What Is TCP? Understanding the Backbone of Internet Communication
Updated on June 24, 2025, by Xcitium
Ever wondered what is TCP and why it’s so vital to the way we use the internet? Whether you’re streaming a video, sending an email, or accessing a secure FTP site, TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is quietly ensuring everything runs smoothly.
In this blog, we’ll explain the TCP meaning, its role in the TCP/IP model, key features like TCP ports, headers, software applications, and why understanding TCP is critical for anyone in cybersecurity or IT.
TCP Meaning: A Quick Overview
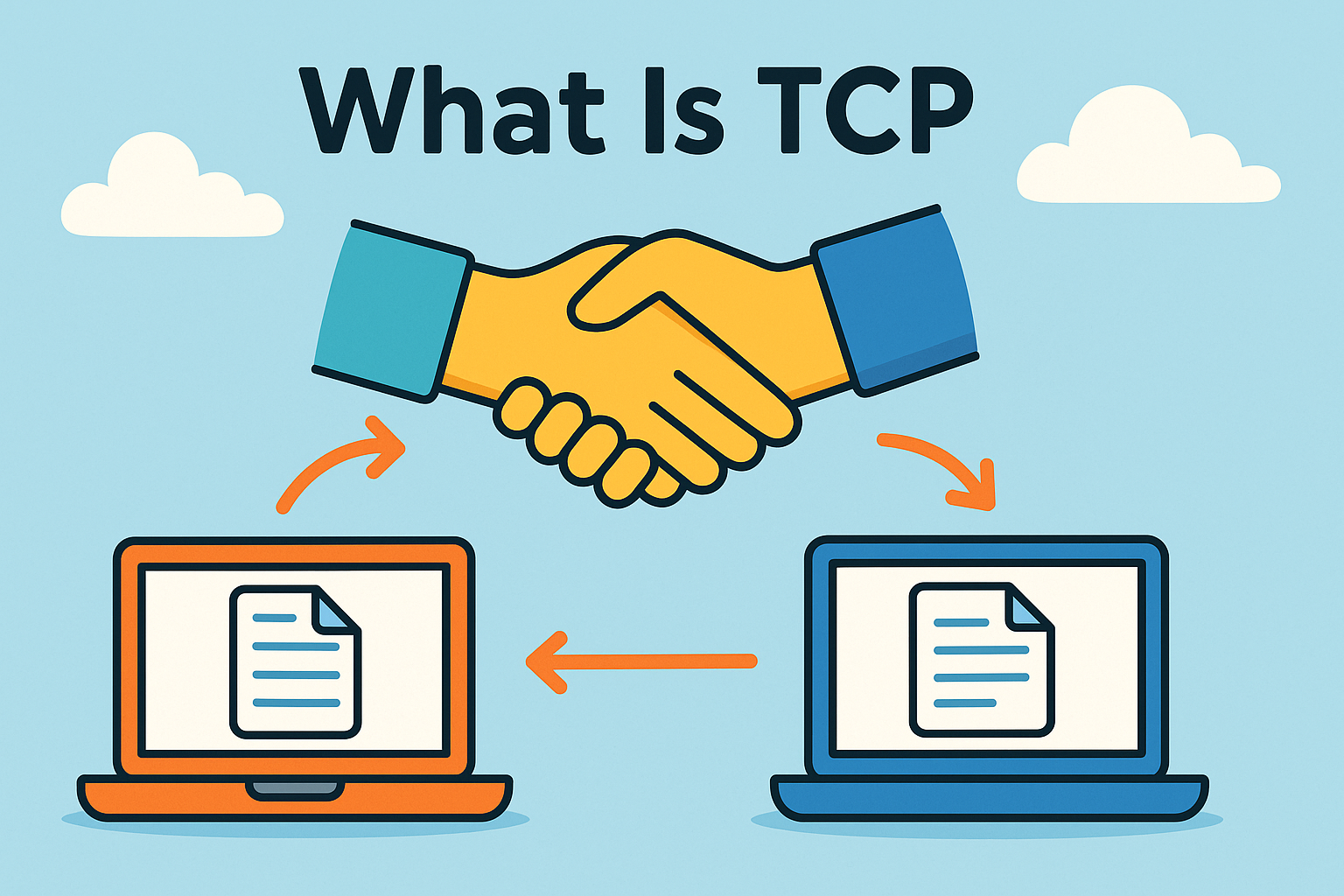
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol. It is a fundamental protocol in the suite of Internet protocols and is responsible for delivering data between computers reliably and in the correct order.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. That means it establishes a connection before transmitting data and ensures that no data is lost, duplicated, or arrives out of order.
