How to Set Your Default Search Engine in Chrome: The Complete 2026 Guide for IT Teams, Cybersecurity Leaders & Business Users
Updated on November 24, 2025, by Xcitium
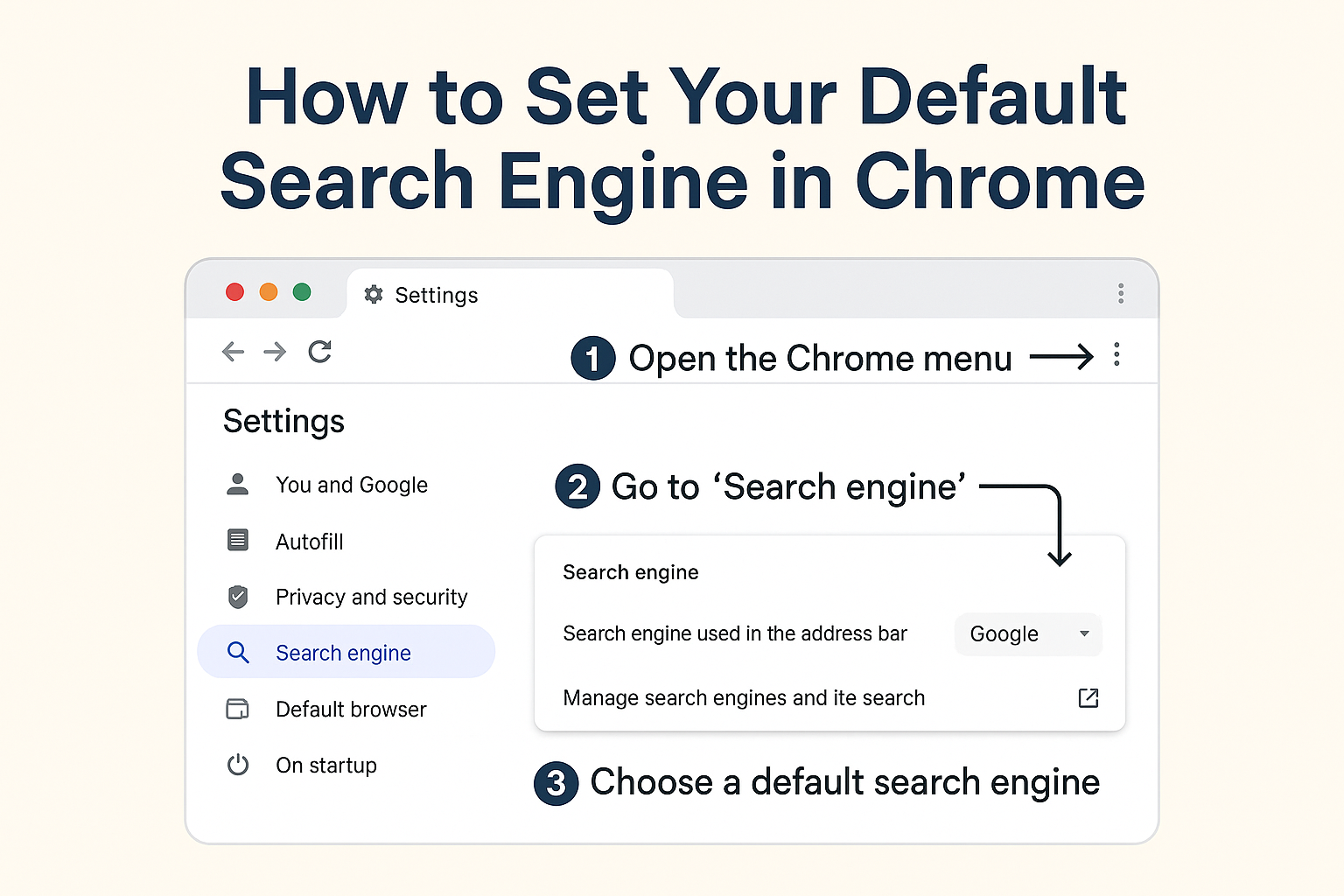
Have you ever opened Chrome, started typing a query, and realized the search wasn’t done by your preferred search engine? Whether you’re in IT, cybersecurity, or leadership, knowing how to set your default search engine in Chrome is more important than ever—especially now that search engines tie directly into privacy, security, and productivity.
