What Does AGI Stand For? A Complete Guide for Business and Technology Leaders
Updated on January 7, 2026, by Xcitium
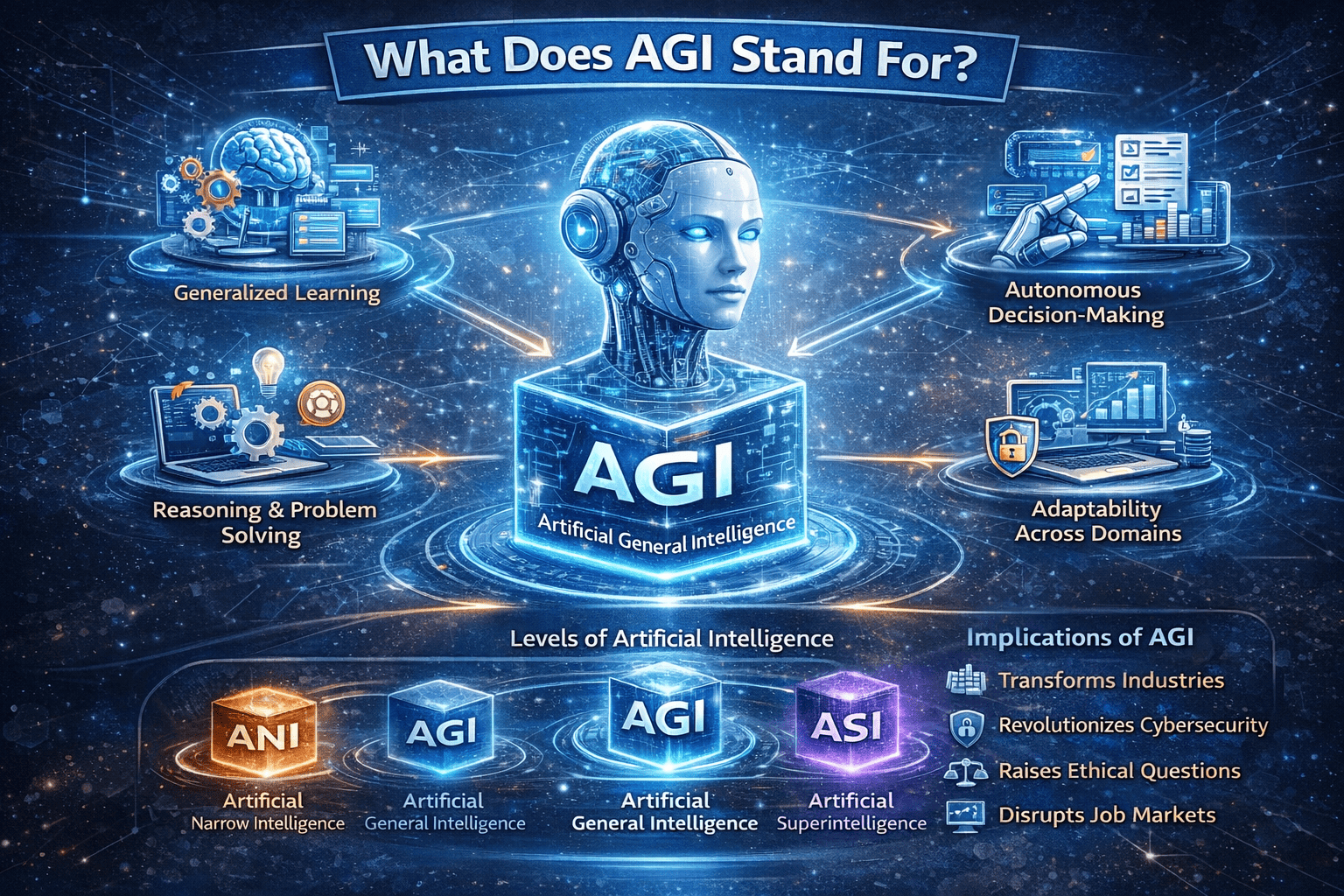
Artificial intelligence is transforming how businesses operate, but many professionals still ask a fundamental question: what does AGI stand for? While AI tools are already automating tasks and improving efficiency, AGI represents a far more powerful and disruptive concept. Understanding AGI is critical for cybersecurity leaders, IT managers, CEOs, and founders planning for the future.
