Encryption What Is: The Complete Guide for Business Leaders and IT Professionals
Updated on August 25, 2025, by Xcitium
In today’s digital-first world, cyberattacks are not a question of if but when. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024, the global average cost of a breach reached $4.88 million. That’s why every IT manager, CEO, or security leader is asking the same question: Encryption what is, and how does it protect my business?
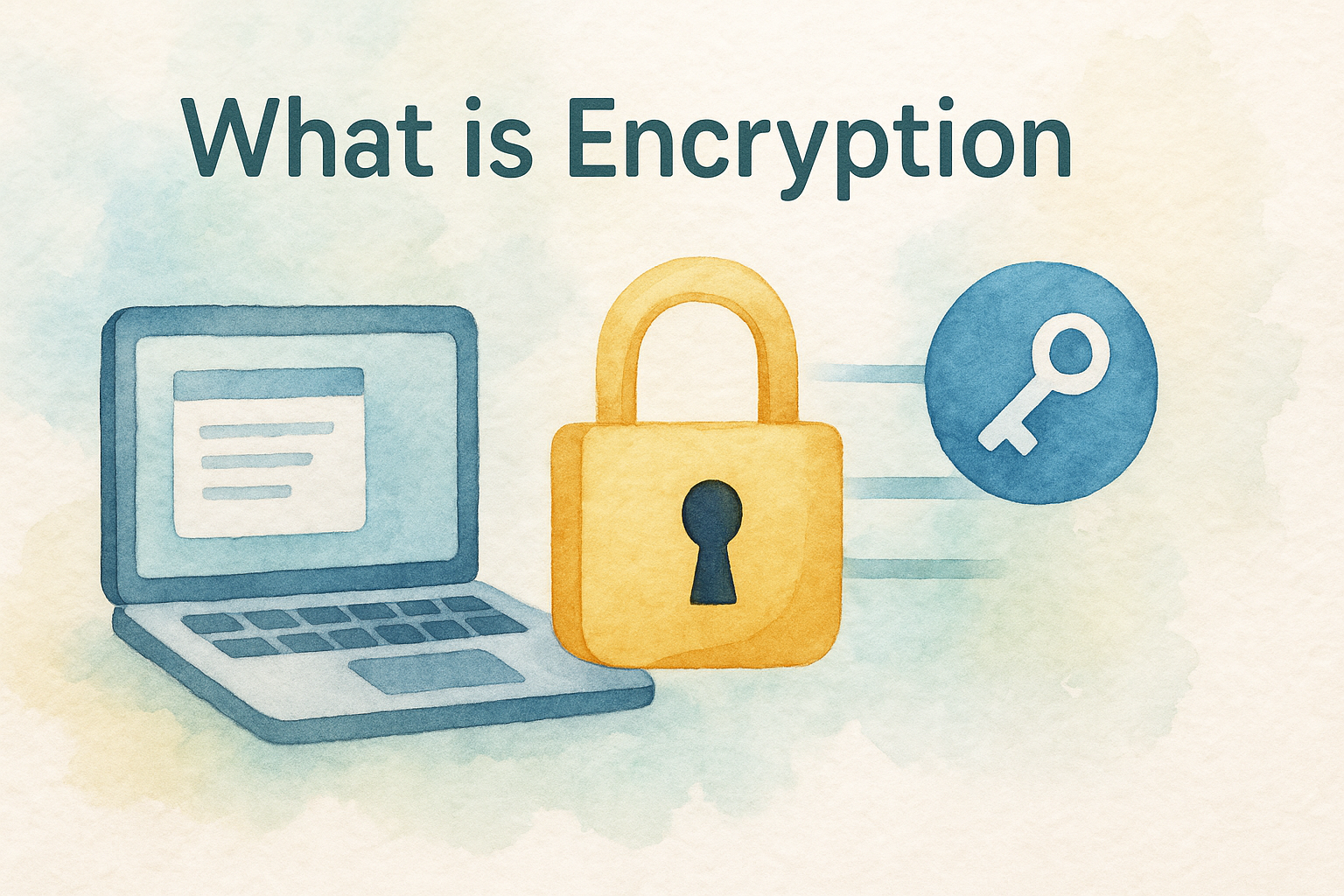
Encryption is the foundation of data security. It converts readable data into an unreadable format, ensuring that only authorized users with the correct key can access it. Whether it’s protecting financial transactions, securing employee communications, or safeguarding intellectual property, encryption plays a critical role in modern cybersecurity.
