What Is a Reverse Proxy? A Complete Guide for Modern Cybersecurity
Updated on January 20, 2026, by Xcitium
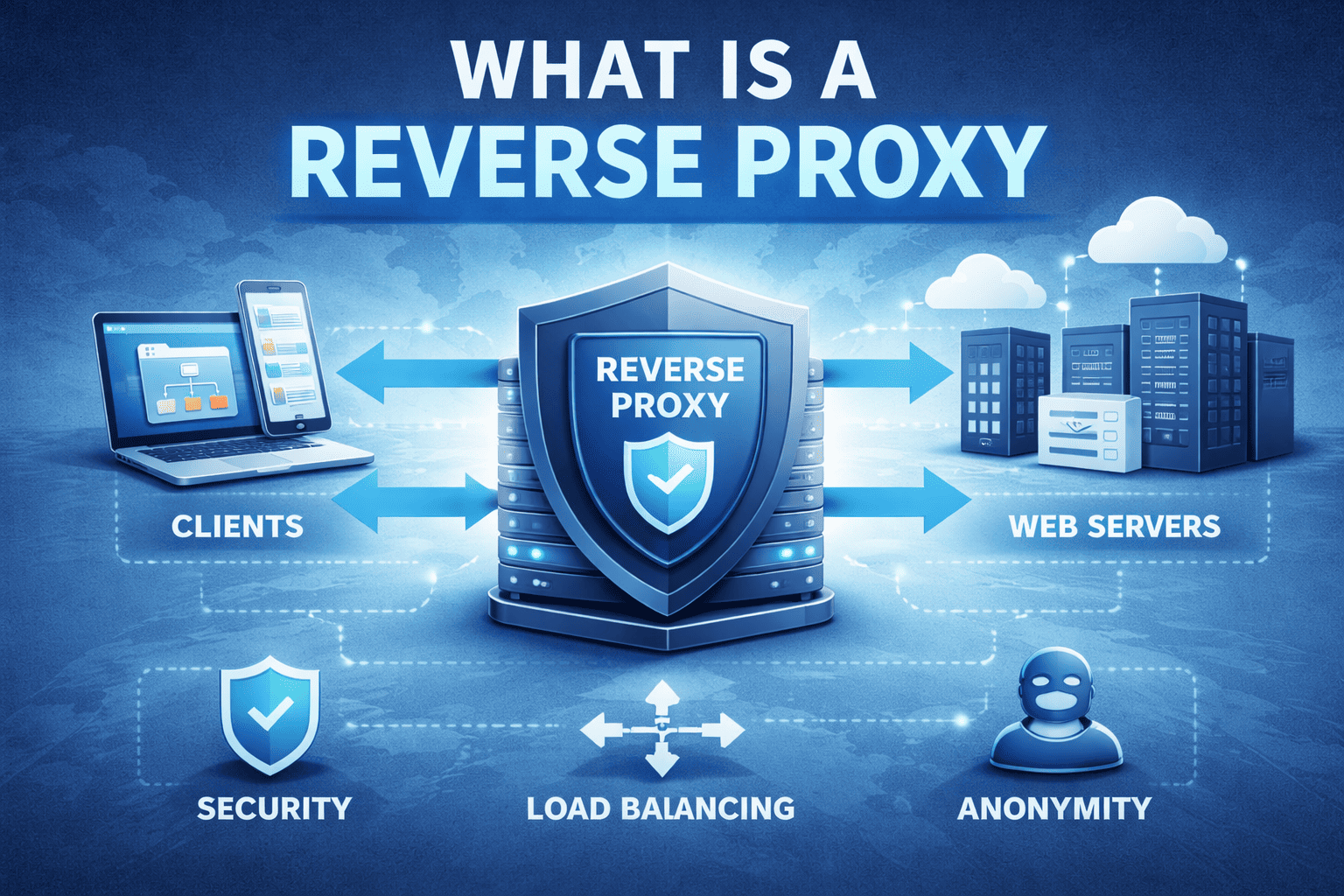
Have you ever wondered how large websites stay fast, secure, and available even during massive traffic spikes or cyberattacks? The answer often lies behind the scenes. If you’re asking what is a reverse proxy, you’re exploring one of the most important components of modern web infrastructure and cybersecurity.
A reverse proxy sits between users and backend servers, managing traffic, improving performance, and adding a powerful security layer. For IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, and business leaders, understanding reverse proxies is critical for building resilient, scalable, and secure digital services.
This guide explains what a reverse proxy is, how it works, why it matters, and how organizations use it to protect and optimize their systems.
What Is a Reverse Proxy?
A reverse proxy is a server that sits in front of one or more backend servers and handles client requests on their behalf. Instead of users connecting directly to application servers, they interact with the reverse proxy, which forwards requests internally.
So, what is a reverse proxy in simple terms? It’s a protective and performance-enhancing intermediary between users and your infrastructure.
Key Characteristics of a Reverse Proxy
-
Hides backend server identities
-
Controls and routes incoming traffic
-
Improves performance and reliability
-
Adds a security enforcement layer
Unlike direct server exposure, a reverse proxy creates a controlled access point.
How a Reverse Proxy Works
Understanding the flow of traffic helps clarify the value of a reverse proxy.
Step-by-Step Reverse Proxy Workflow
-
A user sends a request to a website or application
-
The request reaches the reverse proxy
-
The reverse proxy evaluates the request
-
It forwards the request to the appropriate backend server
-
The server responds to the proxy
-
The proxy returns the response to the user
Throughout this process, the user never interacts directly with backend systems.