In this guide, we’ll explore what AGI stands for, how it differs from today’s AI, why it matters for security and business strategy, and what organizations should prepare for next.
What Does AGI Stand For?
What does AGI stand for? AGI stands for Artificial General Intelligence. It refers to a type of artificial intelligence capable of understanding, learning, and performing any intellectual task that a human can do.
Unlike narrow AI systems that are trained for specific functions, AGI is designed to generalize knowledge across multiple domains. This means AGI could reason, plan, adapt, and solve unfamiliar problems without being explicitly programmed for each task.
In simple terms, AGI aims to match—or potentially exceed—human cognitive abilities.
Why Understanding What AGI Stands For Matters
Understanding what does AGI stand for is no longer just an academic question. AGI has major implications for cybersecurity, business operations, risk management, and long-term innovation.
AGI matters because it could:
-
Transform decision-making processes
-
Automate complex business functions
-
Redefine cybersecurity threats and defenses
-
Accelerate innovation across industries
-
Introduce new ethical and regulatory challenges
For executives and IT leaders, AGI represents both opportunity and risk.
AGI vs AI: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse AGI with artificial intelligence in general. However, there are important distinctions.
Narrow AI (ANI)
Most AI systems today fall under Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI). These systems perform specific tasks, such as image recognition, fraud detection, or language translation.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI goes far beyond narrow AI. When asking what does AGI stand for, it’s important to note that AGI can:
-
Learn new tasks without retraining
-
Apply reasoning across different domains
-
Adapt to unfamiliar environments
-
Understand context like a human
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
ASI refers to intelligence that surpasses human capabilities. While AGI matches human intelligence, ASI exceeds it.
Key Characteristics of Artificial General Intelligence
To fully understand what does AGI stand for, it helps to examine its defining characteristics.
Core Traits of AGI:
-
Generalized learning across domains
-
Reasoning and problem-solving abilities
-
Autonomous decision-making
-
Contextual understanding
-
Self-improvement capabilities
These traits distinguish AGI from today’s task-focused AI systems.
How AGI Could Impact Cybersecurity
AGI has profound implications for cybersecurity—both defensive and offensive.
Defensive Security Benefits
AGI could:
-
Detect advanced threats faster
-
Predict cyberattacks before they occur
-
Automate complex incident responses
-
Adapt defenses in real time
Understanding what does AGI stand for helps security leaders prepare for AI-driven defense systems.
Potential Security Risks
At the same time, AGI could be exploited by attackers to:
-
Automate sophisticated cyberattacks
-
Discover vulnerabilities faster
-
Bypass traditional security controls
-
Scale social engineering campaigns
This dual-use nature makes AGI a critical cybersecurity concern.
AGI and Business Strategy
For CEOs and founders, understanding what does AGI stand for is essential for long-term planning.
AGI could reshape business strategy by:
-
Automating knowledge-based work
-
Improving strategic forecasting
-
Reducing operational inefficiencies
-
Enabling smarter decision-making
Organizations that understand AGI early will be better positioned to adapt and compete.
AGI Use Cases Across Industries
While AGI does not yet exist, potential applications span every industry.
Examples Include:
-
Cybersecurity: Autonomous threat hunting
-
Finance: Advanced risk modeling
-
Healthcare: Personalized treatment planning
-
Manufacturing: End-to-end optimization
-
IT Operations: Fully autonomous infrastructure management
Understanding what does AGI stand for helps leaders anticipate how their industries may change.
Is AGI Already Here?
A common question is whether AGI already exists. The short answer is no.
