What is an DHCP? Understanding the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Updated on July 9, 2025, by Xcitium
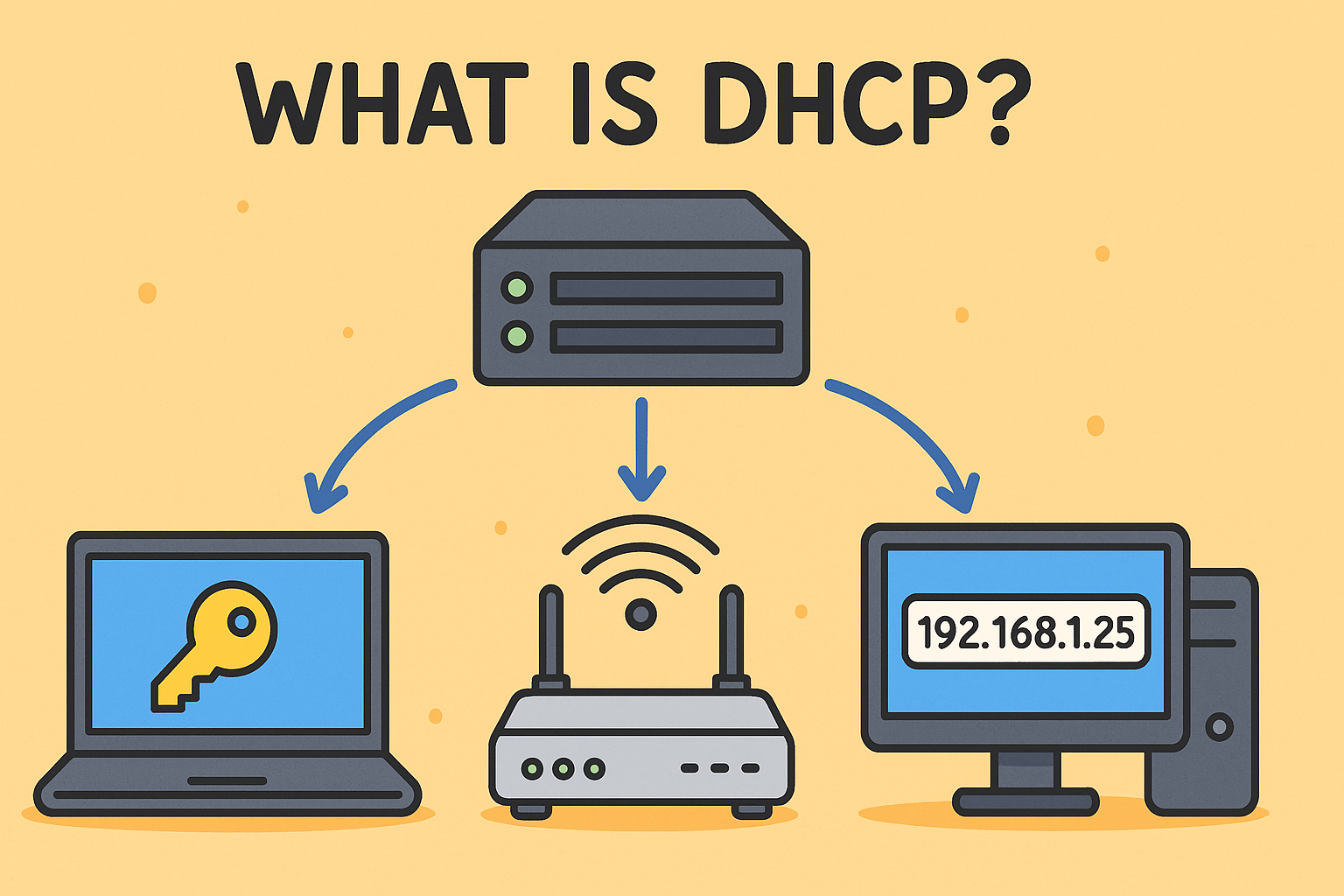
Have you ever wondered how your devices get their IP addresses when you connect to the internet or office network? The answer lies in a critical networking protocol called DHCP.
