Introduction: Is Your Organization HIPAA-Compliant?
Updated on June 9, 2025, by Xcitium

What is HIPAA, and why does it matter to IT leaders, cybersecurity experts, and CEOs? In a world where healthcare breaches cost an average of $10 million per incident, understanding and implementing HIPAA compliance isn’t just about legality—it’s about trust, data integrity, and business continuity.
What Is HIPAA? A Simple Definition
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a U.S. law enacted in 1996 to protect sensitive patient health information (PHI). It ensures that healthcare data remains private, secure, and accessible only to authorized individuals.
The act primarily governs:
- Who can access health information
- How health data is stored and transmitted
- The responsibilities of covered entities and business associates
HIPAA applies to hospitals, clinics, insurers, medical software vendors, and any business that handles Protected Health Information (PHI).
The Core Pillars of HIPAA
HIPAA is built on multiple rules, but the most essential ones for cybersecurity professionals include the HIPAA Privacy Rule and the HIPAA Security Rule.
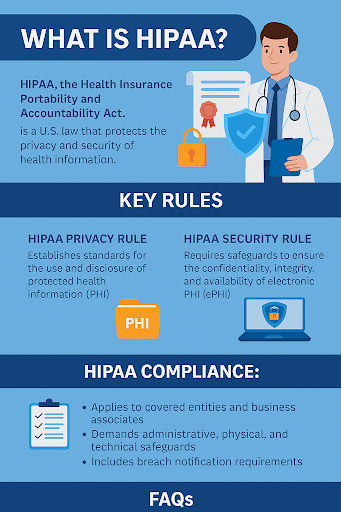
1. HIPAA Privacy Rule
The HIPAA Privacy Rule sets standards for:
- Who can access PHI
- How PHI is disclosed (e.g., to family members, law enforcement, or third parties)
- Patient rights to access and correct their information
🔐 Example: A healthcare provider cannot share your medical record with your employer without your consent.
2. HIPAA Security Rule
The HIPAA Security Rule specifically focuses on electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) and requires:
- Administrative safeguards (e.g., risk analysis, workforce training)
- Physical safeguards (e.g., workstation access controls)
- Technical safeguards (e.g., encryption, secure access control)
🛡 Example: All ePHI must be encrypted when stored or transmitted over a network.
HIPAA Compliance: What Does It Really Involve?
Achieving HIPAA compliance means implementing procedures, policies, and technologies that safeguard PHI. This applies not only to healthcare providers but also to any third-party vendors (like cloud platforms or billing services) handling PHI.
Key HIPAA Compliance Requirements:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment
- Identify vulnerabilities in systems storing ePHI.
- Develop HIPAA Policies
- Cover breach notifications, data handling, and privacy practices.
- Train Your Workforce
- Educate staff about phishing, data handling, and access control.
- Implement Access Controls
- Use multi-factor authentication and audit logs.
- Encrypt and Secure PHI
- Both at rest and in transit.
- Establish a Breach Response Plan
- Detect, contain, and report breaches within 60 days.
💡 Tip: Even an unintentional email sent to the wrong patient containing PHI can be considered a HIPAA violation.
Who Must Follow HIPAA?
HIPAA applies to two main categories:
Covered Entities
- Health care providers
- Health plans (insurers, HMOs)
- Healthcare clearinghouses
Business Associates
- Billing companies
- Cloud storage providers
- EHR vendors
- Managed IT service providers
Even if your organization is not a healthcare provider, if you interact with PHI, you are still subject to HIPAA.
HIPAA Violation Examples and Penalties
Violating HIPAA can lead to fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per incident, and up to $1.5 million annually, depending on the severity.
Common HIPAA Violations:
- Failing to encrypt PHI
- Unauthorized access to medical records
- Inadequate training or documentation
- Delayed breach notification
🔴 Real Case: In 2019, Jackson Health System was fined $2.15 million after losing thousands of patient records and failing to implement basic access controls.
HIPAA and Cybersecurity: A Critical Partnership
Cybersecurity isn’t optional—it’s a HIPAA Security Rule mandate. You must implement measures to prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, or malware attacks.
Recommended Security Practices:
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
- Zero-trust architecture
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS)
- Secure backup and disaster recovery solutions
- Regular penetration testing
HIPAA and Cloud Services: What to Consider
Using cloud vendors? Make sure they:
- Sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA)
- Support data encryption
- Enable access logs and audit trails
- Have incident response protocols
Failure to vet cloud partners is a common HIPAA compliance gap.
HIPAA FAQs: Quick Answers to Common Questions
1. What is HIPAA?
HIPAA is a U.S. law that protects patient health information through security, privacy, and breach notification rules.
2. What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule governs how PHI is used and disclosed, and grants patients rights to access and correct their data.
3. What is the HIPAA Security Rule?
This rule outlines safeguards for protecting electronic PHI, including technical and administrative controls.
4. Who needs to be HIPAA-compliant?
Covered entities like healthcare providers, and business associates that handle PHI, must comply.
5. What are some penalties for HIPAA violations?
Fines range from $100 to $50,000 per violation. Severe breaches can lead to million-dollar settlements.
Final Thoughts: Make HIPAA a Competitive Advantage
Understanding what is HIPAA is essential for securing patient data, maintaining regulatory compliance, and earning customer trust. In the cybersecurity landscape, HIPAA acts as both a legal requirement and a strategic advantage.
Compliance isn’t a one-time event—it’s a continual effort.
👉 Request a Demo from Xcitium to Fortify Your HIPAA Compliance Today