Reverse Proxy vs Forward Proxy: What’s the Difference?
These two concepts are often confused.
Forward Proxy
-
Sits in front of clients
-
Hides client identity
-
Controls outbound traffic
-
Common in corporate networks
Reverse Proxy
-
Sits in front of servers
-
Hides server identity
-
Controls inbound traffic
-
Common in web and cloud environments
Understanding reverse proxy vs forward proxy helps teams choose the right tool for the job.
Why Businesses Use Reverse Proxy Servers
Reverse proxies are widely adopted across industries for both performance and security reasons.
Key Business Benefits
-
Improved website performance
-
Increased uptime and availability
-
Reduced attack surface
-
Simplified infrastructure management
-
Better user experience
For executives, a reverse proxy supports scalability without sacrificing security.
Reverse Proxy and Load Balancing
One of the most common use cases is traffic distribution.
How Load Balancing Reverse Proxy Works
-
Distributes traffic across multiple servers
-
Prevents overload on individual systems
-
Enables high availability
-
Supports horizontal scaling
A load balancing reverse proxy ensures applications remain responsive even during peak demand.
Reverse Proxy Security Benefits
Security is one of the strongest arguments for reverse proxy adoption.
How Reverse Proxy Improves Security
-
Masks internal server IP addresses
-
Blocks malicious traffic before it reaches servers
-
Enforces access controls and authentication
-
Helps mitigate DDoS attacks
Reverse proxy security reduces exposure while improving visibility.
Reverse Proxy and Web Application Protection
Modern web applications face constant threats.
Threats Reverse Proxies Help Mitigate
-
DDoS attacks
-
SQL injection attempts
-
Cross-site scripting (XSS)
-
Credential-stuffing attacks
By filtering traffic at the edge, reverse proxies stop many attacks early.
Reverse Proxy in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
As infrastructure becomes more distributed, reverse proxies play a larger role.
Why Reverse Proxies Fit Cloud Architectures
-
Abstract backend complexity
-
Support microservices
-
Enable dynamic scaling
-
Improve resilience
For cloud-first organizations, understanding what is a reverse proxy is essential.
Reverse Proxy vs Load Balancer: Are They the Same?
While related, they are not identical.
| Feature | Reverse Proxy | Load Balancer |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic routing | Yes | Yes |
| Security controls | Strong | Limited |
| Application awareness | High | Moderate |
| SSL termination | Yes | Sometimes |
Many modern solutions combine both roles into a single platform.
SSL Termination and Reverse Proxy
Reverse proxies often handle encryption tasks.
Benefits of SSL Termination
-
Reduces load on backend servers
-
Simplifies certificate management
-
Improves performance
The reverse proxy decrypts traffic, inspects it, then re-encrypts internally if needed.
Reverse Proxy and Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust assumes no implicit trust.
How Reverse Proxies Support Zero Trust
-
Enforce authentication at the edge
-
Inspect every request
-
Apply least-privilege access
-
Reduce lateral movement
Reverse proxies align naturally with Zero Trust principles.
Common Reverse Proxy Use Cases by Industry
Reverse proxies are used across many sectors.
Industry Examples
-
Finance: Protect online banking portals
-
Healthcare: Secure patient data access
-
E-commerce: Handle traffic spikes securely
-
SaaS: Enable global scalability
Each use case benefits from the same core capabilities.
Best Practices for Deploying a Reverse Proxy
Proper configuration is essential.
Actionable Deployment Tips
-
Place reverse proxies in a DMZ
-
Monitor traffic continuously
-
Keep software updated
-
Integrate with security monitoring tools
-
Limit backend server exposure
Following best practices ensures maximum benefit and minimal risk.
Limitations of Reverse Proxies
While powerful, reverse proxies are not a complete security solution.
What Reverse Proxies Don’t Do Alone
-
Replace endpoint security
-
Eliminate insider threats
-
Prevent all application vulnerabilities
They work best as part of a layered security strategy.
The Future of Reverse Proxy Technology
Reverse proxies continue to evolve.
Emerging Trends
-
AI-driven traffic analysis
-
Integration with XDR platforms
-
Cloud-native reverse proxy services
-
Enhanced application-level visibility
As threats grow, reverse proxies become even more valuable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a reverse proxy used for?
A reverse proxy is used to route traffic, improve performance, and add security between users and backend servers.
2. Is a reverse proxy a firewall?
No, but it complements firewalls by inspecting and controlling application-level traffic.
3. Does a reverse proxy improve performance?
Yes. It can cache content, balance loads, and reduce server strain.
4. Can reverse proxies stop DDoS attacks?
They help mitigate many attacks by filtering and absorbing malicious traffic.
5. Do small businesses need reverse proxies?
Yes. Even small applications benefit from improved security and reliability.
Final Thoughts: Why Reverse Proxies Matter More Than Ever
Understanding what is a reverse proxy is no longer optional in today’s digital landscape. With rising cyber threats, increased traffic demands, and complex infrastructures, reverse proxies provide a critical layer of control, security, and performance.
For IT teams and business leaders alike, reverse proxies enable safer growth, better uptime, and stronger defenses against modern attacks.
Strengthen Your Application Security Today
Gain visibility, protection, and control across your web infrastructure with advanced security solutions.
👉 Request a demo now:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Because secure access starts at the edge—and reverse proxies guard that edge.