What Is IoT Network? Definition, Examples & Use Cases
Updated on July 18, 2025, by Xcitium
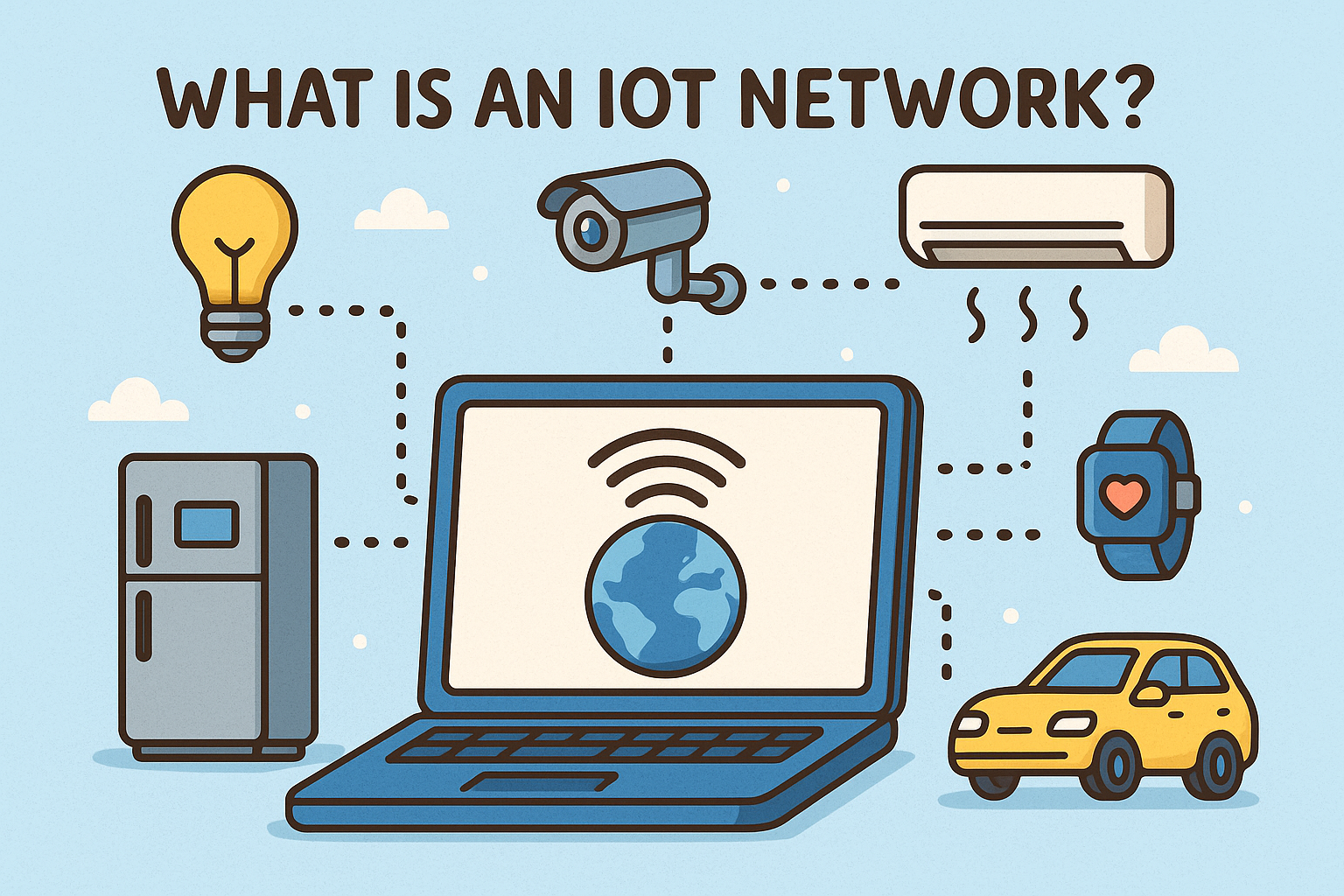
Ever wondered what is IoT network and why it’s transforming business and industry? Today, over 10 billion devices are online, communicating through IoT networks—fueling smart cities, factories, and homes. Understanding these networks is essential for IT managers, cybersecurity leaders, and CEOs looking to harness opportunity while ensuring security.
What Is IoT Network?
What is IoT network? In simple terms, an IoT (Internet of Things) network connects everyday sensors and devices—like thermostats, security cameras, and industrial robots—to the internet and each other. These networks enable smart automation, data analytics, and system-wide efficiency. As IoT adoption grows across industries, knowing what is IoT network used for and how it works is vital for executives, IT pros, and security teams aiming to implement and protect connected systems.
IoT Network — Basic Definition
An IoT network is a digital ecosystem where interconnected devices communicate via network protocols. These include:
- Sensors & actuators – hardware that collects and responds to environmental data
- Gateways – bridge devices from sensor to cloud
- Cloud/server platforms – where data processing and AI happen
Together, they form a seamless flow of data and action.
What Is IoT Network With Example
What is IoT network with example? Consider a smart factory:
- Temperature sensors in machines
- Conveyor belt motor actuators
- Central gateway relaying to cloud
- Cloud runs analytics, triggers alerts
This illustrates IoT definition and examples in real-world industrial deployment.
IoT Network in Computer Network
Networking Protocols
IoT devices use:
- Wi‑Fi and Ethernet (local, high bandwidth)
- Bluetooth and Zigbee (short-range, low energy)
- LoRaWAN and NB-IoT (long-distance, low power)
Edge vs. Cloud
Some data is processed locally on gateways (edge), while heavier tasks occur in the cloud.
What Is IoT Network and How It Works
Step‑By‑Step Data Flow
- Sensor captures data (e.g., temperature)
- Gateway transmits securely over encrypted channels
- Cloud platform analyzes and stores data
- Response commands sent back to actuators
Security & Management
Strong authentication, WPA3/WPA2 encryption, and OTA updates defend against data breaches and IoT-specific threats.
What Is IoT Network Used For – Key Applications
IoT networks drive major transformations:
- Smart Cities: traffic sensors, adaptive street lighting
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): predictive maintenance on machinery
- Healthcare: remote patient health trackers
- Retail: smart inventory and energy-efficient stores
- Agriculture: automated irrigation and crop monitoring
Challenges & Best Practices
Common Problems
- Limited processing power on endpoints
- Fragmented communication protocols
- Security vulnerabilities on IoT devices
Best Practices
- Standardize protocols and device management
- Adopt zero-trust, micro-segmentation, and network monitoring
- Ensure secure over-the-air firmware updates
Conclusion & CTA
Understanding what is IoT network empowers organizations to drive innovation—while managing risk. From smart manufacturing to remote monitoring, IoT connectedness transforms how industries operate. Ready to secure your IoT deployments and protect your data? Request a demo with Xcitium today!
🔍 FAQ
Q1: What is IoT network explain with example?
An IoT network is a system of connected devices exchanging data—for instance, smart home devices interacting via Wi‑Fi and cloud platforms to automate tasks.
Q2: What is IoT network in computer network?
It’s a specialized network where low-power, interoperable devices communicate with back-end servers using various protocols like MQTT or CoAP.
Q3: What is IoT network used for?
Use cases range from smart cities and agriculture monitoring to industrial automation and healthcare telemetry.
Q4: IoT definition and examples?
IoT refers to the internet connectivity of physical devices. Examples include smart speakers, health trackers, and industrial sensors.
Q5: What are common security issues in IoT networks?
IoT networks often suffer from weak authentication, outdated firmware, and unsecured protocols—making them vulnerable to attacks.