What Is Edge Computing? The Future of Faster, Smarter, and Safer Data Processing
Updated on July 29, 2025, by Xcitium
In a world where every millisecond matters, especially in cybersecurity and enterprise environments, speed and efficiency are everything. That’s where edge computing steps in. But what is edge computing, and how is it reshaping industries like IoT, finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity?
This comprehensive guide unpacks everything from edge computing architecture to real-world applications. Whether you’re a CTO, cybersecurity professional, or business leader, this article will help you understand how this cutting-edge technology works—and why it matters.
🔍 What Is Edge Computing?
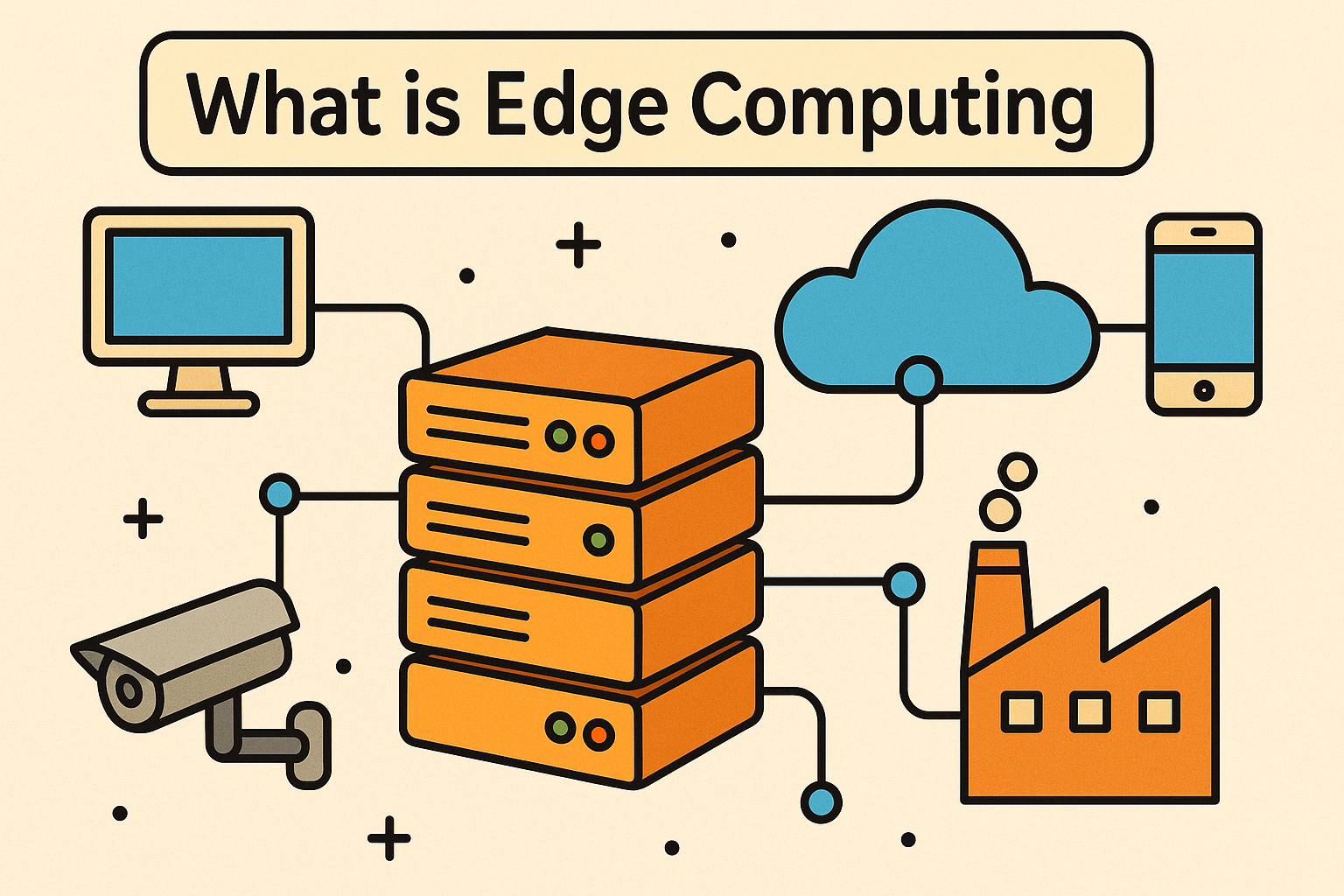
At its core, edge computing is a distributed computing framework that brings data storage and processing closer to the source of data generation—whether that’s IoT sensors, mobile devices, or factory-floor machinery.
