What Is Information Security? The Complete Conversational Guide for Businesses in 2026
Updated on November 19, 2025, by Xcitium

Have you ever stopped to think about how much sensitive information your organization handles every single day? From emails and login credentials to financial records, customer data, and intellectual property — your business is constantly surrounded by information that cybercriminals would love to get their hands on. With cyberattacks increasing every year, it’s no surprise that so many leaders are asking: what is information security, and why is it so important today?
If you’ve ever wondered how information is protected, what frameworks keep data secure, or what threats businesses face in 2025, this guide breaks everything down in simple, conversational language — no confusing jargon required. Whether you’re a CEO, IT manager, cybersecurity specialist, or part of a growing company, this easy-to-read guide will help you understand the foundation of information security and how to strengthen it.
Let’s dive in.
What Is Information Security? (Easy Definition)
Information security (InfoSec) is the practice of protecting information — whether digital or physical — from:
-
Unauthorized access
-
Misuse
-
Disclosure
-
Destruction
-
Modification
-
Disruption
It ensures that your data stays confidential, accurate, and available when needed. You may recognize these as the CIA Triad, one of the core pillars of information security.
Information security protects:
-
Computer systems
-
Networks
-
Data storage
-
Cloud environments
-
Applications
-
Endpoints
-
Physical documents
In short, InfoSec is all about protecting data in all its forms.
⭐ Why Information Security Matters More Than Ever in 2025
If you think cybercriminals are only targeting big corporations, think again. More than 43% of attacks now target small and medium-sized businesses, and the average data breach costs companies millions.
Here’s why information security is so critical:
✔ Cyber threats are growing fast
Ransomware, phishing, insider threats, supply-chain attacks — the list keeps growing.
✔ Businesses rely on data for everything
Customer support, financial operations, marketing, product development — data is the backbone of every process.
✔ Regulations demand stronger protection
With GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and other frameworks, organizations must prove that data is secure.
✔ Remote and hybrid work expanded attack surfaces
More devices, more networks, more exposure.
✔ Reputation is on the line
A single breach can destroy customer trust.
Information security isn’t optional anymore — it’s essential for business stability and growth.
🔐 The CIA Triad: The Foundation of Information Security
To understand what is information security, you must understand its three core principles.
1. Confidentiality
Keeping information out of the wrong hands.
Examples:
-
Encryption
-
Access controls
-
Multi-factor authentication
-
Zero-trust security
2. Integrity
Ensuring information is accurate and unaltered.
Examples:
-
Hashing
-
Digital signatures
-
Version control
-
Change monitoring
3. Availability
Ensuring data and systems are accessible when needed.
Examples:
-
Backups
-
Redundant servers
-
Disaster recovery
-
Uptime SLAs
If a security system fails at any part of the CIA triad, information security breaks down.
🧩 Types of Information Security (Complete Breakdown)
Information security covers multiple domains.
1. Network Security
Protects networks from attacks, intrusions, and unauthorized access.
Tools and methods:
-
Firewalls
-
Intrusion detection systems
-
Secure Wi-Fi configurations
-
Network segmentation
2. Endpoint Security
Protects laptops, desktops, servers, and mobile devices.
Common tools:
-
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response)
-
Antivirus
-
Device encryption
-
Patch management
Example: Xcitium OpenEDR monitors malware, exploits, and suspicious behavior in real time.
3. Application Security
Ensures software is secure from vulnerabilities.
Includes:
-
Secure coding
-
Penetration testing
-
API security
-
WAF (Web Application Firewalls)
4. Cloud Security
Protects data, identities, and workloads in cloud platforms.
Controls include:
-
IAM
-
Zero trust
-
CSPM tools
-
Encryption
5. Data Security
Keeps information secure across its life cycle.
Methods include:
-
Encryption
-
Data masking
-
Backups
-
Access restrictions
6. Physical Security
Protects buildings, servers, and hardware from theft or damage.
This includes:
-
Surveillance cameras
-
Badges
-
Locked server rooms
-
Biometric access
Common Cyber Threats Targeting Information Security
To understand what is information security, you must understand the threats it protects against.
Here are the biggest ones businesses face today:
✔ Phishing attacks
Cybercriminals trick users into giving away credentials.
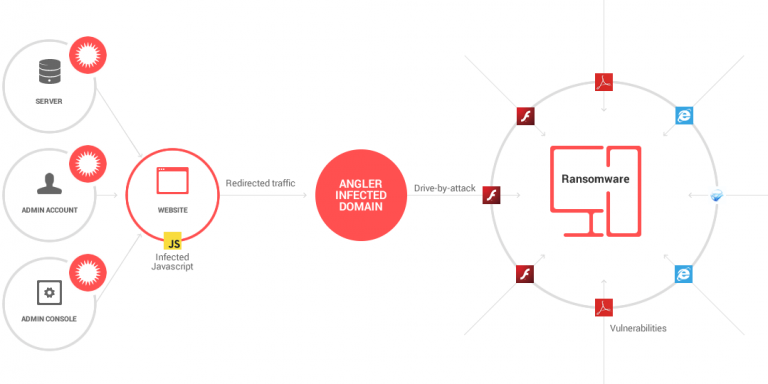
✔ Ransomware
Hackers encrypt data and demand payment.
