What Is Middleware Software? A Complete Guide for Modern Businesses
Updated on December 31, 2025, by Xcitium
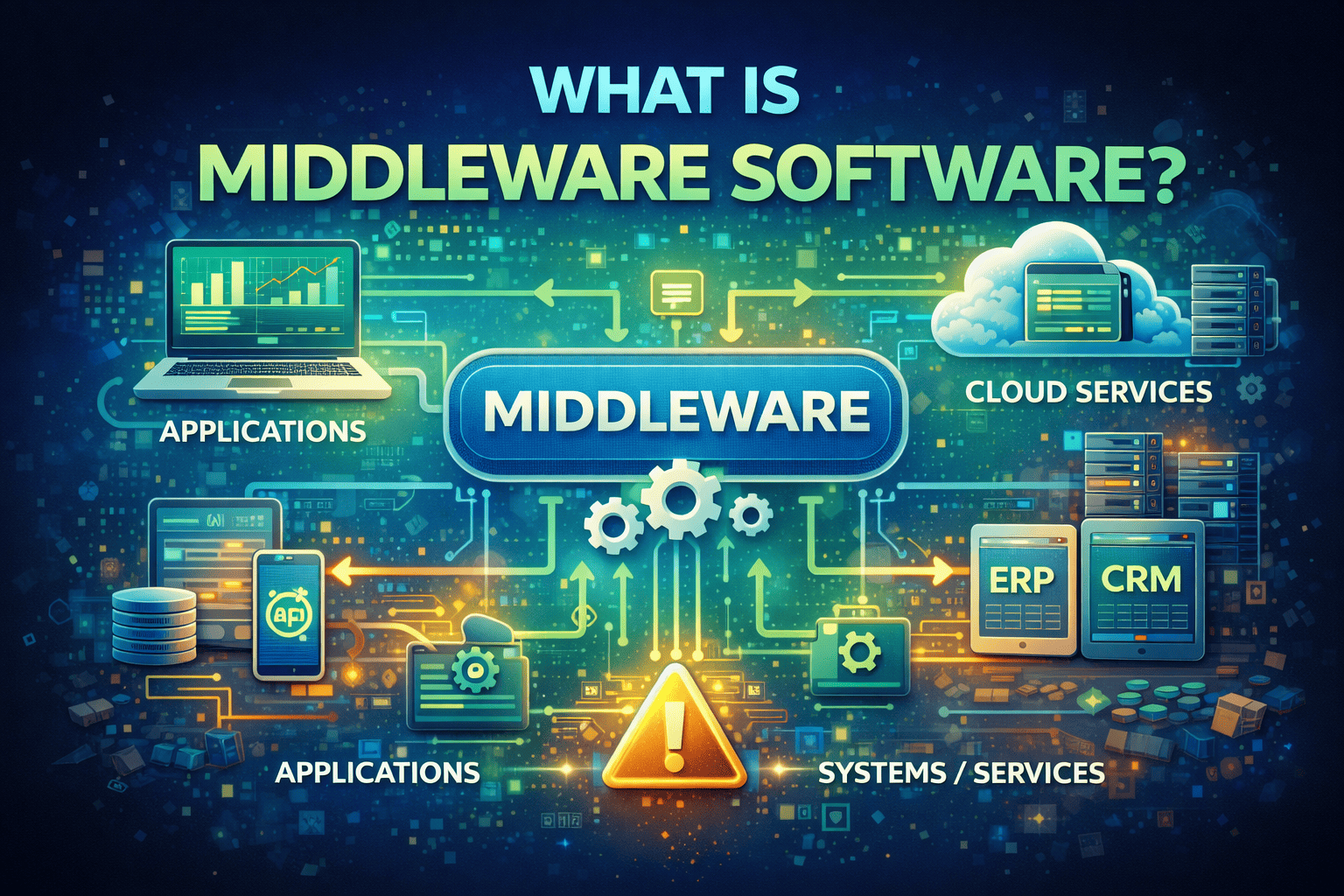
Modern IT systems rarely operate in isolation. Applications, databases, cloud platforms, and devices must constantly communicate with one another. This is where many organizations pause and ask an important question: what is middleware software, and why is it essential?
