How Does Encryption Work? A Complete Guide for Modern Cybersecurity
Updated on February 9, 2026, by Xcitium
Every time you log in to a website, send an email, or make an online payment, your data is traveling across networks that attackers constantly try to exploit. So how does that information stay protected?
The answer lies in how does encryption work. Encryption is one of the most fundamental technologies in cybersecurity, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. Whether you’re a business leader safeguarding customer data or an IT manager securing systems, understanding how encryption works is essential in today’s digital world.
In this guide, we’ll break down how encryption works, the different types of encryption, where it’s used, and why it’s critical for security, compliance, and trust.
What Is Encryption?
Before exploring how does encryption work, let’s define what encryption actually is.
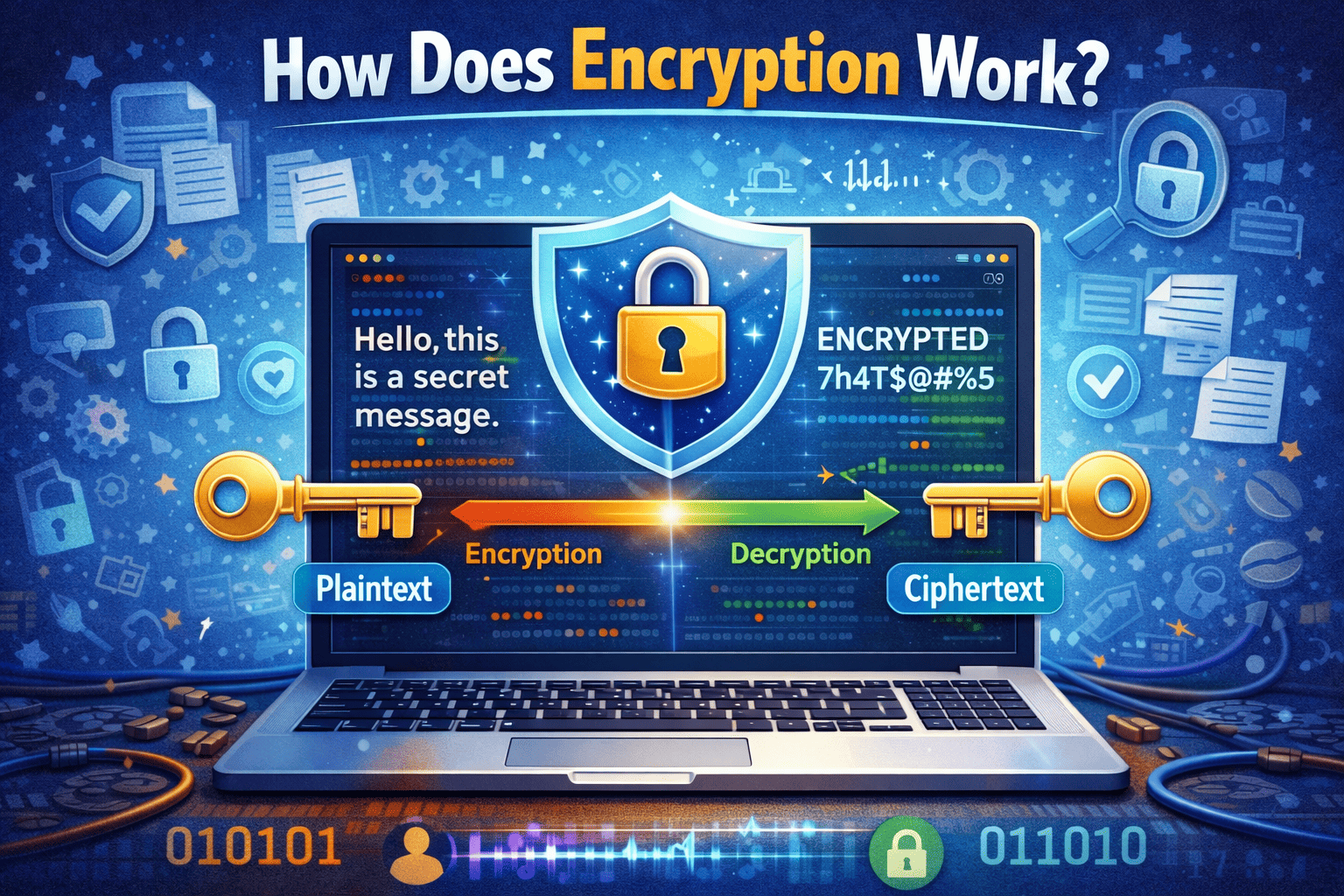
Encryption is the process of converting readable data (called plaintext) into an unreadable format (called ciphertext) using a mathematical algorithm and a secret value known as a key. Only authorized parties with the correct key can decrypt the data back into its original form.
In simple terms, encryption locks your data so that even if it’s intercepted, it can’t be understood or used.
Why Encryption Is So Important Today
Understanding how does encryption work matters because data is constantly under threat.
Key reasons encryption is critical:
-
Protects sensitive personal and business data
-
Prevents unauthorized access during data breaches
-
Secures data in transit and at rest
-
Supports regulatory compliance
-
Builds customer trust
Without encryption, sensitive data would be exposed every time it moves or is stored.
How Does Encryption Work? Step by Step
To truly understand how does encryption work, let’s walk through the process step by step.
Step 1: Data Is Created
Data starts in a readable format—such as a message, file, or database record.
Step 2: An Encryption Algorithm Is Applied
An encryption algorithm uses complex mathematics to scramble the data.