So, what is an DHCP?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices on a network. This means your computer, phone, or printer doesn’t need to be manually configured every time it connects.
In this post, we’ll cover how DHCP works, why it’s essential for modern networks, the DORA process, and how it compares to static IP addressing.
What is an DHCP?
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a client/server protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses to devices in a network. This helps avoid IP conflicts and reduces administrative tasks.
🎯 Primary keyword used: what is an DHCP
Without DHCP, IT teams would have to manually configure IPs on every device—a time-consuming and error-prone task.
How DHCP Works
Here’s a simplified explanation of how DHCP operates in a network:
- Step 1: A device (DHCP client) joins a network.
- Step 2: It sends a broadcast message requesting an IP.
- Step 3: The DHCP server receives the request and assigns an IP along with gateway and DNS details.
- Step 4: The device now communicates using the assigned IP.
This process happens in a few milliseconds, making it seamless for end users.
Understanding the DORA Process in DHCP
The DORA process outlines the four key steps in a DHCP transaction:
- D – Discover: The client sends a broadcast to find available DHCP servers.
- O – Offer: A DHCP server responds with an available IP address offer.
- R – Request: The client accepts one of the offers and requests the IP lease.
- A – Acknowledge: The DHCP server confirms and leases the IP.
This DORA handshake ensures smooth, conflict-free IP assignment.
Enable DHCP vs Static IP
You can either enable DHCP or manually assign a static IP to your device. Here’s how they differ:
| Feature | DHCP | Static IP |
| IP Assignment | Automatic | Manual |
| Ease of Use | Easy for large networks | More control, but time-consuming |
| IP Consistency | IP may change | IP remains fixed |
| Ideal For | Home, guest, dynamic environments | Servers, printers, static networks |
In most business environments, DHCP is the default because of its efficiency.
DNS vs DHCP: What’s the Difference?
While DNS and DHCP both support networking, they serve different functions:
- DHCP assigns IP addresses dynamically.
- DNS (Domain Name System) translates domain names (like example.com) into IP addresses.
In short:
- DHCP = IP assignment
- DNS = IP resolution
Together, they enable seamless communication on the internet.
DHCP Port and Protocol Details
DHCP uses the UDP protocol and operates on two ports:
- UDP Port 67 for the server
- UDP Port 68 for the client
Because DHCP relies on broadcast messages, it’s typically limited to the local subnet unless DHCP relays are configured.
Security Implications and Best Practices
Although DHCP simplifies network management, it introduces security risks:
Risks:
- Rogue DHCP Servers: An attacker can introduce a fake DHCP server to distribute malicious settings.
- Unauthorized Devices: DHCP might assign IPs to unauthorized systems if not properly managed.
Best Practices:
- Use MAC filtering or Network Access Control (NAC).
- Secure physical access to network ports.
- Implement DHCP snooping on switches.
- Monitor for DHCP starvation attacks.
Final Thoughts:
Now you understand what is an DHCP, how it works, and how it differs from static IPs and DNS. In enterprise environments, DHCP is the cornerstone of scalable, efficient network management.
But with ease comes responsibility—especially in cybersecurity. IT professionals must ensure DHCP configurations are secure, monitored, and aligned with best practices.
✅ Want Help Securing Your Network?
Let Xcitium help you build a secure, scalable, and threat-proof infrastructure.
FAQs
1. What is the main function of DHCP?
DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configurations to client devices on a network.
2. What is the DORA process in DHCP?
DORA stands for Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge. It’s the 4-step process used to assign an IP address to a client.
3. Is DHCP better than static IP?
Yes, in dynamic environments. DHCP reduces manual effort and prevents IP conflicts, though static IPs are still preferred for servers and critical devices.
4. Which ports does DHCP use?
DHCP uses UDP ports 67 (server) and 68 (client).
5. How do I enable DHCP on my router?
Log into your router’s admin panel, find the DHCP settings under LAN or Network settings, and ensure it’s enabled.