What is a Microservice? Complete Guide for IT and Security Leaders
Updated on August 29, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever wondered, what is a microservice and why are so many enterprises shifting to this model? As businesses migrate to the cloud, embrace DevOps, and battle increasing cyber threats, the way applications are built and deployed is undergoing a massive transformation.
A microservice is more than just a buzzword—it’s a modern architectural approach that helps enterprises build scalable, secure, and resilient applications. For IT managers, cybersecurity teams, and CEOs, understanding microservices is crucial to stay competitive, enhance security, and reduce downtime.
What is a Microservice?
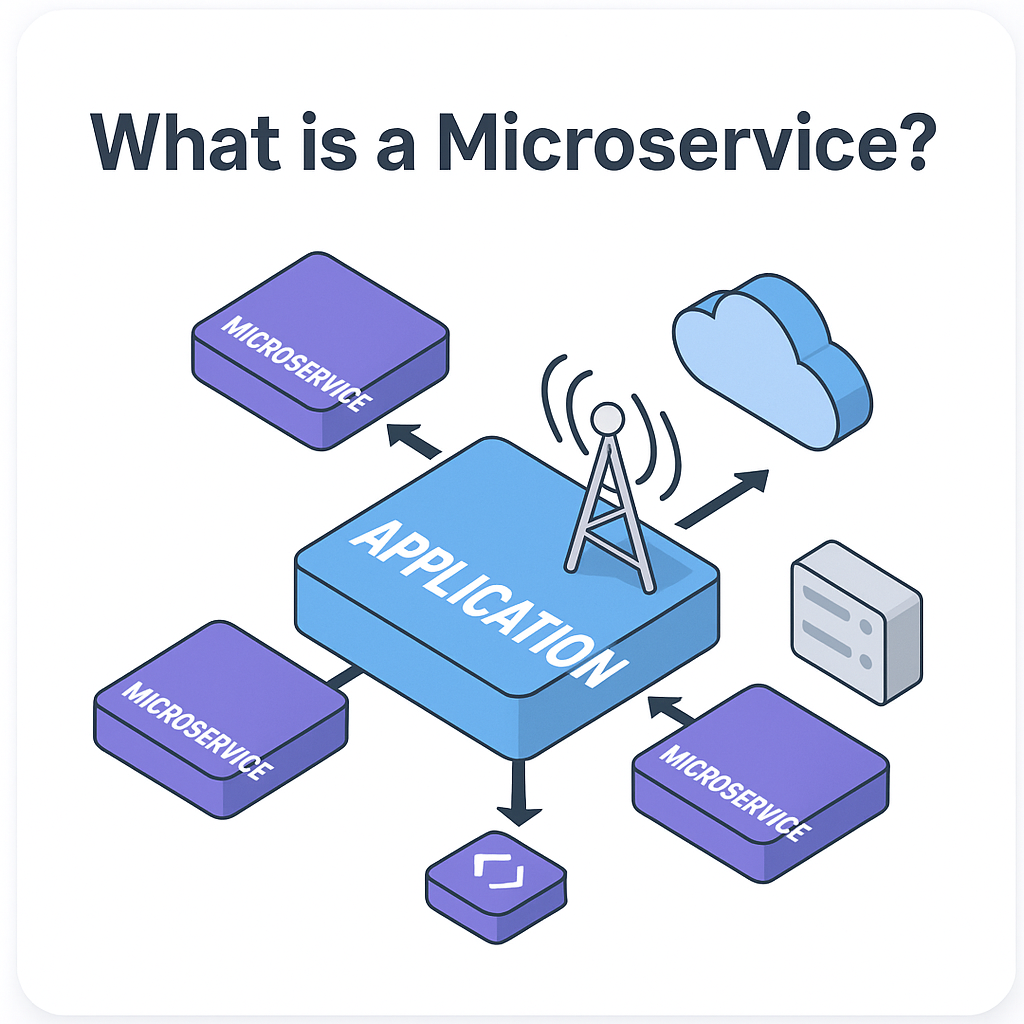
A microservice is a small, independent, and loosely coupled service within a larger application. Each microservice is designed to perform one specific function, such as authentication, payment processing, or data storage.
Unlike monolithic applications, where all components are tightly integrated, microservices operate independently and communicate via APIs or messaging protocols.
Key Features of Microservices:
- Independence: Each service runs separately.
- Scalability: Can be scaled individually based on demand.
- Resilience: Failure in one service doesn’t crash the whole system.
- Agility: Supports continuous deployment and DevOps pipelines.
👉 In simple terms: A microservice is like a Lego block—you can build, replace, or upgrade it without breaking the entire system.
Microservices vs Monolithic Architecture
| Feature | Monolithic Application | Microservices Architecture |
| Structure | Single, tightly integrated codebase | Multiple independent services |
| Scalability | Entire app scales together | Each service scales individually |
| Deployment | Complex, requires full redeployment | Faster, modular deployments |
| Resilience | One failure can crash the system | Isolated failures, minimal impact |
| Technology Stack | Single stack for all modules | Flexible, service-specific stack |
👉 Microservices give enterprises flexibility, resilience, and speed—all essential in today’s digital-first economy.
