What Is a Transformer? Understanding the Core of Electrical Systems
Updated on July 4, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever wondered how electricity efficiently powers your home, office, or data center? The unsung hero behind this seamless power delivery is the transformer. Knowing what is a transformer and how it functions is critical for those in IT infrastructure, cybersecurity, or running tech-driven businesses. Whether you’re managing a server room or overseeing energy-hungry operations, understanding transformers can boost your operational resilience.
What Is a Transformer?
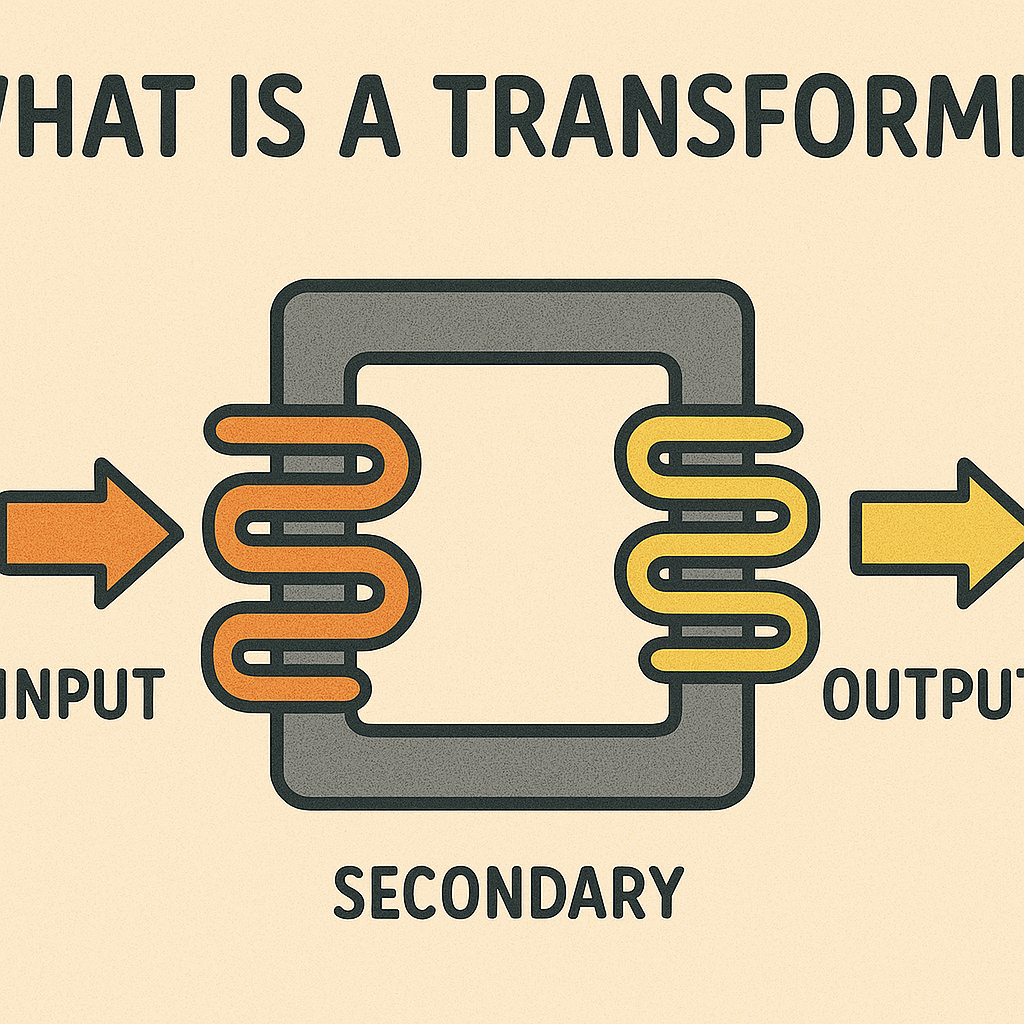
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It either increases (steps up) or decreases (steps down) voltage levels while maintaining the same frequency. The primary purpose is to ensure safe, efficient power transmission across long distances or within complex machinery.
In electrical systems, transformers are essential for voltage regulation, equipment protection, and energy optimization.
How Does a Transformer Work?
The transformer working principle is based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. When alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, effectively transferring power.
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Primary coil receives AC voltage.
- Core (usually iron) channels the magnetic flux.
- Secondary coil outputs voltage—either higher or lower depending on the design.
🔁 This process occurs without any physical connection between the coils—purely through magnetic induction.
Construction of Transformer
A transformer typically consists of:
- Core: Made of laminated steel to reduce energy losses.
- Primary winding: Connected to the input power source.
- Secondary winding: Connected to the load (output side).
- Insulating material: Separates coils to prevent short circuits.
🛠️ Transformers vary in size—from small PCB-mounted types to large units used in substations.
Types of Transformers
Understanding the types of transformer is key to choosing the right one for your use case.
Based on Voltage:
- Step-Up Transformer: Increases voltage (used in power plants).
- Step-Down Transformer: Decreases voltage (used in residential power delivery).
Based on Core Design:
- Core Type: Coils wrapped around the core’s limbs.
- Shell Type: Core surrounds the coils—better for high voltage.
Based on Use:
- Power Transformers (used in transmission networks)
- Distribution Transformers (deliver power to homes/businesses)
- Isolation Transformers (used in sensitive equipment to block noise)
Transformer in Electrical Systems
In the electrical industry, transformers are integral. Their applications include:
- Power transmission across long distances
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Industrial automation setups
- Cybersecurity hardware where voltage regulation is crucial
🔌 Without transformers, efficient and scalable power distribution wouldn’t be possible.
Advantages of Using Transformers
✅ Voltage adjustment for safer transmission
✅ Reduces power loss over long distances
✅ Isolates systems to reduce electric noise
✅ Protects devices from voltage spikes
✅ Increases energy efficiency in enterprise operations
Real-World Use Cases
- Data Centers: Step-down transformers ensure server safety.
- Cybersecurity Labs: Isolation transformers protect sensitive hardware.
- Smart Grids: Enable flexible power routing using programmable transformers.
- Manufacturing Units: Operate heavy machinery safely at varied voltages.
What Happens If a Transformer Fails?
🔥 A faulty transformer can lead to:
- Power surges
- Data loss
- Equipment damage
- Downtime—especially critical in cybersecurity systems
🛡️ Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial.
FAQs: Understanding Transformers in Detail
1. What is a transformer used for?
A transformer adjusts voltage levels to enable safe and efficient electricity transmission and distribution.
2. What is the working principle of a transformer?
Transformers work on electromagnetic induction—voltage is induced in the secondary coil due to the changing magnetic field from the primary coil.
3. What are the different types of transformers?
Step-up, step-down, isolation, power, and distribution transformers are among the most commonly used.
4. Can transformers be used in cybersecurity or IT setups?
Yes! Isolation transformers are used in sensitive setups like cybersecurity labs or data centers to protect against electric surges and noise.
5. Are transformers energy-efficient?
Modern transformers are designed with laminated cores and efficient windings to reduce energy loss, often achieving >98% efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is a transformer empowers cybersecurity leaders, IT managers, and industrial decision-makers to make smarter infrastructure choices. From safeguarding server rooms to powering entire data ecosystems, transformers are at the core of stable, scalable, and secure operations.
Ready to Fortify Your Tech Infrastructure?
Looking to enhance your energy infrastructure or cybersecurity hardware setup?
🚀 Request a free demo with Xcitium now and secure your digital future.