What Is Casework Management? A Complete Guide
Updated on October 28, 2025, by Xcitium
How do modern organizations efficiently handle complex cases, manage sensitive client data, and ensure that every task gets the attention it deserves? The answer lies in casework management — a structured, technology-driven approach to organizing, tracking, and resolving cases or incidents effectively.
In today’s fast-paced industries — from cybersecurity and IT management to healthcare, law, and finance — understanding what casework management is can transform how teams operate. This system not only improves efficiency but also enhances transparency, accountability, and client satisfaction.
Let’s explore how casework management systems work, their key components, benefits, and why they are essential.
What Is Casework Management?
Casework management refers to the systematic process of handling cases — from initiation to resolution — using defined workflows, documentation, and collaboration tools. A “case” can be any issue, service request, investigation, or incident that requires detailed follow-up and record-keeping.
In business and IT environments, casework management software automates the collection, organization, and tracking of information related to these cases. It allows teams to manage workflows efficiently, communicate effectively, and ensure nothing falls through the cracks.
Example:
-
In cybersecurity, a case might involve investigating a data breach.
-
In HR, it could mean handling an employee grievance.
-
In customer service, it may refer to resolving a client complaint.
Each of these cases involves people, data, and processes — which is precisely what casework management aims to streamline.
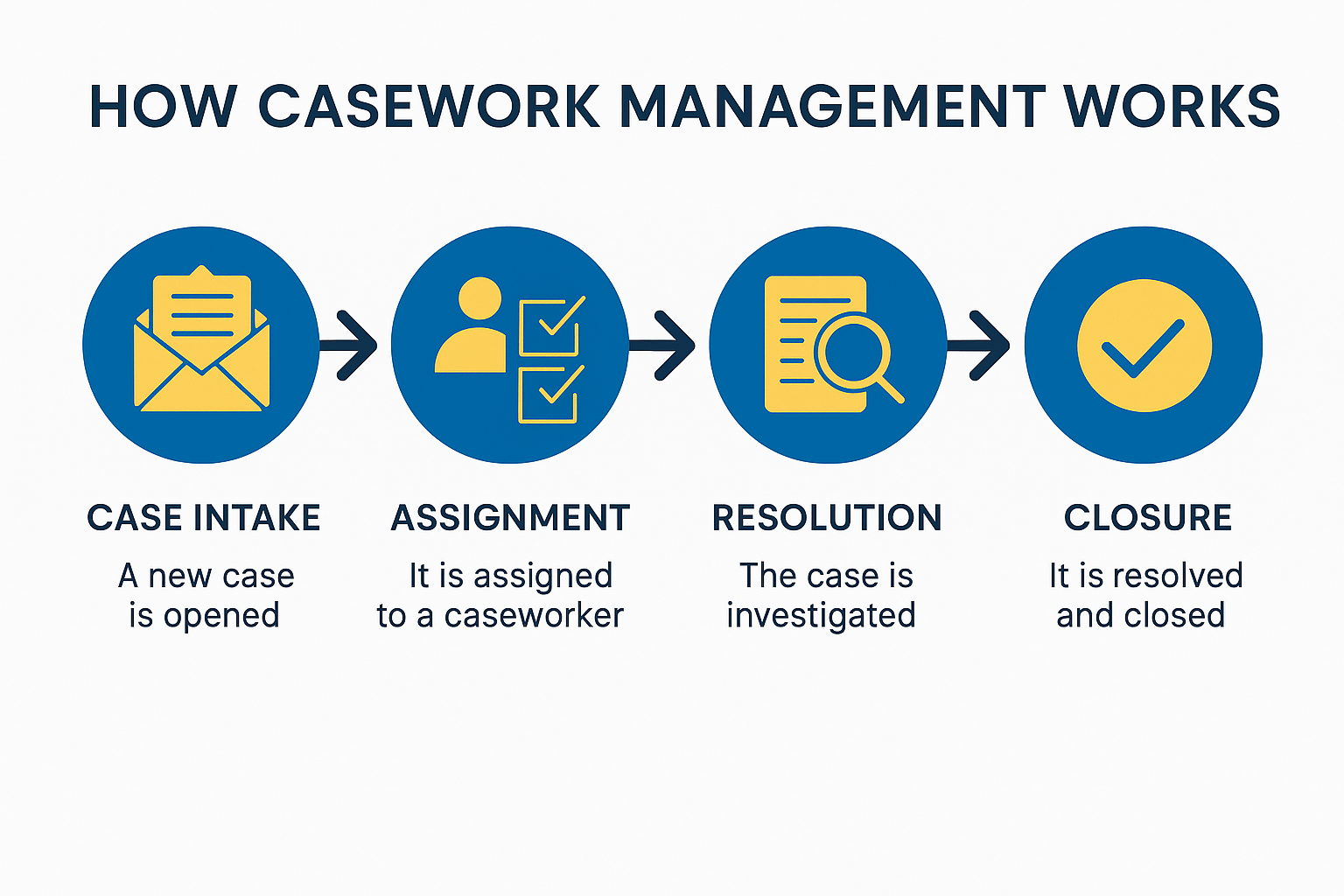
How Casework Management Works
Casework management typically involves five key stages:
-
Case Intake:
The process starts when a new case is opened, whether through a customer portal, email, or automated detection system. -
Case Classification:
The case is categorized (e.g., “Cyber Incident,” “Legal Request,” or “Client Complaint”) and prioritized based on severity or urgency. -
Assignment:
The case is assigned to a responsible team or individual based on expertise, workload, or business rules. -
Investigation & Resolution:
Caseworkers collect evidence, analyze data, collaborate, and take actions to resolve the issue. -
Closure & Reporting:
Once resolved, the case is closed with documentation and audit trails for compliance and performance evaluation.
Each step can be automated through case management software, making the entire process faster, more transparent, and auditable.
