What Is Threatware?
Updated on October 11, 2022, by Xcitium
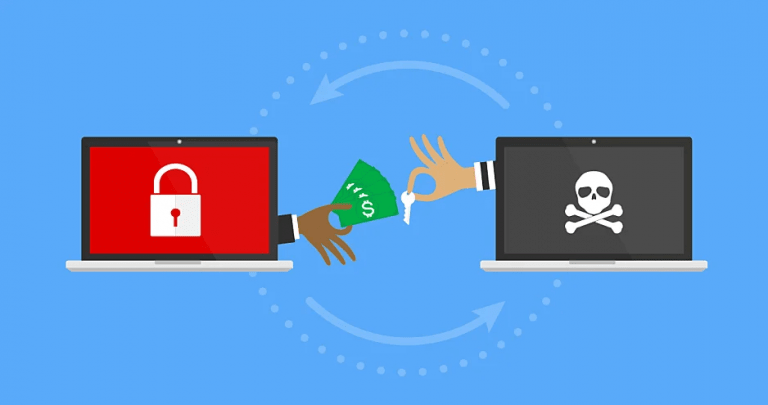
Threatware, spyware, malware, are all terms used to describe malicious codes that harm your computers, steal your information, or hold your computer to a ransom. These malicious codes are spread by cybercriminals with the intent of wreaking havoc to your system. In recent times, ransomware has been in the news as one of the malware that threatens businesses’ growth.
How Does Ransomware Threaten The Growth Of Businesses?
As you may know, ransomware is a type of malware that takes over your computer and sensitive data, encrypts them and prevents you from accessing the files. There are numerous records about ransomware attacks, crippling businesses for over a month before the owners can regain access. Since the first ransomware attack in 1989, more recent attacks have targeted the healthcare industry, finance and other large businesses.
How Ransomware Affects Your Computer
Though attackers develop the codes that harm computers, one might have compromised before the code gets to your computer. Ransomware is spread to computers via phishing scams. The same applies to other threatware. Here is a detailed look at how ransomware and other related malware infects your computer:
Phishing Emails
These are emails sent to your phone with the intent of stealing your information or encrypting your files. These emails are usually deceptive, mimicking your business associates and other service providers. They trick you into opening an infected attachment to carry-out their deeds. You’d prevent any form of malware attacks if you do not open such attachments.
Unsafe Websites
As you probably know, unsafe websites can reveal your information to cybercriminals. However, it’s a bit tricky to identify unsafe websites as cybercriminals create websites with all safety features but with hidden codes to steal or gain access to your data. It’s best not to enter your details on any random website you stumble on to prevent malware attacks.
Cold Calling
This method of phishing scam is also widely used by scammers. It works similarly to email phishing. The criminals will call you, claiming to be one of your service providers or something related to what you do. They’d further ask you to verify an account or update your details via a link sent to you. On doing what they asked, you are in—for the attack. So it’s best to always verify calls or messages from your service providers before you take the requested action.
Websites Pop-Ups
You may have noticed that some websites display a pop-up when you navigate through their pages. Most notifications will ask you to subscribe to a service, email list, updates, etc. Attackers also use this method to carry out their deeds. Mostly, they will display a deceitful pop up asking you to update software on your computer or sign up for a promotional offer. If you’re not sure of a website, do not be hasty in clinking links. Try to verify the site before you do anything that might open you up for malware attacks.
Preventing Threatware Attacks
Cybersecurity can help you avoid any form of malware attacks. Here are some basic cybersecurity tips that can help you:
Keep Your System Updated
Your computer runs an operating system, as well as various applications. These applications are updated from time to time by the developers, and you need to ensure you update as new updates are available. Most new updates are intended to patch security loopholes, so ensure you update to protect attackers from taking advantage of the outdated software to your detriment.
Do Not Use Weak Passwords
Examples of weak passwords are your name, date of birth, or common words. These kinds of passwords can be easily guessed, so avoid using them. A strong password is a combination of upper and lower case letters with numbers and symbols. This can help you prevent common malware attacks.
Get An Active Antivirus
Antiviruses can help repel common malware attacks. You should get a premium antivirus with all features and ensure you keep the software updated.
Use Advanced Endpoint Protection (AEP)
Fileless and other sophisticated malware do bypass antiviruses no matter how active. You need advanced endpoint protection to block superior threat ware such as ransomware. AEP uses the most sophisticated security technology to detect and rid stubborn malware.
Final Thoughts
Malware attacks can harm your businesses or personal data, and you don’t want to experience that. Protecting your computer from attacks is the best thing to do. Do not rely only on the traditional security systems as some malware can bypass them. Advanced Endpoint Protection can help you combat notorious malware.


 (4 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5, rated)
(4 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5, rated)