While modern AI systems are impressive, they lack:
-
True reasoning across domains
-
Independent goal formation
-
Human-level understanding
Today’s systems are still narrow AI. However, progress toward AGI continues rapidly.
Ethical and Regulatory Concerns Around AGI
As organizations explore what does AGI stand for, ethical considerations become unavoidable.
Key Ethical Challenges:
-
Decision transparency
-
Bias and fairness
-
Accountability
-
Job displacement
-
Security misuse
Governments and regulatory bodies are beginning to address AGI governance, but frameworks remain immature.
AGI and the Future of Work
AGI could dramatically change how work is performed.
Potential Workforce Impacts:
-
Automation of cognitive tasks
-
Shift toward strategic and creative roles
-
Increased demand for AI oversight
-
New cybersecurity job categories
Understanding what does AGI stand for helps organizations prepare workforce transition strategies.
AGI vs Machine Learning and Deep Learning
AGI builds upon—but is not the same as—machine learning and deep learning.
| Technology | Scope | Adaptability |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Task-specific | Limited |
| Deep Learning | Pattern recognition | Moderate |
| AGI | General intelligence | High |
AGI integrates multiple AI approaches into a unified intelligence system.
AGI and Zero Trust Security Models
Zero Trust assumes no user or system is trusted by default. AGI could enhance Zero Trust by continuously assessing risk and context.
AGI-driven Zero Trust could:
-
Adapt access policies in real time
-
Detect insider threats faster
-
Reduce manual policy management
Understanding what does AGI stand for highlights its relevance to modern security frameworks.
How IT Managers Should Prepare for AGI
IT managers should begin preparing for AGI now, even if full AGI adoption is years away.
Actionable Preparation Steps:
-
Invest in AI literacy and training
-
Strengthen data governance
-
Modernize security architecture
-
Adopt automation responsibly
-
Monitor emerging AI regulations
Preparation reduces risk and accelerates adoption when AGI becomes viable.
Common Misconceptions About AGI
Understanding what does AGI stand for also means debunking myths.
Common Myths:
-
AGI is the same as current AI tools
-
AGI will replace all jobs overnight
-
AGI is science fiction
-
AGI will be uncontrollable
In reality, AGI development is gradual and heavily researched.
AGI and Risk Management
AGI introduces new risk categories that businesses must address.
Risk Areas Include:
-
Security misuse
-
Compliance challenges
-
Ethical violations
-
Operational dependency
-
Strategic misalignment
Proactive risk management frameworks are essential.
The Timeline for AGI Development
Experts disagree on when AGI will emerge. Estimates range from decades to sooner than expected.
What matters more than timing is readiness. Understanding what does AGI stand for allows organizations to adapt regardless of timeline.
Best Practices for Businesses Exploring AGI
Organizations should approach AGI strategically.
Best Practices:
-
Focus on governance first
-
Align AGI goals with business outcomes
-
Prioritize security and compliance
-
Start with controlled AI implementations
-
Monitor global AI developments
Responsible adoption is key to long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does AGI stand for?
AGI stands for Artificial General Intelligence, a form of AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can.
2. How is AGI different from AI?
AGI has general reasoning and learning abilities, while most AI today is task-specific.
3. Is AGI dangerous?
AGI can pose risks if misused, which is why governance, security, and ethics are critical.
4. Will AGI replace jobs?
AGI may automate some roles, but it will also create new opportunities and job categories.
5. When will AGI be available?
There is no confirmed timeline, but research and development are accelerating.
Final Thoughts: Why AGI Matters Now
Understanding what does AGI stand for is essential for modern business and technology leaders. AGI represents a shift from task automation to true machine intelligence. While it offers incredible opportunities, it also introduces new risks that require preparation, governance, and advanced security strategies.
Organizations that begin planning today will be best positioned to thrive tomorrow.
👉 See how advanced security solutions prepare organizations for AI-driven threats:
Request a demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/