In fact, 89% of employees rely on Chrome daily—and misconfigured search settings can lead to data leaks, unwanted tracking, or security vulnerabilities. This comprehensive guide walks you through how to change the default search engine, secure Chrome settings for enterprise use, and apply best practices across teams.
Why Changing Your Default Search Engine Matters
Choosing a default search engine isn’t just a convenience—it’s a security decision.
For IT teams, a misconfigured search engine can introduce:
-
Data tracking by unwanted providers
-
Exposure through malicious redirect malware
-
Reduced employee productivity
-
Privacy or compliance violations
Companies in regulated industries (finance, healthcare, legal, government) often standardize search engines to meet compliance needs.
That’s why understanding how to set your default search engine in Chrome is essential for both cybersecurity and workflow optimization.
How to Set Your Default Search Engine in Chrome (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Open Google Chrome
Start Chrome on your device (Windows, macOS, Linux, or ChromeOS).
Step 2: Go to Chrome Settings
Click the vertical three dots (⋮) at the top-right corner.
Select:
Settings → Search Engine
Step 3: Choose Your Default Search Engine
Under Search engine used in the address bar, select from the built-in list:
-
Google
-
Bing
-
DuckDuckGo
-
Yahoo
-
Ecosia
Chrome automatically saves your selection.
Step 4: Manage Search Engines (Advanced)
For full control, click:
Manage search engines and site search
Here you can:
-
Delete unwanted search engines
-
Add a custom search engine
-
Set a new default provider
-
Remove hijacked or malicious entries
Step 5: Adding a Custom Search Engine
This is important for enterprise or internal search tools.
Click Add → Fill in fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Search engine | Your preferred name |
| Shortcut | Alias you want to use |
| URL | Search URL with %s as query placeholder |
Example for DuckDuckGo:https://duckduckgo.com/?q=%s
Step 6: Remove Malicious Search Engines
If your search keeps redirecting unexpectedly, remove suspicious ones.
Click the three dots next to the unwanted engine → Delete
(Tip: Redirect malware often creates engines with random names.)
Quick Summary: Default Search Engine Setup
-
Open Chrome
-
Settings → Search Engine
-
Choose a default
-
Manage engines for deeper control
-
Remove unknown or malicious entries
These steps are essential for mastering how to set your default search engine in Chrome safely and effectively.
How Browser Search Engine Settings Affect Cybersecurity
Most users think search engine preferences only affect convenience. But security experts know otherwise.
Here’s why Chrome search configuration matters:
1. Search Hijacking Malware
Malware can silently modify Chrome’s default search engine.
Attackers use this to:
-
Redirect users to ad-filled pages
-
Inject malicious scripts
-
Track search behavior
-
Capture personal or business data
Regularly check your search settings to ensure integrity.
2. Privacy Compliance Requirements
Industries like healthcare, government, and finance require strict data handling.
Using privacy-focused engines (DuckDuckGo, Brave Search) helps:
-
Minimize user tracking
-
Reduce data collection
-
Lower compliance risks
3. Enterprise Search Standardization
Organizations often standardize on:
-
Google for productivity
-
Bing for Microsoft ecosystems
-
DuckDuckGo for privacy policies
Knowing how to set your default search engine in Chrome ensures consistency across devices.
4. Reducing Employee Risk
A secure search engine prevents:
-
Clicks to malicious links
-
Exposure to spammy results
-
Redirection to counterfeit sites
-
Credential theft attempts
Security begins at the browser level.
Advanced Chrome Search Settings for IT & Cybersecurity
Below are optional—but powerful—settings for managing search engines across teams.