What Is Encryption?
At its core, encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Imagine sending a confidential letter locked inside a safe — only the person with the right key can open it.
Key Characteristics of Encryption:
- Confidentiality: Keeps sensitive data private.
- Integrity: Prevents data from being altered during transfer.
- Authentication: Verifies the sender/receiver.
- Non-repudiation: Ensures proof of data origin.
In cybersecurity, encryption is one of the most powerful ways to protect data — whether stored on a server, transmitted via email, or shared in the cloud.
How Encryption Works
Encryption relies on mathematical algorithms and cryptographic keys.
- Plaintext: Original readable data (e.g., a password).
- Algorithm: The formula that scrambles data.
- Key: A unique code used to encrypt/decrypt.
- Ciphertext: The scrambled, unreadable output.
- Decryption: The process of converting ciphertext back into plaintext.
For example, if you send a message like “Meet at 3 PM”, encryption converts it into something like “X5G7d9Qz”. Only the person with the right key can unlock and read it.
Types of Encryption
1. Symmetric Encryption
- Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption.
- Faster but less secure if the key is exposed.
- Common algorithms: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
2. Asymmetric Encryption
- Uses two keys: a public key (for encryption) and a private key (for decryption).
- Common in digital certificates, SSL/TLS.
- Algorithms: RSA, ECC.
3. Hashing (One-Way Encryption)
- Converts data into a fixed-length value.
- Commonly used for password storage.
- Example: SHA-256.
4. End-to-End Encryption
- Ensures only the sender and recipient can read messages.
- Used in apps like WhatsApp, Signal, and enterprise communications.
Why Businesses Need Encryption
Cybersecurity is no longer optional. For executives and IT managers, here’s why encryption is non-negotiable:
- Regulatory Compliance: Required under GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and CCPA.
- Data Breach Prevention: Encrypted data is useless to hackers without the decryption key.
- Customer Trust: Encrypted communications foster confidence.
- Business Continuity: Prevents reputational and financial loss.
Industries Most at Risk:
- Finance & Banking – Protecting transactions and customer records.
- Healthcare – Safeguarding patient health information (PHI).
- E-commerce – Securing payment data.
- Technology & SaaS – Protecting intellectual property and customer accounts.
Real-World Use Cases of Encryption
- Cloud Storage Security – Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive use encryption for stored files.
- Online Banking – SSL/TLS encryption protects online transactions.
- Corporate Communications – Encrypted email and messaging platforms prevent data leaks.
- Mobile Devices – iPhones and Androids use full-disk encryption to secure user data.
Benefits of Implementing Encryption
- 🔒 Stronger Data Security
- ⚡ Fast and Reliable Performance with modern algorithms
- 📊 Regulatory Compliance simplified
- 👥 Customer Confidence boosted
- 🛡️ Reduced Financial Risk in case of a breach
Challenges of Encryption
While encryption is essential, it comes with challenges:
- Key Management: Lost keys can mean lost data.
- Performance Impact: Complex encryption can slow systems.
- Implementation Errors: Poorly implemented encryption can create vulnerabilities.
Solution? Partner with trusted cybersecurity providers that offer enterprise-grade encryption tools and robust key management systems.
Best Practices for Strong Encryption
To maximize security:
- ✅ Use AES-256 for sensitive data.
- ✅ Regularly rotate keys.
- ✅ Apply end-to-end encryption for communications.
- ✅ Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- ✅ Audit and test encryption systems regularly.
FAQ: Encryption What Is and Why It Matters
- What is encryption in simple terms?
Encryption is the process of converting readable data into an unreadable format to protect it from unauthorized access. - Is encryption 100% secure?
No system is 100% foolproof, but strong encryption makes it extremely difficult for hackers to break in. - What is the strongest encryption today?
AES-256 is widely regarded as the strongest commercially available encryption standard. - Do small businesses need encryption?
Yes, small businesses are often targeted by cybercriminals because they typically have weaker defenses. - What is the difference between encryption and hashing?
Encryption can be reversed with a key, while hashing is one-way and cannot be reversed.
Conclusion: Secure Your Future with Encryption
Encryption is no longer optional — it is the foundation of cybersecurity. From protecting customer data to meeting compliance standards, businesses must prioritize strong encryption strategies.
If you’re ready to safeguard your business with enterprise-grade cybersecurity, Request a Free Demo from Xcitium today and see how encryption can transform your security posture.