What Is a Zero Day Exploit? A Complete Guide for Cybersecurity Leaders
Updated on November 13, 2025, by Xcitium

If you’ve ever wondered what is a zero day exploit or why security teams fear it more than most cyberattacks, you’re not alone. Zero day exploits target vulnerabilities that developers haven’t patched yet—meaning cybercriminals have a powerful advantage. These attacks strike fast, spread quietly, and often cause millions in damage before they’re even discovered.
For IT managers, cybersecurity analysts, CISOs, and business leaders, understanding zero day exploits is no longer optional—it’s essential. As threats evolve, so must your defense strategy.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly what zero day exploits are, how they work, why they’re so dangerous, and how to protect your environment using modern prevention technologies.
What Is a Zero Day Exploit?
A zero day exploit is a cyberattack that targets a security vulnerability unknown to the software vendor, security community, or IT teams. Because the vulnerability is unknown, there is zero day available to fix it—hence the name.
In other words:
A zero day exploit is a method used by attackers to take advantage of a security flaw before a patch or fix exists.
These attacks often strike silently and spread rapidly because no antivirus signature, firewall rule, or traditional detection mechanism can stop an unknown threat.
Zero Day Vulnerability vs Zero Day Exploit vs Zero Day Attack
These three terms are often confused, so let’s break them down:
1. Zero Day Vulnerability
A flaw in software, firmware, or hardware that developers don’t yet know about.
2. Zero Day Exploit
The technique or code attackers use to take advantage of the vulnerability.
3. Zero Day Attack
The execution of the exploit on a target system.
Think of it like this:
-
Vulnerability = unlocked door
-
Exploit = burglar’s tool to open it
-
Attack = the break-in
How Zero Day Exploits Work (Step-by-Step)
Zero day attacks typically follow a predictable pattern:
1. Vulnerability Discovery
Attackers, hackers, or security researchers identify an unknown flaw.
2. Exploit Development
Cybercriminals write custom code that weaponizes the flaw.
3. Delivery of Exploit
Common delivery channels include:
-
Phishing emails
-
Malicious attachments
-
Compromised websites
-
Watering hole attacks
-
Software supply chain attacks
4. Execution & Control
Once the exploit lands, it can:
-
Install malware or ransomware
-
Steal credentials
-
Escalate privileges
-
Exfiltrate data
-
Move laterally across the network
5. Covering Tracks
Advanced attackers remain hidden for weeks or months.
Why Zero Day Exploits Are So Dangerous
Zero day exploits are one of the most feared attack vectors because:
1. No Existing Signature or Patch
There’s no known fix at the time of attack.
2. High Market Value
Zero day exploits are sold for millions on dark markets.
3. Perfect for Targeted Attacks
Nation-state groups often rely on zero days for espionage.
4. Can Evade Traditional Security
Traditional antivirus, firewalls, and EDR often fail to detect brand-new attacks.
5. Fast, Aggressive Spread
Once discovered publicly, attackers race to exploit it before a patch is deployed.
Examples of Famous Zero Day Exploits
Here are major real-world zero day attacks that changed cybersecurity:
➤ Stuxnet Worm (2010)
Used four zero day exploits to sabotage Iranian nuclear facilities.
➤ Adobe Flash Zero Days
Attackers regularly exploited Flash vulnerabilities for a decade.
➤ Log4j (Log4Shell)
One of the most exploited zero day remote execution flaws in history.
➤ Google Chrome Zero Days
Chrome receives dozens of emergency zero day patches each year.
These incidents highlight that even major, well-maintained platforms can fall victim.
Common Targets of Zero Day Exploits
Zero day vulnerabilities can exist anywhere in your digital environment:
Software Applications
-
Browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge)
-
Email clients
-
Office productivity apps
Operating Systems
-
Windows
-
macOS
-
Linux
Firmware & Hardware
-
Routers
-
IoT devices
-
Network appliances
Cloud Platforms & APIs
-
SaaS products
-
Identity systems
-
CI/CD pipelines
No organization is immune—especially those relying on outdated detection tools.
