What Is Cloud Software? Everything You Need to Know
Updated on July 7, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever wondered what is cloud software and why it’s reshaping the digital world? Whether you’re an IT manager, cybersecurity expert, or CEO planning digital transformation, understanding cloud software is vital. In this blog, we’ll explore how it works, types, real-world examples, and why it’s a cornerstone of modern computing.
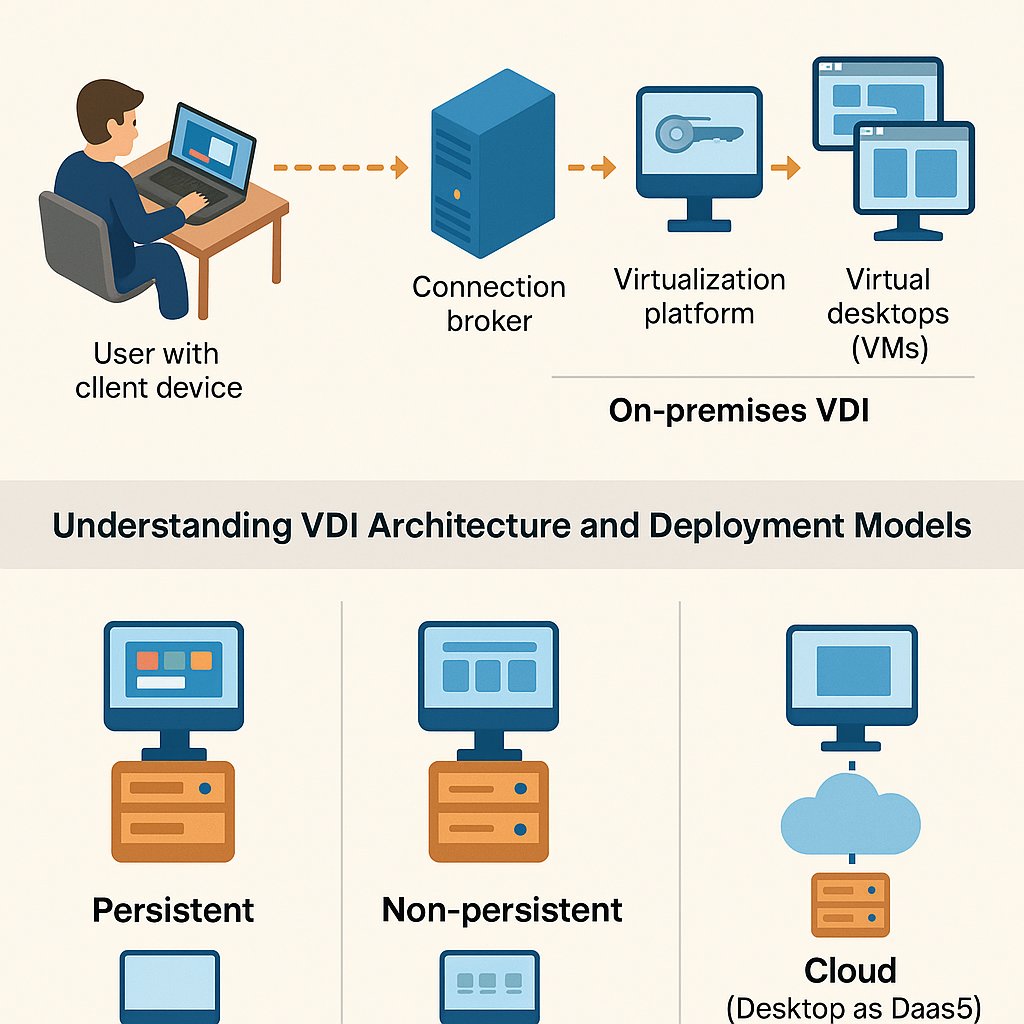
Cloud software refers to applications or services delivered via the internet rather than installed locally on a device. It is a major component of cloud computing, enabling users to access tools, data, and services from virtually anywhere.
