How to Launch Excel VBA: A Step-by-Step Guide for Professionals
Updated on September 16, 2025, by Xcitium
Have you ever asked yourself, “How to launch Excel VBA to automate repetitive tasks?” Microsoft Excel is one of the most widely used tools in business, but many professionals don’t leverage its full potential. By using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), you can automate reports, create custom functions, and improve productivity.
For IT managers, cybersecurity experts, and CEOs, learning how to launch Excel VBA is more than a technical skill—it’s a way to save time, reduce errors, and secure workflows. This guide will explain how to access VBA in Excel, use it effectively, and apply it to enterprise operations.
What Is Excel VBA?
Before learning how to launch Excel VBA, it’s important to understand what it is.
- VBA (Visual Basic for Applications): A programming language built into Microsoft Office applications.
- Purpose: Automates tasks, customizes Excel beyond built-in features, and integrates with other applications.
- Use Cases: Generating reports, building dashboards, cleaning datasets, and applying security-driven automation.
👉 In short: VBA turns Excel from a spreadsheet tool into a business automation powerhouse.
How to Launch Excel VBA: Step-by-Step
Let’s walk through different methods to access and start using VBA.
Method 1: Using the Developer Tab
- Open Excel.
- Go to File > Options > Customize Ribbon.
- Enable the Developer Tab by checking its box.
- On the Developer Tab, click Visual Basic.
This opens the VBA Editor, where you can start writing code.
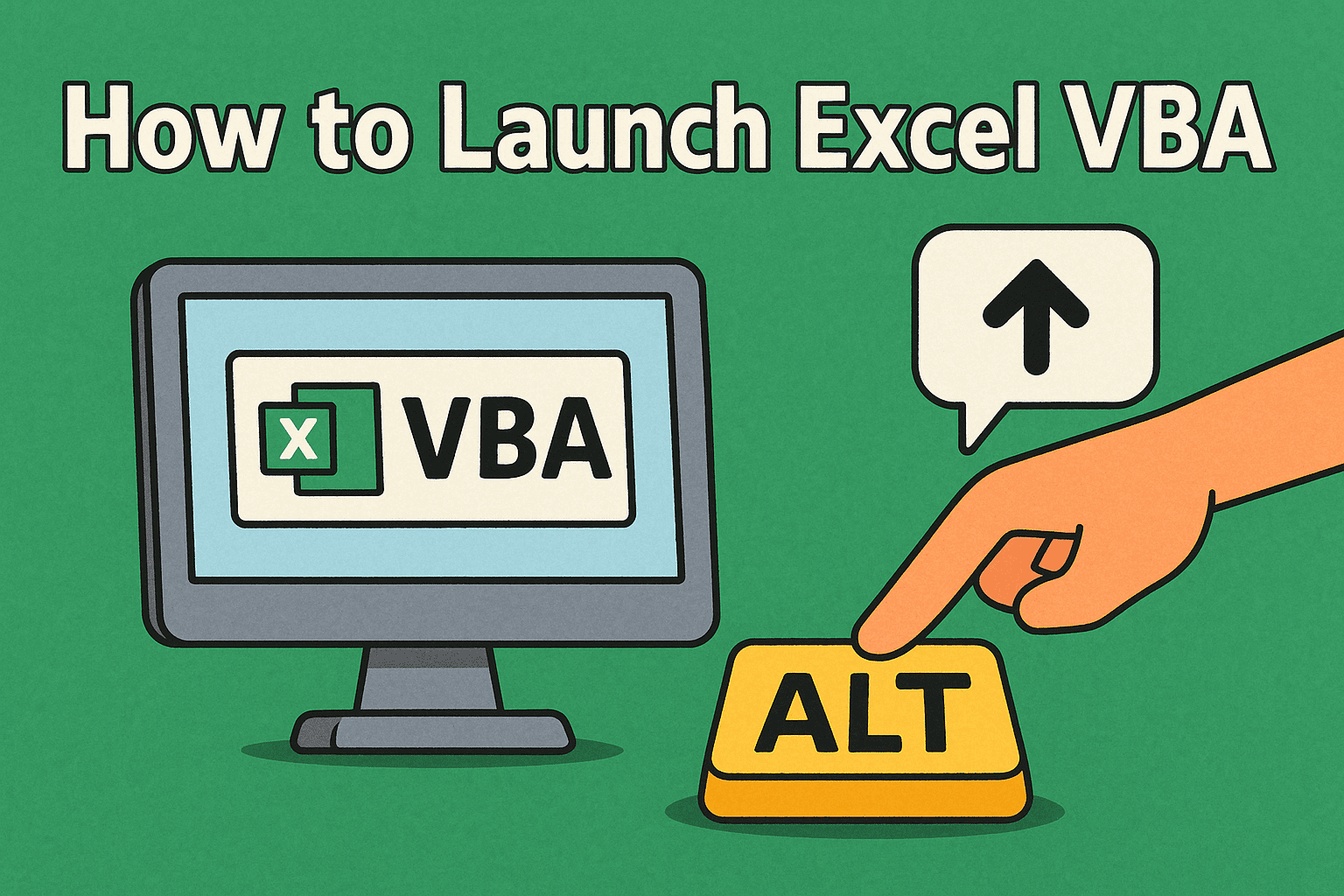
Method 2: Shortcut Key
- Press Alt + F11 in Excel.
