What Is a Gateway? Understanding Network Entry Points & Security
Updated on August 1, 2025, by Xcitium
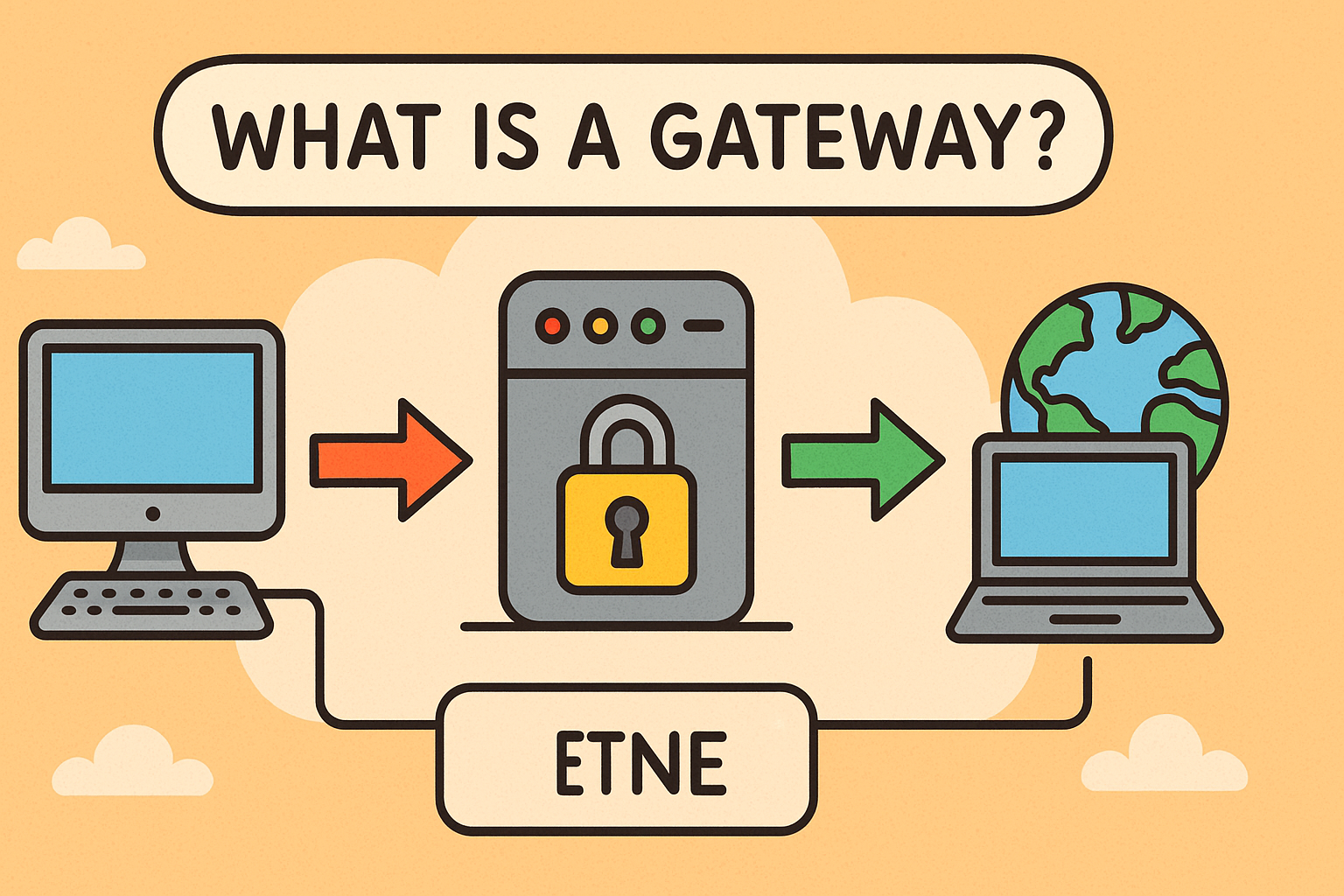
Have you ever wondered what is a gateway in networking and why it’s essential to your IT infrastructure? Whether you’re configuring a firewall, building a secure VPN, or managing enterprise networks, understanding network gateways is critical. A gateway acts as the entry and exit point between different networks or systems, often performing crucial tasks like routing, translating protocols, enforcing security policies, and enabling remote access. In this guide, we’ll cover gateway types such as router gateway, VPN gateway, and secure web gateway, explain how they work, and share best practices to protect your network effectively.
🚪 What Is a Gateway in Networking?