What Is Cloud Software?
Cloud software (also known as cloud-based software) refers to software that runs on remote servers and is accessed through the internet. Unlike traditional software that is installed on a single device, cloud software allows access from any device with internet connectivity.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
- On-demand availability
- Scalability
- Resource pooling
- Broad network access
- Pay-as-you-go model
Cloud software is a critical part of cloud computing, which includes a combination of infrastructure, platforms, and applications hosted and managed over the cloud.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Cloud computing works by using a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data. These servers are owned and operated by cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Here’s a simplified flow:
- User requests data or service via the internet.
- Request is routed to the cloud server.
- Cloud software processes it and delivers the result.
- User accesses the result via a browser or application.
✅ Cloud software in cloud computing ensures that your data and services are not tied to one physical location, increasing flexibility and reliability.
Types of Cloud Software
There are three primary types of cloud computing models, often referred to as “cloud stack.”
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Cloud-hosted applications accessed via browsers
- Examples: Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Tools for developers to build and host applications
- Examples: Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Services
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Virtualized computing resources like servers and storage
- Examples: Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine
Each type of cloud software has its own use case, but all support digital scalability and remote access.
Cloud-Based Software Examples
Here are some of the most popular and widely-used cloud software examples across industries:
- Google Drive – File storage & collaboration
- Microsoft Office 365 – Productivity software in the cloud
- Slack – Team communication tool
- Zoom – Cloud-based video conferencing
- QuickBooks Online – Cloud accounting software
These examples show how cloud-based software is deeply embedded in daily business operations.
Benefits of Cloud Software
Why are organizations increasingly adopting cloud software?
✅ Flexibility
Access your tools and data from anywhere, at any time.
✅ Cost Efficiency
No need for expensive hardware or maintenance. You pay only for what you use.
✅ Automatic Updates
Stay current with the latest features and security patches.
✅ Scalability
Easily scale resources based on demand without downtime.
✅ Collaboration
Enable seamless teamwork with shared access and real-time updates.
Cloud software and its types offer immense value to both small businesses and enterprises.
Cloud Software vs Traditional Software
| Feature | Cloud Software | Traditional Software |
| Accessibility | Internet-based, anywhere access | Device-specific |
| Updates | Automatic by provider | Manual installation |
| Cost Structure | Subscription-based | One-time licensing |
| Maintenance | Provider-managed | User-managed |
| Storage | Cloud-based | Local storage |
This comparison shows how cloud software in cloud computing outperforms legacy systems in most modern use cases.
Security and Cloud Software
Security is often the top concern in cloud adoption. Reputable cloud providers implement:
- Data encryption
- Access controls
- Regular audits
- Compliance certifications (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO)
Still, businesses must apply their own cybersecurity practices, including:
- Strong password policies
- Two-factor authentication
- Employee security training
Cloud software should be part of a comprehensive IT security strategy.
Conclusion and CTA
Now that you know what is cloud software, its types, and how it fits into the larger ecosystem of cloud computing, it’s time to evaluate your business needs.
From cost-efficiency to unparalleled flexibility, cloud-based software is the future of digital infrastructure.
Ready to modernize your IT environment?
🚀 Request a demo today and discover how Xcitium can help secure your cloud-based infrastructure.
FAQs
1. What is cloud software in cloud computing?
Cloud software refers to applications hosted in cloud environments, accessible via the internet, without needing local installations.
2. What are the different types of cloud software?
The main types include SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Each serves a unique function from software usage to infrastructure provisioning.
3. How does cloud computing work?
It uses remote servers hosted online to process and store data, enabling anytime-anywhere access and resource scalability.
4. What are some cloud-based software examples?
Popular examples include Google Workspace, Dropbox, Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Slack.
5. Is cloud software secure?
Yes, when configured properly. It includes encryption, access controls, and compliance standards, but user-side practices are equally important.