Algorithms Are Everywhere—But What Are They?
Updated on June 10, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever wondered how search engines rank results, how Netflix recommends your next binge, or how firewalls detect threats in real time? All of these tasks rely on one fundamental concept: algorithms.
So, what is an algorithm? An algorithm is a finite set of well-defined instructions or steps designed to perform a specific task or solve a problem. In cybersecurity, IT infrastructure, and software development, algorithms are the silent engines powering automation, analytics, and decision-making.
Whether you’re an IT manager streamlining operations or a CEO driving data strategy, understanding algorithms is crucial to staying competitive and secure.
What is an Algorithm?
At its core, an algorithm is a precise procedure or formula for solving a problem. Think of it like a recipe: it tells a computer exactly what steps to take, in what order, and under what conditions.
Key Characteristics of Algorithms:
- Finite – They complete after a limited number of steps.
- Unambiguous – Each step is clearly and logically defined.
- Effective – Each instruction is executable.
- Input/Output – Algorithms consume inputs and generate outputs.
In computing, algorithms are the basis of everything from antivirus software to AI-based threat detection.
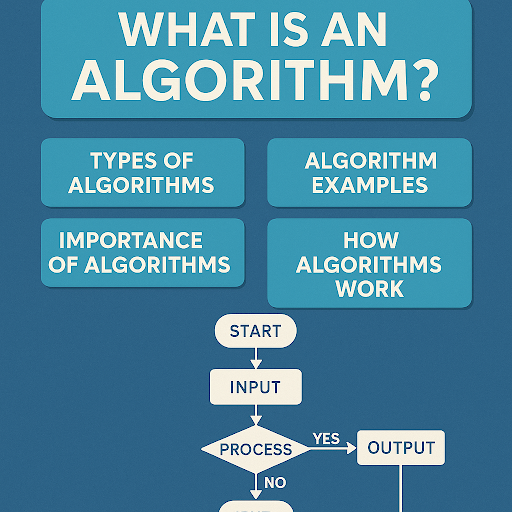
How Algorithms Work: The Basics Explained
To better understand how algorithms work, let’s break the process into key steps:
- Define the Problem – What needs to be solved?
- Input Collection – Gather data or conditions to process.
- Logic Execution – Follow the sequence of steps based on conditions or iterations.
- Output Generation – Return a result or trigger an action.
- Optimization – Evaluate and refine for speed and accuracy.
Real-World Analogy:
Think of an algorithm like a GPS. You input your destination (goal), and the system calculates the shortest or fastest route (the solution).
Algorithms can be implemented using pseudocode, flowcharts, or coding languages like Python, Java, or C++.
Types of Algorithms: From Basics to Advanced
Algorithms can be categorized in many ways, depending on their design and use case. Below are the main types of algorithms:
1. Sorting Algorithms
Used to arrange data in a particular order (e.g., ascending or descending).
- Examples: QuickSort, MergeSort, BubbleSort
2. Searching Algorithms
Used to locate a specific item in a dataset.
- Examples: Binary Search, Linear Search
3. Recursive Algorithms
Break a problem into smaller instances of itself.
- Example: Calculating factorial, Tower of Hanoi
4. Greedy Algorithms
Make the best decision at each step for a local optimum.
- Example: Huffman Encoding, Dijkstra’s Algorithm
5. Dynamic Programming
Solve complex problems by breaking them into simpler sub-problems and storing results.
- Example: Fibonacci sequence, Knapsack problem
6. Backtracking Algorithms
Try all possibilities and backtrack when a condition fails.
- Example: N-Queens, Sudoku Solver
Algorithm Examples in Real Life
Let’s explore where algorithm examples show up in everyday cybersecurity, IT, and digital workflows:
🔐 In Cybersecurity
- Signature-based malware detection uses pattern-matching algorithms.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) employ anomaly detection algorithms.
- Firewall rulesets follow decision-tree-like logic.
💻 In IT Operations
- Load balancing algorithms like Round Robin ensure uptime.
- Backup rotation schemes follow fixed scheduling logic.
- Disk scheduling algorithms optimize I/O operations.
🧠 In Machine Learning
- K-Nearest Neighbors, Random Forest, and Gradient Boosting are algorithm families for classification and prediction tasks.
🛒 In Business
- Recommendation algorithms personalize user experience (e.g., Netflix, Amazon).
- Fraud detection algorithms flag suspicious behavior in banking.
The Importance of Algorithms in Modern Technology
Understanding the importance of algorithms helps leaders make informed decisions about the technologies they implement.
Why Algorithms Matter:
- Speed & Efficiency – Automate processes at scale.
- Security – Algorithms power encryption, authentication, and anomaly detection.
- Scalability – Well-optimized algorithms adapt to increasing data loads.
- Cost Savings – Reduce manual work and human error.
- Innovation – Algorithms are the core of AI, data science, and cloud computing.
In a data-driven world, algorithms turn raw inputs into actionable insights.
Common Myths About Algorithms (Debunked)
| Myth | Truth |
| Algorithms are only for programmers | Business leaders use algorithm-based tools daily |
| More complex means better | Simpler algorithms can be more effective and easier to maintain |
| Algorithms are always neutral | Algorithms can inherit bias from data or design |
| You need to code to understand them | Visuals and examples can help anyone grasp algorithm logic |
How to Choose the Right Algorithm
If you’re building or evaluating a system, here’s how to pick the right algorithm:
- Understand the Problem Domain
Is it a search problem? Optimization? Pattern recognition? - Define the Data Type
Structured, unstructured, text, images, or real-time streams? - Analyze Time & Space Complexity
Will it scale with growth? - Consider Accuracy vs. Speed
Do you need real-time answers or 99.99% accuracy? - Test with Real Scenarios
Simulate your algorithm under real-world conditions.
Conclusion: Algorithms Are the Invisible Workforce of the Digital Era
If you’ve been wondering what is an algorithm, the answer goes far beyond textbook definitions. Algorithms are the engines that drive cybersecurity, optimize IT operations, power AI, and transform business decision-making.
By understanding how they work—and what types are best suited for your goals—you equip yourself with the insight to lead smarter, faster, and more secure innovation.
🔗 Want to secure your infrastructure with intelligent automation? Request a free demo and see how algorithm-driven cybersecurity tools protect your business.
FAQs: Common Questions About Algorithms
1. What is an algorithm in simple terms?
An algorithm is a step-by-step set of instructions used to solve a specific problem or complete a task.
2. What are some common types of algorithms?
Sorting, searching, recursion, greedy, dynamic programming, and backtracking are commonly used types.
3. Where are algorithms used in cybersecurity?
They’re used in encryption, intrusion detection, malware analysis, and secure communications.
4. Are algorithms always written in code?
No. Algorithms can be written as flowcharts, pseudocode, or even natural language before being coded.
5. Can algorithms be biased?
Yes. If algorithms are trained or designed using biased data, they may produce biased outcomes.