✔ Insider threats
Employees with access misuse information, intentionally or accidentally.
✔ DDoS attacks
Hackers overwhelm systems to take them offline.
✔ Malware & spyware
Malicious software designed to steal or destroy information.
✔ Zero-day exploits
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities before patches are available.
✔ Social engineering
Manipulating people instead of systems.
Cyber threats are becoming more frequent — and more advanced. That’s why information security strategies must continuously evolve.
Information Security Frameworks Businesses Rely on
The most common frameworks include:
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Provides a simple, flexible guide to building a strong InfoSec program.
2. ISO/IEC 27001
A global standard for information security management systems (ISMS).
3. CIS Critical Security Controls
A prioritized list of the most effective defensive measures.
4. SOC 2
Commonly used by SaaS companies and cloud service providers.
5. Zero-Trust Architecture
“Never trust, always verify” — the future of access security.
These frameworks help organizations strengthen processes, reduce risk, and maintain compliance.
🧭 How Information Security Works (Step-by-Step Process)
To truly understand what is information security, let’s break down how an InfoSec program is implemented.
Step 1: Identify Your Information Assets
Data, devices, cloud services, networks, users.
Step 2: Perform a Risk Assessment
Identify vulnerabilities, threats, and impact.
Step 3: Implement Security Controls
Controls may be:
-
Administrative (policies, training)
-
Technical (firewalls, EDR, encryption)
-
Physical (locks, cameras)
Step 4: Monitor Continuously
Use tools like:
-
SIEM
-
EDR
-
Network monitoring
-
Threat intelligence feeds
Step 5: Respond & Recover
Incident response includes:
-
Containment
-
Eradication
-
Forensics
-
Recovery
-
Documentation
🔐 How Information Security Protects Your Organization
Information security has enormous benefits.
✔ Prevents data breaches
✔ Reduces financial loss
✔ Protects brand reputation
✔ Supports compliance
✔ Improves customer trust
✔ Enhances operational stability
✔ Detects threats early
A strong InfoSec program is a competitive advantage, not just a technical requirement.
🛠️ Essential Tools Used in Information Security
Here are the top categories:
⭐ Endpoint detection (EDR/XDR)
Detects and responds to device threats.
Example: OpenEDR
⭐ Firewalls & network protection
Blocks intrusions and suspicious connections.
⭐ Vulnerability scanners
Identify weaknesses before attackers do.
⭐ SIEM systems
Centralized logging and real-time analytics.
⭐ Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Controls who can access what.
⭐ Backup & recovery tools
Protect data from loss or ransomware.
These tools work together to enforce security across the entire ecosystem.
Information Security Best Practices (2026 Edition)
To stay ahead of emerging threats, follow these best practices:
✔ Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
✔ Keep all software updated
✔ Train employees frequently
✔ Encrypt sensitive data
✔ Implement zero-trust security
✔ Monitor endpoints with EDR
✔ Back up all critical data
✔ Use strong password policies
✔ Conduct regular penetration tests
✔ Review access permissions quarterly
These proactive steps dramatically reduce the risk of breaches.
🤝 Information Security vs. Cybersecurity: What’s the Difference?
Many people think they are the same — but they’re not.
✔ Information security = Protects all information (digital + physical).
✔ Cybersecurity = Protects digital assets and networks from cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity is actually part of the larger information security discipline.
🎯 Conclusion: Information Security Is the Backbone of Modern Business
If you’re still wondering what is information security, the answer is simple:
It’s how you safeguard your organization’s most valuable asset — information.
In a world filled with cyber threats, stronger security frameworks, and complicated compliance requirements, having a solid InfoSec strategy is no longer optional. It’s essential for protecting your business, employees, and customers.
But strong information security starts with one critical layer: endpoint protection.
🔐 Protect Every Endpoint With Xcitium (FREE Demo Available)
Experience enterprise-grade threat containment and detection.
👉 https://www.xcitium.com/request-demo/
❓ FAQs About Information Security
1. What is information security in simple terms?
It’s the protection of information from unauthorized access, misuse, or damage.
2. What is the purpose of information security?
To protect confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
3. Is information security the same as cybersecurity?
No — cybersecurity focuses on digital threats, while InfoSec covers digital + physical information.
4. What are common risks in information security?
Phishing, ransomware, malware, insider threats, and misconfigurations.
5. What tools help protect information?
EDR systems, firewalls, encryption tools, SIEM, IAM, and vulnerability scanners.