Why Casework Management Matters
In a digital-first world, organizations handle massive amounts of information daily. Without structured systems, data silos, miscommunication, and delayed resolutions can occur.
Casework management matters because it helps:
-
Maintain organization and accountability across teams.
-
Ensure compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
-
Enhance data visibility for informed decision-making.
-
Improve client and employee satisfaction through faster responses.
-
Reduce operational inefficiencies and human error.
For cybersecurity and IT departments, strong case management practices can mean the difference between quickly containing a security threat and suffering a full-scale breach.
Key Features of Casework Management Software
Modern casework management tools come equipped with features designed to streamline operations and safeguard sensitive information.
1. Workflow Automation
Automates repetitive tasks such as notifications, follow-ups, and document routing — allowing caseworkers to focus on problem-solving.
2. Centralized Data Repository
All case-related documents, communications, and updates are stored in one secure, searchable system.
3. Role-Based Access Control
Ensures that only authorized personnel can view or modify specific data, crucial for data security and compliance.
4. Real-Time Collaboration
Multiple users can update, track, and comment on cases simultaneously without losing context.
5. Analytics and Reporting
Generates real-time dashboards and reports to monitor performance, identify bottlenecks, and measure resolution times.
6. Integration Capabilities
Integrates with tools like CRM systems, email platforms, and cyber incident response tools for seamless data flow.
Casework Management in Different Industries
While the concept of casework management is universal, its applications vary by sector:
1. Cybersecurity and IT
Used to manage incidents, vulnerabilities, and threat investigations efficiently. Integration with SIEM tools and EDR systems enhances detection and response.
2. Legal and Compliance
Law firms and compliance departments use case management to track cases, manage evidence, and ensure regulatory adherence.
3. Healthcare
Supports patient case tracking, billing disputes, and medical record management with strict privacy standards.
4. Social Services
Helps caseworkers manage client information, appointments, and service delivery documentation.
5. Customer Support
Automates complaint handling, escalations, and feedback tracking for better customer experiences.
