What Is DDoSing? Understanding the Threat and How to Defend Against It
Updated on October 9, 2025, by Xcitium
Imagine your business website suddenly becomes inaccessible—customers can’t log in, employees can’t access cloud systems, and every second of downtime costs thousands of dollars. This scenario often results from a DDoS attack. But what is DDoSing, and why should IT managers, cybersecurity leaders, and CEOs care?
Introduction: Why You Need to Understand DDoSing
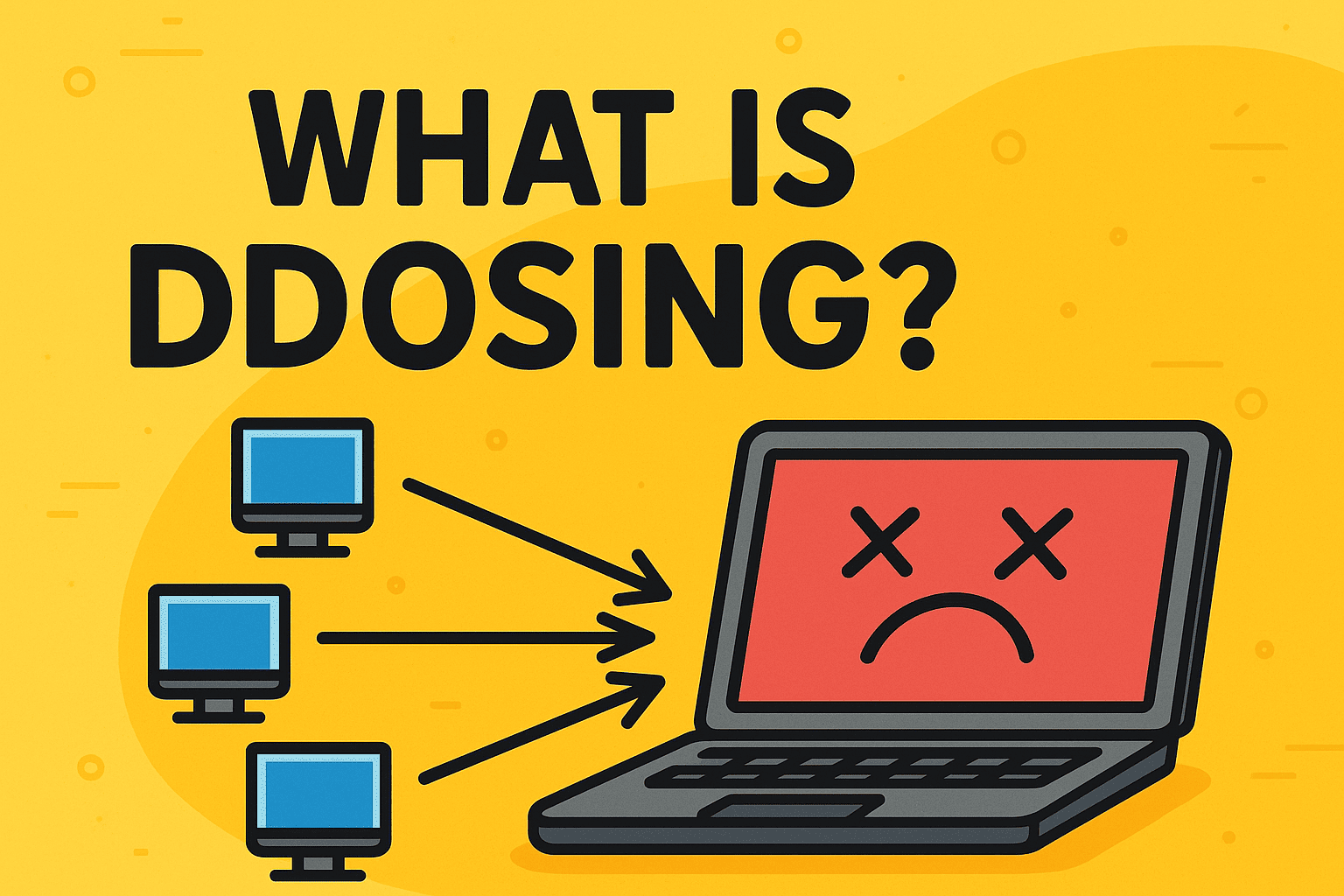
DDoSing, short for Distributed Denial-of-Service, is a type of cyberattack where multiple compromised systems flood a target with massive amounts of traffic, overwhelming it until it crashes. As digital operations become the backbone of every industry, understanding DDoSing is essential to safeguarding online infrastructure and reputation.
What Is DDoSing?
At its core, DDoSing refers to the act of launching a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack. Unlike a standard Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack that originates from a single system, a DDoS attack leverages thousands—or even millions—of compromised devices to overwhelm a server, network, or service.