- This immediately launches the VBA Editor.
👉 This is the fastest method and widely used by IT professionals.
Method 3: Insert a Macro
- Go to the Developer Tab > Macros.
- Create a new macro.
- Click Edit, and the VBA Editor opens with the macro’s code window.
Navigating the VBA Editor
Once you’ve learned how to launch Excel VBA, you’ll see the VBA Editor (VBE) interface.
Key Components:
- Project Explorer: Shows all open workbooks and modules.
- Code Window: Where you write and edit VBA code.
- Immediate Window: Useful for testing snippets of code.
- Properties Window: Displays object properties for customization.
Writing Your First VBA Script
Now that you know how to launch Excel VBA, let’s create a simple automation.
Example: Automate a Greeting Message
- Press Alt + F11 to open VBA.
- Insert a new module: Insert > Module.
Enter this code:
Sub HelloWorld()
MsgBox “Hello, welcome to Excel VBA!”
End Sub
- Run the macro by pressing F5 or using Developer > Macros.
👉 This small script shows the basics of automation with VBA.
Business Use Cases of Excel VBA
For IT managers and executives, VBA provides strategic advantages:
- Automating Reports: Schedule and generate financial or compliance reports.
- Data Cleaning: Quickly remove duplicates, format data, or validate inputs.
- Cybersecurity Audits: Automate log imports and anomaly checks in Excel.
- Integration: Connect Excel with databases, APIs, or Outlook for enterprise tasks.
Security Considerations When Using VBA
While VBA is powerful, it can introduce risks if misused.
- Macro Malware Risks: Malicious macros can compromise systems.
- Safe Practices:
- Only enable macros from trusted sources.
- Use digitally signed VBA projects.
- Implement group policies to control macro execution in enterprises.
- Audit Trails: Ensure sensitive automation scripts are logged and monitored.
👉 For cybersecurity professionals, VBA scripts must be managed like any other executable code.
Advantages of Using Excel VBA
- Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks.
- Customization: Tailors Excel to organizational needs.
- Integration: Works seamlessly with other Microsoft Office apps.
- Scalability: Handles large datasets better with automation.
Challenges and Limitations
While learning how to launch Excel VBA is simple, scaling it in business has challenges.
- Learning Curve: Requires basic programming knowledge.
- Maintenance: Scripts must be updated for new Excel versions.
- Security Risks: Without proper governance, macros can be exploited.
- Performance Limits: VBA is slower compared to modern programming languages like Python.
Best Practices for IT Managers
- Train Staff: Provide VBA training for finance, HR, and IT teams.
- Standardize Scripts: Maintain a library of approved macros.
- Apply Zero-Trust: Verify and monitor macro execution.
- Use Version Control: Store critical scripts in repositories.
- Audit Regularly: Review VBA scripts for compliance and security.
FAQs on Launching Excel VBA
Q1. How do I enable the Developer Tab in Excel?
Go to File > Options > Customize Ribbon, then check Developer Tab.
Q2. What’s the shortcut to launch VBA in Excel?
Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor.
Q3. Is VBA still supported in Excel?
Yes. Microsoft continues to support VBA, though Power Automate is a modern alternative.
Q4. Can VBA macros run automatically?
Yes, you can configure macros to run on workbook open, close, or specific events.
Q5. Are Excel VBA macros secure?
They can be if managed correctly. Always verify the source before enabling.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of VBA
So, how to launch Excel VBA? It’s as easy as enabling the Developer Tab or pressing Alt + F11. But the real value lies in how you use it—automating workflows, improving efficiency, and ensuring security across enterprise processes.
For IT managers, CEOs, and cybersecurity experts, VBA is more than a tool—it’s a productivity and security enabler. By applying best practices, you can leverage Excel VBA to streamline operations safely.
👉 Want to strengthen your enterprise’s automation and security strategy? Discover how Xcitium’s zero-trust solutions can protect your digital workflows.