Middleware software acts as the invisible bridge that connects different systems, applications, and services. Without it, modern digital environments would struggle with integration, scalability, and security. In this guide, we’ll explain what is middleware software, how it works, why it matters, and how organizations use it to build reliable, secure, and scalable IT ecosystems.
What Is Middleware Software?
Middleware software is a layer of software that sits between operating systems and applications, enabling communication, data exchange, and integration between different systems. It allows applications to work together—even if they were built using different languages, platforms, or architectures.
In simple terms, middleware software acts as a translator and traffic controller. It ensures that data moves smoothly between components without developers needing to rebuild or tightly couple systems.
Understanding what is middleware software is critical for businesses operating in hybrid, cloud, and distributed environments.
Why Middleware Software Is Important
As organizations adopt cloud computing, microservices, and APIs, complexity increases. Middleware software helps manage that complexity.
Middleware software is important because it:
-
Enables system integration
-
Improves application scalability
-
Simplifies development
-
Enhances reliability
-
Supports security and governance
Without middleware, IT teams would need to manually handle communication logic for every system interaction—an inefficient and error-prone approach.
How Middleware Software Works
To fully understand what is middleware software, it helps to see how it functions behind the scenes.
Middleware typically performs the following roles:
-
Receives requests from applications
-
Translates data formats or protocols
-
Routes messages to the correct destination
-
Handles errors and retries
-
Ensures secure communication
This abstraction allows applications to focus on business logic instead of connectivity.
Common Types of Middleware Software
Middleware is not a single product category. It includes several types, each serving specific use cases.
1. Message-Oriented Middleware (MOM)
Message-oriented middleware enables asynchronous communication between systems.
Key features include:
-
Message queues
-
Event-driven architecture
-
Reliable message delivery
Examples include RabbitMQ and Apache Kafka.
2. API Middleware
API middleware enables communication between applications using APIs.
It handles:
-
Request routing
-
Authentication
-
Rate limiting
-
Data transformation
API middleware is essential in microservices and cloud-native environments.
3. Database Middleware
Database middleware connects applications to databases.
It manages:
-
Database connections
-
Query translation
-
Load balancing
-
Failover
This type of middleware improves performance and reliability.
4. Application Server Middleware
Application servers provide a runtime environment for applications.
They support:
-
Transaction management
-
Security services
-
Session handling
-
Resource pooling
Examples include WebLogic and JBoss.
5. Cloud and Integration Middleware
Cloud middleware enables integration across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
It supports:
-
SaaS integration
-
Data synchronization
-
Workflow automation
This is critical for modern digital transformation initiatives.
Middleware Software vs Application Software
A common point of confusion when learning what is middleware software is how it differs from application software.
| Feature | Middleware Software | Application Software |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects systems | Performs business tasks |
| User Interaction | Minimal or none | Direct user interaction |
| Function | Integration & communication | Productivity & operations |
| Visibility | Often invisible | User-facing |
Middleware works behind the scenes, but its impact is significant.
Middleware Software in Modern Architectures
Middleware plays a critical role in modern IT architectures.
Microservices Architecture
Middleware enables services to communicate independently using APIs and messaging systems.
Cloud Computing
Middleware connects on-premise systems to cloud services securely.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Middleware manages communication between devices, gateways, and platforms.
Understanding what is middleware software is essential to managing these architectures effectively.
Benefits of Middleware Software
Organizations invest in middleware because it delivers measurable value.
Key Benefits
-
Faster application development
-
Reduced system complexity
-
Improved scalability
-
Better system reliability
-
Easier maintenance
For executives, middleware supports agility and innovation while controlling costs.
Middleware Software and Security
Security is a critical consideration when implementing middleware software.
