Show Folder Size Linux: The Complete 2026 Guide for Professionals, IT Teams & Cybersecurity Experts
Updated on November 26, 2025, by Xcitium
Managing storage is a critical part of system administration, especially in environments where performance, compliance, and security all depend on clean and optimized file systems. Whether you’re troubleshooting a server running out of space, analyzing logs, monitoring user directories, or performing regular maintenance, knowing how to show folder size in Linux is essential.
Linux gives users incredibly powerful tools to check directory sizes—from the classic du command to interactive tools like ncdu, and even graphical file explorers. In this guide, we cover multiple ways to view folder size in Linux, including commands, flags, utilities, GUI methods, and best practices for storage management. This article is crafted for cybersecurity teams, IT managers, DevOps professionals, and anyone maintaining Linux systems.
Why Knowing Folder Sizes Matters in Linu
Before jumping into commands, let’s look at why this skill is so important in Linux system administration.
1. Prevent Servers from Running Out of Space
A full disk can cause:
-
Application crashes
-
Inability to write logs
-
Failed system updates
-
Security scanning failures
2. Identify Large Directories
This is critical when cleaning up space, especially:
-
Log folders
-
Cache folders
-
Backup directories
-
Database storage
3. Support Cybersecurity & Compliance
Oversized logs or growing suspicious files may point to:
-
Intrusion attempts
-
Malware activity
-
Misconfigurations
-
Unwanted data growth
4. Improve System Performance
File-heavy systems with limited storage can slow down significantly.
5. Support DevOps Pipeline Optimization
Build pipelines and container systems require tight storage control.
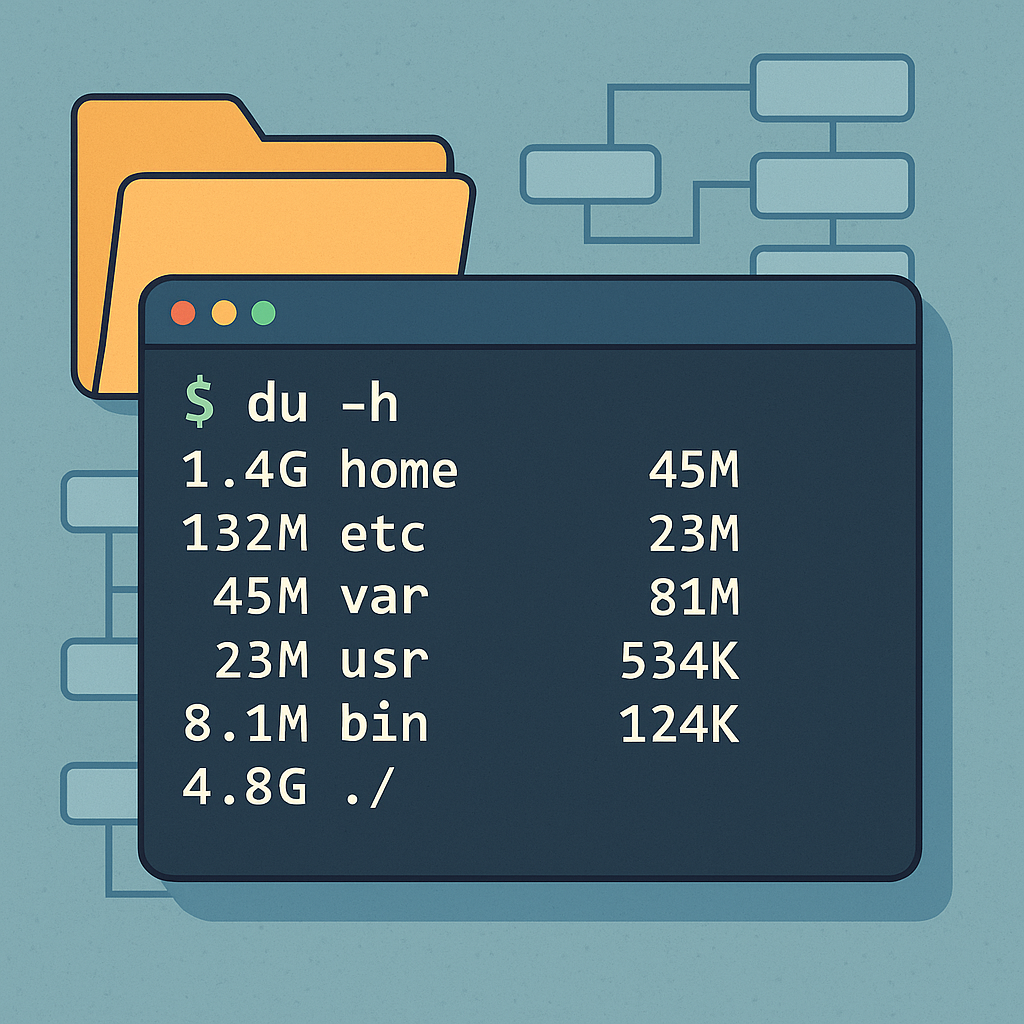
How to Show Folder Size in Linux Using the du Command
The most commonly used tool for showing folder size in Linux is the du (Disk Usage) command.
