Why Machine Learning Is Reshaping the Future of Technology
Updated on June 10, 2025, by Xcitium

Can machines really learn like humans? If you’ve ever used a voice assistant, received a fraud alert from your bank, or seen product recommendations online, you’ve interacted with machine learning—a technology that’s rapidly transforming how we work, live, and secure our data.
So, what is machine learning? It’s a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables systems to automatically learn from data and improve without being explicitly programmed. From cybersecurity defenses to predictive analytics, machine learning is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s mission-critical for IT managers, security professionals, and tech-forward CEOs.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning (ML) is a field of computer science that uses statistical techniques to enable machines to learn from data and make decisions or predictions. Unlike traditional programming where rules are hard-coded, machine learning systems identify patterns and adapt based on new input.
Key Characteristics of Machine Learning:
- Learns from data (past experiences)
- Improves performance over time
- Makes predictions or classifications
- Works without explicit instructions
In essence, machine learning empowers systems to act intelligently, without human intervention.
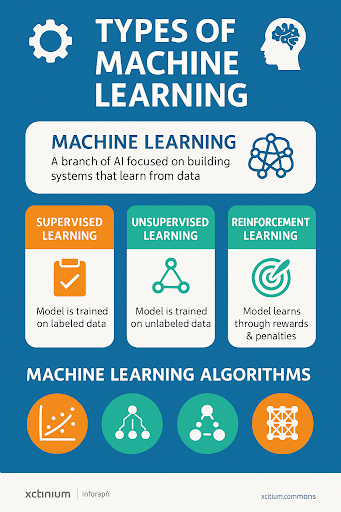
Types of Machine Learning
There are three primary types of machine learning, each suited to different business problems and data scenarios:
1. Supervised Learning
The most common type, where the algorithm is trained on labeled data. It learns from examples and applies the learning to new, unseen data.
Use Cases: Email spam detection, credit scoring, fraud detection
2. Unsupervised Learning
The system is given unlabeled data and must find patterns, such as grouping or clustering.
Use Cases: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection, recommendation engines
3. Reinforcement Learning
The model learns through trial and error by receiving rewards or penalties based on its actions in a dynamic environment.
Use Cases: Robotics, game AI, automated trading systems
Machine Learning Algorithms: The Building Blocks
Machine learning algorithms are the engines that power intelligent systems. Here are the most widely used ones:
| Algorithm | Type | Purpose |
| Linear Regression | Supervised | Predict numeric outcomes |
| Decision Trees | Supervised | Classification & regression |
| K-Means Clustering | Unsupervised | Group data into clusters |
| Support Vector Machines | Supervised | Classify data with clear margins |
| Random Forest | Supervised | Ensemble method for high accuracy |
| Neural Networks | Both | Mimic brain-like processing for complex tasks |
Each algorithm has strengths depending on the dataset size, structure, and business goals.
Machine Learning vs AI: What’s the Difference?
Though often used interchangeably, machine learning and AI are not the same.
| Aspect | Machine Learning | Artificial Intelligence |
| Definition | Enables systems to learn from data | Mimics human intelligence |
| Scope | Subset of AI | Broad field encompassing ML, NLP, robotics |
| Goal | Improve prediction accuracy | Achieve intelligent behavior |
| Example | Spam filter, image recognition | Chatbots, autonomous vehicles |
So while machine learning is a subset of AI, not all AI systems use machine learning.
Applications of Machine Learning Across Industries
Machine learning is redefining how businesses operate, especially in cybersecurity, IT infrastructure, and enterprise software.
🔐 Cybersecurity
- Threat detection and prevention
- Malware classification
- Behavioral analytics for insider threats
🖥️ IT Operations
- Predictive maintenance
- Log anomaly detection
- Capacity planning
💼 Business Use Cases
- Customer churn prediction
- Sales forecasting
- Dynamic pricing
🏥 Healthcare
- Disease prediction
- Diagnostic imaging
- Drug discovery
ML turns raw data into actionable intelligence across sectors.
Benefits of Machine Learning in Enterprise Environments
For IT managers and CISOs, the benefits of machine learning are strategic and measurable:
- Enhanced Security: ML models detect threats faster than rule-based systems.
- Scalability: Automates tasks that scale with data growth.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduces false positives in alerts and predictions.
- Real-Time Decision-Making: Powers intelligent automation in critical systems.
- Competitive Advantage: Drives innovation in products and services.
Getting Started with Machine Learning
If you’re exploring how to implement machine learning in your organization, here’s a roadmap:
- Define the Business Problem – What are you trying to predict or improve?
- Collect and Prepare Data – Ensure data quality, structure, and labeling.
- Choose the Right Algorithm – Based on your problem type (classification, regression, etc.)
- Train and Validate – Split your data into training and testing sets.
- Deploy and Monitor – Integrate into real-world systems and refine with new data.
Best Practices for Machine Learning in Secure Environments
- Use secure data pipelines and encrypted storage
- Regularly audit training datasets for bias or leakage
- Monitor models in production for drift and performance degradation
- Integrate DevSecOps principles into your ML lifecycle
- Comply with privacy laws like GDPR, HIPAA
Conclusion: Why Now is the Time to Invest in Machine Learning
Understanding what machine learning is isn’t just about grasping algorithms—it’s about embracing a smarter, faster, and more secure way to drive decisions. Whether you’re defending enterprise networks, optimizing IT systems, or exploring digital transformation, machine learning offers the tools to lead the future.
🔗 Want to see machine learning in action? Request a demo to explore how it can transform your cybersecurity and IT strategy.
FAQs: What People Also Ask About Machine Learning
1. What is machine learning in simple terms?
Machine learning is a way for computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being manually programmed.
2. Is machine learning the same as AI?
No. Machine learning is a part of AI. AI is the broader concept of machines acting intelligently, and ML is one way to achieve that.
3. What are examples of machine learning applications?
Examples include spam filters, fraud detection, recommendation systems, and predictive maintenance.
4. What industries use machine learning?
Cybersecurity, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, and more use ML to improve operations and innovation.
5. Is machine learning secure?
It can be, but it must be deployed with proper data governance, monitoring, and adversarial defense strategies.