Middleware often handles:
-
Authentication and authorization
-
Data encryption
-
Secure API access
-
Logging and monitoring
If compromised, middleware can become a high-value attack target. This makes security-focused design and monitoring essential.
Common Middleware Security Risks
When understanding what is middleware software, it’s important to understand its risks.
Key Security Risks
-
Unsecured APIs
-
Weak authentication
-
Misconfigured access controls
-
Excessive permissions
-
Lack of monitoring
Attackers often target middleware to gain access to multiple systems at once.
Best Practices for Securing Middleware Software
To reduce risk, organizations should follow proven best practices.
Middleware Security Best Practices
-
Enforce strong authentication
-
Apply least-privilege access
-
Encrypt data in transit
-
Monitor middleware traffic
-
Patch and update regularly
Security must be built into middleware from the start—not added later.
Middleware Software and Performance
Middleware can significantly impact performance.
Performance Advantages
-
Load balancing
-
Connection pooling
-
Caching
-
Asynchronous processing
When properly designed, middleware improves system responsiveness and availability.
Middleware Software Use Cases by Industry
Middleware is used across nearly every industry.
Financial Services
-
Transaction processing
-
Fraud detection
-
Legacy system integration
Healthcare
-
Electronic health record integration
-
Data exchange between systems
-
Compliance enforcement
Retail and E-Commerce
-
Inventory synchronization
-
Payment processing
-
Customer experience optimization
Manufacturing
-
IoT device integration
-
Supply chain visibility
-
Real-time analytics
Understanding what is middleware software helps industry leaders optimize operations.
Challenges of Middleware Software
Despite its benefits, middleware introduces challenges.
Common Challenges
-
Configuration complexity
-
Performance tuning
-
Security management
-
Vendor lock-in
-
Monitoring at scale
These challenges require skilled planning and governance.
Middleware Software vs Integration Platforms
Some organizations confuse middleware with integration platforms.
Middleware focuses on runtime communication, while integration platforms often include:
-
Data mapping
-
Workflow orchestration
-
Business process automation
Both play important roles and are often used together.
Choosing the Right Middleware Software
Selecting middleware requires aligning technical and business needs.
Key Evaluation Criteria
-
Scalability
-
Security features
-
Compatibility
-
Performance
-
Vendor support
Decision-makers should evaluate middleware as a long-term strategic investment.
Middleware Software and Digital Transformation
Digital transformation depends heavily on middleware.
Middleware enables:
-
Legacy modernization
-
Cloud adoption
-
API ecosystems
-
Agile development
Without middleware, transformation efforts often stall due to integration barriers.
The Future of Middleware Software
Middleware continues to evolve with technology trends.
Emerging Trends
-
Cloud-native middleware
-
Serverless integration
-
Event-driven architectures
-
AI-assisted integration
-
Unified observability
Future middleware will be more automated, intelligent, and secure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is middleware software used for?
Middleware software connects applications, systems, and services, enabling communication and data exchange.
2. Is middleware software the same as an API?
No. APIs define how systems communicate, while middleware manages and facilitates that communication.
3. Does middleware software improve security?
Yes, when properly configured, middleware can enforce authentication, encryption, and access control.
4. Is middleware required in cloud environments?
Most cloud and hybrid environments rely heavily on middleware for integration and scalability.
5. Can middleware software fail?
Yes. Poor configuration, lack of monitoring, or security gaps can cause middleware failures.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding What Is Middleware Software Matters
Middleware software may not be visible to end users, but it is foundational to modern IT systems. Understanding what is middleware software helps organizations build resilient architectures, integrate systems efficiently, and secure critical data flows.
For IT managers and executives, middleware is not just a technical tool—it’s a strategic enabler of growth, agility, and digital transformation.
Secure and Monitor Your Middleware Ecosystem
Middleware connects everything—making visibility and protection essential. To detect threats, monitor system behavior, and secure integrations in real time:
👉 See how Xcitium helps protect complex IT environments
Request a Demo