How It Works:
-
Botnet Creation: Hackers infect computers, IoT devices, or servers with malware.
-
Command & Control: Attackers remotely control these compromised systems.
-
Traffic Flooding: The botnet floods the target system with illegitimate requests.
-
System Crash: The victim’s resources are exhausted, leading to downtime or total shutdown.
👉 In short, DDoSing turns innocent devices into weapons against businesses.
Types of DDoS Attacks
Not all DDoS attacks are the same. Cybercriminals use different strategies depending on their target’s weaknesses.
Common Forms of DDoSing:
-
Volumetric Attacks: Overwhelm bandwidth with high traffic.
-
Protocol Attacks: Exploit weaknesses in server protocols (e.g., SYN floods).
-
Application Layer Attacks: Target specific web applications with fake requests.
-
Multi-Vector Attacks: Combine different techniques for maximum disruption.
Why Businesses Should Worry About DDoSing
The cost of a DDoS attack extends far beyond temporary downtime.
Business Impacts:
-
Financial Losses: Average cost per DDoS incident can reach millions.
-
Reputation Damage: Customers lose trust in unreliable services.
-
Security Breach Risks: Attackers may use DDoSing as a distraction to infiltrate networks.
-
Operational Disruption: Productivity halts when critical services go offline.
👉 For industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, DDoSing can be catastrophic.
Real-World Examples of DDoS Attacks
-
Dyn Attack (2016): A massive DDoS attack disrupted major websites like Twitter, Netflix, and Reddit.
-
GitHub Attack (2018): One of the largest attacks, peaking at 1.35 terabits per second.
-
Banking Sector Attacks: Financial institutions frequently face DDoS threats as part of extortion schemes.
These incidents highlight why understanding what is DDoSing is critical for cybersecurity planning.
Warning Signs of a DDoS Attack
Early detection is vital. Here are signs your organization might be under attack:
-
Unusually slow network performance.
-
Website outages or timeouts.
-
Suspicious traffic spikes from multiple geolocations.
-
Service disruptions without hardware or software failures.
👉 Proactive monitoring helps distinguish between legitimate traffic surges and malicious floods.
How to Prevent DDoS Attacks
Stopping DDoSing requires a layered security strategy.
Best Practices for Protection:
-
Deploy a Web Application Firewall (WAF): Blocks malicious requests.
-
Use Anti-DDoS Services: Cloud providers like AWS Shield or Cloudflare mitigate attacks.
-
Monitor Network Traffic: Continuous analytics detect anomalies early.
-
Rate Limiting: Restrict the number of requests from suspicious IPs.
-
Incident Response Plan: Prepare teams with a clear playbook for attacks.
Cybersecurity leaders should invest in preventive measures before an attack happens, not after.
The Role of IT Managers and Cybersecurity Teams
IT leaders are on the frontline of defending against DDoSing. Their responsibilities include:
-
Establishing security policies to mitigate risks.
-
Training staff on identifying suspicious activity.
-
Coordinating with Internet Service Providers (ISPs) during attacks.
-
Investing in advanced detection systems and endpoint security.
👉 For CEOs and founders, supporting these initiatives is not optional—it’s business-critical.
Future Trends in DDoSing
As technology evolves, so do attackers. Emerging trends include:
-
IoT Botnets: Millions of unsecured devices create powerful attack networks.
-
AI-Driven Attacks: Smarter DDoS strategies adapt in real time.
-
Ransom DDoS (RDoS): Attackers demand payment to stop an attack.
-
5G Exploitation: Higher speeds could fuel faster, larger-scale DDoS campaigns.
Businesses must evolve cyber defense strategies to stay ahead of these threats.
FAQs: What Is DDoSing?
1. What is the difference between DoS and DDoS?
DoS comes from a single source, while DDoS involves multiple systems flooding a target.
2. Can DDoSing cause permanent damage?
While it rarely causes physical damage, it can cripple operations, drain revenue, and harm brand reputation.
3. Is DDoSing illegal?
Yes. Launching or participating in a DDoS attack is a criminal act with severe penalties.
4. Can small businesses be targeted?
Absolutely. Hackers often target smaller companies due to weaker defenses.
5. How can I protect my company from DDoSing?
By combining anti-DDoS services, firewalls, monitoring tools, and employee training.
Conclusion: Staying Resilient Against DDoSing
So, what is DDoSing? It’s one of the most disruptive forms of cyberattacks, capable of shutting down businesses, damaging reputations, and exposing sensitive data. For IT managers, cybersecurity leaders, and CEOs, preparing for these attacks is not optional—it’s a necessity.
With the right prevention strategies, monitoring systems, and response plans, businesses can reduce the risk of DDoS-related downtime and maintain customer trust.
👉 Take the next step in securing your organization. Request a Demo today and build resilience against cyber threats.