Unlike traditional cloud models that rely on centralized data centers, edge computing devices perform computations “at the edge” of the network. This drastically reduces latency, improves speed, enhances privacy, and helps in real-time decision-making.
✅ Primary benefit: Less data travels to the cloud = faster, more secure processing.
🆚 What Is Edge Computing and Cloud Computing?
While cloud computing centralizes resources in massive remote data centers, edge computing decentralizes computing to local or on-premises systems. Both are often used together in hybrid environments.
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
| Latency | Higher (remote servers) | Lower (local processing) |
| Bandwidth Usage | High | Lower |
| Use Cases | Data backup, analytics | Real-time processing, IoT |
| Scalability | Excellent | Moderate (device-dependent) |
⚙️ How Does Edge Computing Work?
Here’s how the edge computing architecture typically operates:
- Data is generated by devices (sensors, smartphones, etc.)
- It’s processed locally on edge nodes or gateways
- Only relevant data is sent to the cloud for long-term storage or deeper analysis
Edge nodes may include:
- Routers and switches
- IoT devices
- Local servers
- Smart appliances
This localized computation enables faster response times and reduces exposure to external cyber threats.
🧠 What Is Edge Computing in IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the biggest beneficiaries of edge computing. Why? Because connected devices produce massive amounts of data—far too much to send back and forth to the cloud.
Example:
A smart thermostat in a factory detects an overheating motor. Using edge computing, it can:
- Analyze the data instantly
- Trigger an alarm
- Shut down machinery
All within milliseconds—no cloud delay.
🚀 Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing is not just a buzzword. It’s powering mission-critical applications across industries:
🏥 Healthcare:
- Real-time patient monitoring
- Portable diagnostic tools
- On-premise imaging analysis
🚗 Automotive:
- Autonomous driving (real-time sensor data)
- Traffic management systems
🏭 Manufacturing:
- Predictive maintenance
- Automated quality control
🏢 Enterprise IT:
- Data loss prevention
- Cybersecurity threat detection
⭐ Advantages of Edge Computing
Why is edge computing gaining so much traction? Let’s explore the major benefits:
- Reduced Latency: Faster data processing where it’s needed
- Enhanced Security: Limits exposure to cloud-based threats
- Bandwidth Savings: Less need to transfer large datasets
- Operational Efficiency: Faster decision-making = better performance
- High Availability: Operates even with limited cloud access
📡 Edge Computing Devices You Should Know
Some common edge devices include:
- IoT sensors
- Smart cameras
- Local edge servers
- Network gateways
- Mobile phones
- Edge-enabled routers
These are often embedded with processors capable of running AI or ML algorithms.
🧩 Challenges of Edge Computing
Like all technologies, edge computing isn’t without its hurdles:
- Security Risks: More endpoints = more attack surfaces
- Device Management: Harder to update and monitor dispersed devices
- Limited Resources: Some devices have low storage/processing capabilities
- Standardization: Varying protocols and hardware architectures
Still, its benefits far outweigh the drawbacks when paired with solid endpoint protection.
🛡️ Edge Computing & Cybersecurity: A Crucial Alliance
In cybersecurity, edge computing adds an extra layer of defense by processing data locally, minimizing exposure to internet-based attacks.
Cyber Benefits:
- Localized intrusion detection
- Fast response to ransomware or malware threats
- More control over sensitive data (especially in regulated industries)
🤖 Future of Edge Computing
By 2025, Gartner predicts that 75% of enterprise-generated data will be created and processed outside a traditional data center or cloud.
Emerging trends include:
- AI at the Edge
- 5G-enhanced edge computing
- Micro data centers
- Cloud-native edge platforms
🙋 FAQ: What Is Edge Computing?
1. What is edge computing with example?
Edge computing processes data near its source. Example: A self-driving car making split-second decisions without relying on a remote server.
2. What are the advantages of edge computing?
Key benefits include lower latency, better data privacy, and reduced cloud bandwidth usage.
3. How does edge computing differ from cloud computing?
Cloud computing is centralized; edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby nodes.
4. What is edge computing in IoT?
It allows IoT devices to process data locally, enabling real-time responses and reducing cloud dependency.
5. What are examples of edge computing devices?
Routers, IoT sensors, edge servers, and smart appliances.
✅ Conclusion
So, what is edge computing? It’s the decentralized future of real-time data processing, poised to transform everything from cybersecurity to smart cities. By handling data closer to the source, businesses can achieve greater speed, security, and efficiency.
Whether you’re integrating IoT, optimizing infrastructure, or enhancing threat detection—edge computing is no longer optional. It’s essential.
👉 Want to Future-Proof Your Cybersecurity with Edge?
Let Xcitium help you integrate edge computing into your enterprise security strategy.