Casework Management vs. Workflow Management
| Aspect | Casework Management | Workflow Management |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Individual case resolution | Task or process completion |
| Data Handling | Dynamic and unpredictable | Structured and repetitive |
| Customization | High (tailored per case) | Standardized |
| Collaboration | Team-based | Departmental |
| Example | Handling a cybersecurity incident | Automating invoice approvals |
In short, workflow management handles predictable processes, while casework management deals with dynamic, information-rich situations.
Benefits of Implementing Casework Management
Implementing an efficient casework management system delivers numerous organizational advantages:
-
Improved Efficiency:
Automated routing and tracking minimize delays and reduce manual intervention. -
Enhanced Collaboration:
Real-time updates ensure all stakeholders are on the same page. -
Better Compliance:
Maintains detailed audit trails and version control for regulatory purposes. -
Faster Decision-Making:
Centralized information and analytics help leaders act decisively. -
Higher Customer Satisfaction:
Streamlined workflows lead to faster case resolution and improved service quality. -
Reduced Costs:
By optimizing resources and minimizing errors, organizations save time and money.
Best Practices for Casework Management
To get the most from your casework management system, follow these best practices:
-
Define Clear Case Categories:
Establish standardized classification criteria to ensure consistency. -
Automate Routine Processes:
Use automation for repetitive tasks like notifications and escalations. -
Prioritize Security:
Protect sensitive case data using encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls. -
Monitor KPIs:
Measure metrics such as average resolution time, open vs. closed cases, and SLA compliance. -
Train Your Team:
Provide ongoing training to ensure all users understand the tools and procedures. -
Use AI and Machine Learning:
Integrate smart analytics to predict case outcomes, detect anomalies, and suggest resolutions.
Tools for Effective Casework Management
Several modern solutions can enhance your casework management process:
-
Salesforce Service Cloud – For CRM-driven case tracking.
-
Zendesk – Ideal for customer support case handling.
-
ServiceNow – Used widely for IT service and incident management.
-
Xcitium OpenEDR – A cybersecurity-focused platform that supports case-based incident detection, investigation, and response.
Among these, Xcitium’s OpenEDR stands out for cybersecurity professionals because it automates case detection, correlates threats, and ensures real-time endpoint protection — making it a critical part of your casework management strategy.
The Future of Casework Management
The future of casework management is being shaped by automation, AI, and cloud technology. Expect to see:
-
AI-powered analytics for predictive case resolution.
-
Cloud-based platforms that enable secure remote collaboration.
-
Zero-trust security models integrated into case management systems.
-
Enhanced data visualization through dashboards and machine learning insights.
-
Cross-department integration to unify HR, IT, and compliance workflows.
As organizations continue digital transformation, casework management will become a cornerstone of efficient, secure, and compliant business operations.
Conclusion
Understanding what casework management is helps businesses transform complex, chaotic processes into streamlined, accountable workflows. By centralizing data, automating tasks, and promoting collaboration, casework management systems enable teams to deliver faster, more secure outcomes.
success will depend on how effectively your organization handles sensitive information, ensures transparency, and responds to evolving threats — all of which start with robust case management systems.
👉 Take your next step toward smarter case management.
Try Xcitium to strengthen your cybersecurity case resolution and automation capabilities.
FAQs About Casework Management
1. What is casework management software?
Casework management software is a digital solution that helps organizations track, manage, and resolve cases efficiently through automation, collaboration, and centralized data storage.
2. Who uses casework management systems?
IT teams, cybersecurity professionals, healthcare providers, legal offices, and government agencies all use case management tools for structured, compliant workflows.
3. How does casework management improve security?
By maintaining access controls, encryption, and activity logs, it protects sensitive information and ensures accountability across all users.
4. What’s the difference between case management and project management?
Case management handles individual, dynamic cases, while project management focuses on structured, time-bound projects.
5. Can AI improve casework management?
Yes. AI can automate triaging, predict case outcomes, and identify data patterns — enhancing accuracy and speed in decision-making.