s needs.
⭐ Types of Robotic Process Automation
There are three main RPA types:
1. Attended RPA
Bots work alongside humans, triggered by a user.
Example:
A support agent clicks a button and an RPA bot retrieves customer data instantly.
2. Unattended RPA
Bots run completely on their own, often overnight.
Example:
A bot processes invoices every night without human input.
3. Hybrid RPA
Combines attended + unattended bots for large, complex workflows.
Example:
Humans handle exceptions while bots process everything else.
🔍 What Makes a Good RPA Opportunity?
RPA works best for tasks that are:
✔ Repetitive
(Do the same steps every time)
✔ Rule-based
(No human judgment needed)
✔ High-volume
(Frequently performed)
✔ Digital
(Can be done on a computer)
✔ Structured
(Data comes in predictable formats)
Perfect examples include:
-
Processing forms
-
Reconciling payments
-
Sending automated emails
-
Copying data between systems
-
Updating CRM records
-
Onboarding employees
If the task is predictable and repeatable, RPA can do it.
🏢 Common Business Use Cases for RPA
RPA is used across nearly every industry. Here are the most popular applications:
1. Finance & Accounting
-
Invoice processing
-
Accounts receivable
-
Expense approvals
-
Bank reconciliations
2. IT & Cybersecurity
-
Automated alerts
-
Patch validation
-
User account provisioning
-
Security log collection
-
Threat monitoring support
-
Reducing false positives
RPA improves SOC efficiency dramatically.
3. Healthcare
-
Patient data entry
-
Claims processing
-
Appointment scheduling
-
Medical coding
4. Retail & E-commerce
-
Inventory updates
-
Order tracking
-
Customer service automation
5. Human Resources
-
Onboarding/offboarding
-
Payroll
-
Employee data management
6. Manufacturing
-
Compliance reporting
-
Supply chain updates
7. Government
-
Licensing
-
Document verification
-
Benefit processing
Bots make public services faster and more accurate.
RPA and Cybersecurity: A Powerful Combination
You may not realize it, but RPA plays a huge role in cybersecurity.
RPA helps security teams:
✔ Automate threat detection
✔ Respond to incidents faster
✔ Reduce alert fatigue
✔ Collect and analyze logs
✔ Enforce compliance
✔ Patch vulnerabilities
✔ Isolate suspicious activity
RPA bots can even be integrated with:
-
SIEM
-
SOAR
-
EDR (such as Xcitium OpenEDR)
-
Identity management systems
This automation helps cybersecurity teams respond to threats in seconds instead of hours.
🧠 Benefits of RPA (Why Companies Love It)
Let’s look at the biggest advantages:
✔ 1. Saves time
Tasks that used to take hours now take minutes.
✔ 2. Reduces human error
Bots don’t make mistakes — unless humans configure them incorrectly.
✔ 3. Cuts operational costs
Less manual labor = lower expenses.
✔ 4. Increases productivity
Teams work on strategic tasks, not repetitive ones.
✔ 5. Improves compliance
Reports and audit trails are automated.
✔ 6. Boosts accuracy
Bots are 100% consistent.
✔ 7. Scales easily
Need more automation? Just deploy more bots.
✔ 8. Operates 24/7
Bots never take vacations or sick days.
⚠️ Limitations of RPA
RPA is powerful — but not perfect.
Limitations include:
-
Struggles with unstructured data
-
Breaks when user interface changes
-
Requires ongoing management
-
Cannot replace human judgment
-
May fail if rules aren’t clearly defined
For complex tasks, AI automation may be needed alongside RPA.
🛠️ How to Implement RPA in Your Organization (Step-by-Step)
Here’s a simple plan for getting started:
Step 1: Identify automation opportunities
Focus on repetitive, rule-based processes.
Step 2: Choose an RPA platform
Examples include UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, etc.
Step 3: Build automation workflows
Bots are configured using drag-and-drop tools.
Step 4: Test thoroughly
Make sure the bot handles exceptions well.
Step 5: Deploy bots into production
Launch your bots and monitor behavior.
Step 6: Measure performance
Track ROI, time saved, errors reduced.
Step 7: Scale automation
Automate new departments across the organization.
🔍 RPA vs AI: What’s the Difference?
People often confuse the two, but they’re very different.
| Feature | RPA | AI |
|---|---|---|
| Does tasks | ✔ | ✔ |
| Makes decisions | ✖ | ✔ |
| Handles unstructured data | ✖ | ✔ |
| Predicts outcomes | ✖ | ✔ |
| Follows rules | ✔ | ✖ |
RPA = Task automation
AI = Decision-making intelligence
Together, they create Intelligent Automation.
🎯 Conclusion: What Is RPA? A Game-Changer for Businesses
If you’ve been wondering what is robotic process automation RPA, here’s your takeaway:
👉 RPA is software automation that handles repetitive tasks so people can focus on higher-value work.
It boosts productivity, reduces costs, eliminates errors, and supports cybersecurity — all while operating 24/7.
As organizations continue to grow digitally, RPA will become a core tool for operational efficiency and cyber resilience.
🔐 Improve Your Cybersecurity with Xcitium (Free Demo)
Protect your endpoints, automate your security operations, and strengthen your defenses with advanced containment technology.
👉 https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
❓ FAQs About RPA
1. What does RPA stand for?
Robotic Process Automation.
2. Can RPA replace human workers?
Not entirely — it handles repetitive tasks but not strategic decision-making.
3. Is coding required for RPA?
Most platforms offer no-code or low-code tools.
4. Is RPA the same as AI?
No. RPA follows rules, while AI learns and makes decisions.
5. What industries use RPA?
Finance, healthcare, retail, cybersecurity, manufacturing, government, and more.