1. Enforce Search Engine via Group Policy (Windows)
Using GPO:
Navigate to:Administrative Templates → Google → Google Chrome → Default search provider
You can enforce:
-
Search engine
-
Search URL
-
Suggestion URL
-
Query format
This ensures standardization.
2. Using Chrome Enterprise Cloud Management
For organizations using Chrome Enterprise:
You can remotely control:
-
Default search engine
-
Allowed search providers
-
Browser policies
-
Security configurations
Perfect for remote and hybrid teams.
3. Prevent Users From Changing Search Settings
Admins can lock search engine settings to prevent:
-
Hijacking
-
Employee misconfiguration
-
Privacy risks
Available via Google Workspace Admin Console.
4. Detecting Search Engine Hijacking
Symptoms include:
-
Redirecting to unknown search pages
-
Pop-up ads in search
-
New “default engines” appearing
-
Loss of control of Chrome settings
Tools like Xcitium Endpoint Security, EDR, and Zero-Trust isolation can detect and prevent browser hijacking attacks.
Troubleshooting Chrome Search Engine Problems
If Chrome is not letting you change the default search engine, here’s what you can do:
Fix 1: Remove Malicious Extensions
Go to:chrome://extensions/
Disable or remove suspicious extensions.
Fix 2: Reset Chrome Settings
Go to:
Settings → Reset and clean up → Restore settings to their original defaults
Fix 3: Run Chrome Cleanup Tool
Chrome automatically scans for harmful software.
Fix 4: Reset Search Engine to Default
Follow earlier steps to re-select Google or your preferred provider.
Fix 5: Update Chrome
Outdated browsers may lock configuration settings.
Fix 6: Scan for Malware
Cybersecurity teams should run:
-
EDR tools
-
AV scans
-
Browser hijack detection
Where to Place Your Cybersecurity Image in This Article
Your chosen image has a cybersecurity theme, making it perfect for these sections:
✔ “How Browser Search Engine Settings Affect Cybersecurity”
✔ “Search Hijacking Malware”
✔ “Protecting Personal Information While Browsing”
✔ “Enterprise Security Practices”
This ensures SEO alignment and relevance.
Best Practices for Secure Chrome Search Usage
To prevent security issues when managing Chrome search configurations:
1. Use a Trusted Search Engine
Avoid unknown providers.
2. Disable Unnecessary Extensions
Each extension adds risk.
3. Keep Chrome Updated
New versions patch vulnerabilities.
4. Enable Safe Browsing
Chrome offers standard and enhanced protections.
5. Use Endpoint Detection Tools
Prevents hijacking and malware modifications.
6. Educate Employees
Training reduces accidental exposure.
Benefits of Customizing Your Default Search Engine
✔ Faster workflows
✔ Better data privacy
✔ Improved cybersecurity posture
✔ Reduced distractions
✔ Standardization across teams
✔ Optimized search results for your business niche
Mastering how to set your default search engine in Chrome unlocks all these advantages.
FAQ Section
1. Why does my Chrome default search engine keep changing?
You may have a malicious extension, browser hijacker, or unwanted software altering settings.
2. Can I force Chrome to always use one search engine?
Yes. IT admins can enforce policies using Google Admin Console or Group Policy.
3. What search engine is best for security?
DuckDuckGo, Brave Search, and StartPage are top choices for privacy.
4. Can malware modify my search engine?
Yes. Browser hijackers often alter default search providers to redirect traffic.
5. Does changing the search engine affect performance?
No, but it may improve search speed and privacy depending on provider.
Final Thoughts: Make Chrome Work the Way You Need It To
Understanding how to set your default search engine in Chrome is not only about convenience—it’s about user safety, productivity, and data protection. For organizations, controlling search settings strengthens compliance, prevents malware redirection, and keeps browsing secure.
Whether you’re an IT manager optimizing endpoint configurations or a cybersecurity professional hardening browsers, mastering Chrome’s search engine settings is essential in 2025.
🚀 Strengthen Your Browser Security Infrastructure Today
Take the next step toward securing your organization’s endpoints.
👉 Request a Demo: https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/