🧰 Basic du Command Syntax
1. Show Folder Size in Human-Readable Format
Use the -h flag to display sizes in KB, MB, GB:
This gives you the size of each subdirectory.
2. Show Total Folder Size Only
If you only want the final size of the folder:
Flags explanation:
-
-s= summarize -
-h= human-readable
3. Show Size of All Folders in Current Directory
This is extremely useful for identifying which directories are large.
4. Show Size of a Specific Directory
Example:
5. Show Folder Size Sorted by Size
Combine du with sort:
This gives a list sorted from smallest to largest.
Or reverse:
6. Show Folder Size Including Hidden Files
7. Display Size in Block Format
-
-k= show size in KB -
Replace with
-mfor MB
Understanding du Output
If you run:
You might see:
The last line usually shows the total size of the directory.
📦 Using ncdu: A Better, Interactive Way to Show Folder Size
ncdu stands for NCurses Disk Usage, and it is one of the best tools for quickly and interactively analyzing disk usage.
1. Install ncdu
Ubuntu/Debian:
CentOS/RHEL:
Fedora:
2. Run ncdu
To scan the current directory:
To scan a specific folder:
Why ncdu is Popular
-
Interactive interface
-
Easy browsing
-
Delete files safely
-
Sort by size
-
Fast scanning
-
Great for large servers
📁 Using ls to Show File Sizes (Not Folders)
While ls cannot show folder sizes, it can display file sizes.
Show File Sizes in Human-Readable Format
Show File Sizes Sorted by Size
This helps when diagnosing problems inside a folder.
📊 Using du with Wildcards and Filters
Show All Folders Larger Than 1GB
Excluding Certain Folders
Show Only Folders (Exclude Files)
💻 Show Folder Size in Linux with Graphical Tools
If you’re using a Linux desktop environment like GNOME or KDE, you can view folder sizes visually.
1. GNOME Disk Usage Analyzer (baobab)
Install:
Then launch:
-
Activities → Disk Usage Analyzer
-
Or run
baobab
Features:
-
Sunburst graphs
-
Treemap views
-
Visual folder size mapping
-
Easy troubleshooting
2. KDE Filelight
Install:
Features:
-
Beautiful radial charts
-
Great for large directories
-
Interactive navigation
🧹 Best Practices for Managing Folder Sizes in Linux
Keeping Linux storage under control is a long-term challenge. Here are practical tips:
1. Monitor /var/log Regularly
Run:
Large logs may indicate errors or attacks.
2. Clean up apt cache
3. Remove old kernels (Debian/Ubuntu)
4. Delete old Docker data
5. Analyze large user directories
6. Check mail folders on servers
7. Automate scanning with cron
Example script:
Schedule via crontab.
🛠️ Troubleshooting Folder Size Issues
Issue: du Takes Too Long
Fix:
Issue: Hidden folders not counted
Fix:
Issue: Disk full even after deleting files
Cause: Deleted files still held by running processes.
Check:
Restart services if needed.
❓ FAQ — Show Folder Size Linux
1. What is the best command to show folder size in Linux?
du -sh foldername is the fastest and most reliable method.
2. How do I see a list of all folder sizes?
Use:
3. How can I show folder size with a GUI?
Use tools like Baobab or Filelight.
4. What is the difference between du and df?
-
du= folder and file sizes -
df= filesystem-level disk space
5. Why is my folder size different from file size total?
Linux uses block allocation, causing slight variations.
Final Thoughts: Linux Makes Disk Analysis Simple — If You Know the Right Tools
Knowing how to show folder size in Linux is a foundational skill for system administrators, DevOps engineers, IT teams, cybersecurity professionals, and developers. With du, ncdu, and GUI tools, you can easily manage disk usage, detect anomalies, optimize performance, and secure your Linux systems.
🚀 Strengthen Your Endpoint & Server Security
Combine strong Linux administration with best-in-class Zero-Trust protection.
👉 Request a Free Demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/