A gateway is a network device or server that serves as an access point between two distinct networks—often an internal local network and an external one, like the internet. It translates different communication protocols and ensures data is passed correctly and securely between them.
Key Functions:
- Protocol translation
- Routing traffic
- Enforcing security (firewalls, access control)
- Connecting remote endpoints (VPN)
Types of Gateways Every IT Leader Should Know
1. Router Gateway
- The most common type
- Forwards traffic between LAN and WAN
- Often configured as the default gateway in system network settings
2. VPN Gateway
- Provides secure, encrypted remote access
- Authenticates users before allowing entry into corporate networks
3. Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
- Filters internet-bound traffic based on security policies
- Blocks malware, phishing, and unauthorized sites
4. IoT or Application Gateway
- Handles communication between IoT devices or application layers
- Often used for API security and performance optimization
How Gateways Work: Behind the Scenes
- Packet arrival: A device sends a data packet to the gateway.
- Inspection & Translation: The gateway checks protocols and applies routing rules.
- Forwarding: The packet is sent to its destination network.
- Response handling: Inbound data undergoes reverse processing before delivery.
Common Use Cases for Gateways in Enterprise Environments
- Employees working remotely must connect via VPN gateway to access internal resources.
- Company network traffic goes through a secure web gateway to prevent access to malicious websites.
- Router gateway manages internal traffic, sets DHCP, NAT, and administrates LAN-WAN traffic flow.
These gateways ensure secure, controlled, and efficient communication across your infrastructure.
Benefits of Using Secure Gateways in Cybersecurity
- ✅ Protocol enforcement and traffic filtering
- ✅ Central control over who can access what systems
- ✅ Protection against inbound threats like malware or ransomware
- ✅ Encryption of data, especially in remote access via VPN
- ✅ Monitoring and auditing via logs for threat detection
Statistically, network security breaches reduce by over 40% when proper gateways are enforced—according to industry scans.
Gateway vs Firewall vs Router: What’s the Difference?
| Device | Main Function | Typical Deployment |
| Gateway | Connects and translates between networks | Router gateway, VPN gateway, application gateway |
| Firewall | Blocks unauthorized traffic based on policy | In front of internal networks or DMZ |
| Router | Routes packets between networks | LAN to WAN router serving as default gateway |
In many cases, modern gateways encapsulate firewall and routing capabilities for unified control.
Implementing Strong Gateway Security: Best Practices
Here are practical tips to secure your gateways:
🔐 1. Harden the Default Gateway
- Change default admin credentials immediately
- Disable unused services and ports
🛡️ 2. Apply a Zero-Trust Model
- Authenticate every user or device before granting access
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote access
📊 3. Monitor and Log Traffic
- Use SIEM tools to assess gateway logs
- Identify anomalies such as unusual IP volumes or protocol misuse
🔄 4. Regularly Update Gateway Firmware
- Patches often address critical vulnerabilities
- Outdated firmware is a common attack vector
🌐 5. Use Segmented Networks
- Control internal access per department or function
- Use VLANs or subnets for isolation—not everything should connect through the same gateway
Real-Life Example: Enterprise VPN Gateway Gone Wrong
In one case, a compromised VPN gateway allowed attackers inside a corporate network. They bypassed internal firewalls and accessed sensitive data due to weak password policies and outdated firmware. The breach resulted in system downtime and reputational damage.
That breach was preventable with strong gateway hygiene and monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a gateway vs a router?
A gateway includes routing but also handles protocol translation, security filtering, and policy enforcement—while a router merely sends packets between networks.
2. Can a default gateway be malicious?
If compromised or poorly configured, yes. Such gateways can become security gaps leading to data leaks or unauthorized access.
3. What is a VPN gateway used for?
It enables secure encrypted channels for remote users to connect to internal networks. Ideal for remote work and safeguarding sensitive data.
4. Why use a secure web gateway?
To ensure employees cannot access malicious or non-compliant websites. It filters traffic-based policies before reaching internal systems.
5. Do IoT devices need a gateway?
Yes—IoT gateways manage communication between devices and handle protocol translation, security, and analytics.
Conclusion: Gateways Are Your Network’s Gatekeepers
So, what is a gateway? It’s far more than a router—it’s the access point and policy enforcer of your network. Whether it’s a VPN gateway, web gateway, or application gateway, each plays a key role in securing and managing communication flows.
Neglecting gateway configuration leaves you exposed to cyber threats, unauthorized access, and operational disruptions.
Secure Your Gateways, Secure Your Enterprise
👉 Request a Free Demo from Xcitium Security Suite to find out how our platform protects your gateways, endpoints, and network in real time with zero-trust security controls.