Step 3: A Key Is Used
The algorithm uses a cryptographic key to lock the data.
Step 4: Data Becomes Ciphertext
The encrypted data is unreadable without the correct key.
Step 5: Decryption Restores the Data
Authorized users apply the correct key to decrypt the data back into readable form.
This process happens in milliseconds, often without users realizing it.
Types of Encryption Explained
Encryption is not one-size-fits-all. Different use cases require different methods.
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data.
Key characteristics:
-
Fast and efficient
-
Ideal for large volumes of data
-
Requires secure key sharing
Common symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
Symmetric encryption is widely used for encrypting files, databases, and backups.
Asymmetric Encryption (Public Key Encryption)
Asymmetric encryption uses two keys:
-
A public key to encrypt data
-
A private key to decrypt data
This model explains much of how does encryption work on the internet.
Benefits include:
-
Secure key exchange
-
Strong authentication
-
Widely used in SSL/TLS
Asymmetric encryption enables secure communication between parties who have never met before.
Hybrid Encryption: The Best of Both Worlds
Most modern systems use a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
How hybrid encryption works:
-
Asymmetric encryption securely exchanges a key
-
Symmetric encryption protects the data
This approach balances speed and security and is common in web traffic and enterprise systems.
Encryption in Transit vs Encryption at Rest
Understanding how does encryption work also means knowing where it’s applied.
Encryption in Transit
This protects data while it’s moving across networks.
Examples include:
-
HTTPS web traffic
-
Encrypted email
-
VPN connections
Encryption in transit prevents attackers from intercepting and reading data.
Encryption at Rest
This protects data stored on devices or servers.
Examples include:
-
Encrypted hard drives
-
Secure databases
-
Cloud storage encryption
Encryption at rest ensures stolen data remains unreadable.
Common Encryption Algorithms You Should Know
Encryption relies on trusted algorithms.
Widely used encryption algorithms:
-
AES – Standard for data encryption
-
RSA – Common for key exchange
-
ECC – Efficient and secure for modern systems
-
SHA – Used for hashing and integrity
These algorithms are the mathematical backbone of how encryption works.
Real-World Examples of How Encryption Works
Encryption is everywhere, even when you don’t notice it.
Online Banking
Protects transactions and account information.
Messaging Apps
End-to-end encryption secures private conversations.
Cloud Storage
Encrypts files stored on remote servers.
Password Protection
Passwords are encrypted or hashed before storage.
Encryption quietly protects daily digital activity.
How Encryption Supports Cybersecurity
Encryption plays a central role in cybersecurity strategies.
Security benefits include:
-
Reduced breach impact
-
Protection against insider threats
-
Secure authentication
-
Data confidentiality assurance
Without encryption, even strong perimeter defenses are not enough.
Encryption and Compliance Requirements
Many regulations require encryption to protect sensitive data.
Regulations that rely on encryption:
-
GDPR
-
HIPAA
-
PCI DSS
-
ISO 27001
-
SOC 2
Encryption helps organizations demonstrate due diligence and compliance.
Key Management: The Hidden Challenge
Encryption is only as strong as its key management.
Key management includes:
-
Secure key storage
-
Regular key rotation
-
Access control enforcement
-
Key revocation
Poor key management can undermine even the strongest encryption.
Common Myths About Encryption
Let’s clear up some misunderstandings.
Myth 1: Encryption Is Unbreakable
Encryption is extremely strong—but only when implemented correctly.
Myth 2: Encryption Slows Systems
Modern encryption is optimized for performance.
Myth 3: Only Big Companies Need Encryption
Every organization handling data benefits from encryption.
Understanding how does encryption work helps separate fact from fiction.
Encryption Best Practices for Organizations
Organizations should follow best practices to maximize encryption effectiveness.
Best practices include:
-
Encrypt sensitive data by default
-
Use industry-standard algorithms
-
Secure and rotate encryption keys
-
Monitor encryption usage
-
Educate users and teams
Encryption should be part of a broader security strategy.
Encryption in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Cloud adoption has expanded encryption use.
Cloud encryption considerations:
-
Shared responsibility models
-
Customer-managed keys
-
Data residency requirements
-
Visibility and monitoring
Encryption ensures cloud data remains secure even in shared environments.
The Future of Encryption
Encryption continues to evolve alongside technology.
Emerging trends include:
-
Quantum-resistant encryption
-
Automated key management
-
Zero Trust security models
-
Encryption everywhere by default
As threats grow more advanced, encryption becomes even more essential.
FAQs About How Does Encryption Work
1. How does encryption work in simple terms?
Encryption scrambles data using a key so only authorized users can read it.
2. Is encrypted data completely safe?
Encrypted data is highly secure, but weak keys or poor management can introduce risk.
3. What is the most common encryption method?
AES is one of the most widely used encryption standards today.
4. Does encryption protect against hacking?
Encryption reduces the impact of breaches but should be combined with other controls.
5. Is encryption required for compliance?
Many regulations require encryption to protect sensitive information.
Final Thoughts: Why Encryption Is Non-Negotiable
Understanding how does encryption work is essential for anyone responsible for data security. Encryption protects information, supports compliance, and reduces the damage caused by breaches.
In a world where data is constantly under attack, encryption is not optional—it’s foundational.
Take the Next Step Toward Stronger Data Protection
Want better visibility into how your data is protected and where risks exist?
👉 Request a demo today:
https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
Discover how advanced security and visibility solutions help organizations protect sensitive data with confidence.