How Do Microservices Work?
Understanding what is a microservice requires knowing how they function:
- Service Design: Each microservice is built around a specific business capability (e.g., user authentication).
- Independent Deployment: Services run in separate containers or virtual machines.
- API Communication: Services interact through REST APIs, gRPC, or message queues.
- Data Independence: Each microservice often has its own database for autonomy.
- Orchestration & Monitoring: Tools like Kubernetes manage deployment, scaling, and resilience.
Benefits of Microservices for Enterprises
For IT and cybersecurity leaders, the benefits go beyond technology.
1. Scalability
Microservices allow scaling only the services that need more resources—for example, payment services during Black Friday traffic.
2. Faster Deployment
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines enable frequent, reliable updates without disrupting the entire system.
3. Resilience and Security
Isolated services limit damage. If one microservice is attacked or fails, others remain operational.
4. Technology Flexibility
Teams can choose the best technology stack for each service, optimizing performance and security.
5. Improved Cybersecurity Monitoring
Each service can be monitored individually, making anomaly detection faster and more precise.
Security Considerations in Microservices
When IT managers ask what is a microservice in terms of security, the answer is nuanced. Microservices introduce both opportunities and risks.
Security Challenges:
- Expanded Attack Surface: More services mean more endpoints to secure.
- API Vulnerabilities: APIs are frequent targets for cyberattacks.
- Data Security: Distributed databases increase compliance complexity.
- Service-to-Service Trust: Misconfigurations can lead to lateral movement.
Security Best Practices:
- Implement Zero Trust architecture across all services.
- Use mutual TLS (mTLS) for encrypted service-to-service communication.
- Secure APIs with gateways, authentication, and throttling.
- Integrate SIEM and monitoring tools to detect anomalies.
- Regularly patch and update services independently.
👉 Done right, microservices can enhance resilience, but they require security-first design.
Microservices in Action: Industry Use Cases
Microservices aren’t just theory—they’re powering critical business operations.
- Financial Services: Handle fraud detection, payment gateways, and account services independently.
- Healthcare: Manage patient data, billing, and medical IoT devices securely.
- E-commerce: Scale search engines, carts, and recommendation engines separately.
- Telecom: Improve uptime by isolating billing, customer service, and network management.
- Government: Build secure, modular citizen service platforms.
Microservices and DevOps
Microservices go hand-in-hand with DevOps and CI/CD.
- Developers can update one service without redeploying the entire application.
- Automated testing ensures higher reliability.
- Rolling updates reduce downtime and business disruption.
👉 For executives, this translates to faster innovation and reduced time-to-market.
Challenges of Microservices Adoption
Despite the benefits, adopting microservices isn’t without challenges.
- Complex Management: Hundreds of services require orchestration platforms like Kubernetes.
- Cultural Shift: Teams must adapt to DevOps practices.
- Monitoring Difficulties: More services = more logs, requiring advanced SIEM tools.
- Cost Considerations: Cloud infrastructure costs may increase initially.
The Future of Microservices
Looking forward, microservices will become even more critical as organizations embrace cloud-native, hybrid, and multi-cloud strategies.
- Service Meshes (e.g., Istio): Automating security, observability, and networking.
- AI-driven orchestration: Smarter scaling and anomaly detection.
- Integration with Zero Trust: Stronger defenses against evolving cyber threats.
- Serverless Microservices: Reducing infrastructure complexity while maintaining modularity.
For IT leaders, investing in microservices today is about future-proofing digital transformation.
FAQs on Microservices
Q1: What is a microservice in simple terms?
A microservice is a small, independent service within an application that performs one function and communicates with others via APIs.
Q2: How are microservices different from APIs?
An API is an interface for communication, while a microservice is a complete, independent application unit that uses APIs to interact with others.
Q3: Are microservices more secure than monolithic apps?
Microservices can improve resilience by isolating failures, but they also increase the attack surface. Security must be integrated from design.
Q4: Do all companies need microservices?
Not always. Small businesses may not benefit, but enterprises with complex applications and high scalability needs usually do.
Q5: Which tools help manage microservices?
Popular tools include Kubernetes, Docker, Istio, and API gateways for orchestration, security, and monitoring.
Conclusion: Why Your Enterprise Should Care About Microservices
To sum up, what is a microservice? It’s a modern application architecture that breaks down complex systems into independent, secure, and scalable services. For IT managers, this means simplified deployments. For cybersecurity leaders, it enables better monitoring and containment. For CEOs, it drives agility, innovation, and resilience.
In a digital-first world, adopting microservices is more than a tech decision—it’s a strategic business move.
👉 Ready to explore how microservices can enhance your cybersecurity and IT strategy? Request a Demo with Xcitium