TCP/IP Model: Where TCP Fits In
The TCP/IP model is a framework that governs network communication. TCP operates primarily in the Transport Layer, ensuring end-to-end communication.
TCP/IP Layers Overview:
- Application Layer – HTTP, FTP, SMTP
- Transport Layer – TCP, UDP
- Internet Layer – IP, ICMP
- Network Access Layer – Ethernet, Wi-Fi
Together with IP (Internet Protocol), TCP forms the backbone of modern networking.
How TCP Works: Connection, Transmission, Termination
TCP follows a structured process known as the three-way handshake to establish a connection:
- SYN: Client sends a synchronization request.
- SYN-ACK: Server acknowledges with a SYN-ACK.
- ACK: Client responds with an acknowledgment.
Once connected, TCP manages data transmission using sequencing and acknowledgments. When finished, both parties use a termination process to gracefully close the connection.
Key Components of a TCP Header
The TCP header includes vital control information such as:
- Source and destination port numbers
- Sequence and acknowledgment numbers
- Window size
- Checksum
- Flags (URG, ACK, PSH, RST, SYN, FIN)
This structure ensures accurate and reliable data delivery.
What Is a TCP Port?
A TCP port is an endpoint for communication. Each service on a device listens on a specific port.
Common TCP Ports:
- Port 80 – HTTP
- Port 443 – HTTPS
- Port 21 – FTP
- Port 22 – SSH
- Port 990 – Secure FTP TCP port
Understanding TCP ports is crucial for configuring firewalls and network monitoring.
TCP Software and Applications
Many network tools and platforms rely on TCP for secure and reliable communication.
Examples of TCP-based software:
- Web browsers (HTTPS)
- Email clients (SMTP, IMAP)
- File transfer programs (FTP, SFTP)
- Remote access tools (SSH, RDP)
- SIEM tools that monitor TCP/IP traffic
Whether you’re in IT operations or cybersecurity, knowing which services use TCP helps ensure both functionality and security.
Benefits of TCP in Cybersecurity
TCP is essential for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality in cybersecurity practices.
Key Security Advantages:
- Reliable delivery of threat intelligence data
- Support for encryption protocols like TLS/SSL
- Enables deep packet inspection via headers
- Secure session establishment for VPNs and secure portals
Security teams must understand TCP behavior to detect anomalies, threats, and vulnerabilities.
Future of TCP: Scaling with the Internet
As internet usage scales, TCP continues to evolve. Innovations include:
- TCP Fast Open for reduced latency
- Multipath TCP (MPTCP) to use multiple network paths
- Integration with IPv6 for wider address availability
FAQ: What Is TCP?
1. What is TCP used for?
TCP ensures reliable, ordered, and error-checked data transmission between applications and devices over a network.
2. How does TCP differ from UDP?
TCP is connection-oriented and reliable, while UDP is faster but does not guarantee delivery.
3. What are TCP/IP layers?
They include Application, Transport (where TCP operates), Internet, and Network Access layers.
4. What is a TCP port?
A TCP port is a numerical identifier in a TCP header used to differentiate multiple services on the same device.
5. How does TCP enhance cybersecurity?
It ensures secure data transmission, supports encrypted sessions, and allows traffic inspection.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is TCP isn’t just for network engineers—it’s essential knowledge for IT managers, security pros, and anyone navigating today’s connected world.
Want to see how TCP-driven tools can enhance your organization’s security and operations?
👉 Request a demo now and explore how you can secure your network’s heartbeat with intelligent visibility.