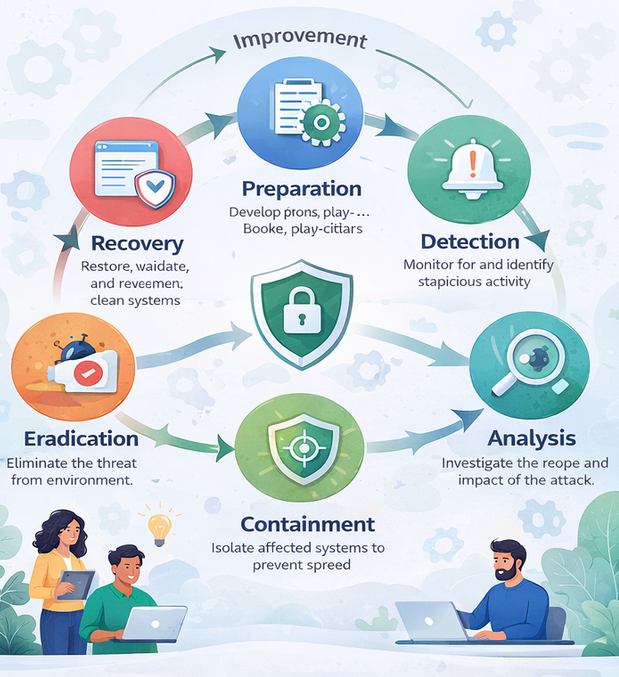
How to Detect Zero Day Exploits
While detecting unknown vulnerabilities is challenging, advanced security teams use:
1. Behavioral Analysis
Monitoring suspicious system changes, even without known signatures.
2. AI-Driven Threat Detection
Machine learning can recognize anomalies in real time.
3. Sandboxing
Running applications in isolated environments to see if they behave maliciously.
4. Network Traffic Monitoring
Detecting:
-
C2 communication
-
Data exfiltration patterns
-
Lateral movement
5. Zero Trust Architecture
Limiting trust reduces attacker mobility.
How to Prevent Zero Day Exploits
No solution guarantees 100% protection, but a layered defense dramatically reduces risk.
1. Use Advanced Endpoint Protection (EDR/XDR/MDR)
Modern AI-based platforms detect behavior, not signatures.
2. Patch Frequently
Apply security updates immediately.
3. Enable Application Sandboxing
Isolate new or untrusted applications.
4. Deploy Network Segmentation
Stops attackers from moving laterally.
5. Implement Zero Trust Security
Never trust — always verify.
6. Use Ransomware Containment Technology
Blocks unknown threats even when they bypass traditional controls.
7. Continuous Monitoring & Threat Hunting
Human analysts + AI = faster detection and response.
Zero Day Exploits & Modern Cybersecurity: Why They Matter Now
With AI-driven malware, automated exploit kits, and global cyber-espionage rising, zero day vulnerabilities are now a top concern for organizations of every size.
Business leaders should treat zero day readiness as a core part of:
-
Cyber resilience
-
Incident response planning
-
Risk management
-
Regulatory compliance
The faster you can contain an unknown threat, the less damage it will cause.
Final Thoughts: Staying Ahead of Zero Day Threats
Understanding what a zero day exploit is helps organizations respond quickly and confidently. The goal isn’t to eliminate risk (that’s impossible), but to minimize attack impact through stronger, behavior-based security controls.
If your environment is still relying on traditional antivirus, outdated EDR, or manual monitoring, you are leaving a massive attack surface exposed.
Ready to strengthen your security against zero day attacks?
👉 Get a free demo of Xcitium’s threat prevention technology:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
FAQs: What Is a Zero Day Exploit?
1. Why is it called a zero day exploit?
Because the vendor has “zero days” to fix the flaw before it’s exploited.
2. How do hackers find zero day vulnerabilities?
Through reverse engineering, fuzz testing, malware analysis, and scanning tools.
3. Are zero day exploits common?
Yes—hundreds are discovered each year, especially in browsers and operating systems.
4. Can antivirus stop a zero day exploit?
Traditional antivirus cannot. Advanced behavior-based security tools can detect anomalies even without signatures.
5. What’s the best defense against zero day attacks?
Layered security combining:
-
Zero Trust
-
Sandboxing
-
AI-powered detection
-
Segmentation
-
Ransomware containment